Cellular Respiration CH2O + O2 CO2 + H2O + Energy
advertisement

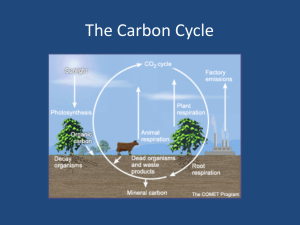
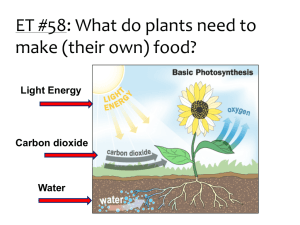
Cellular Respiration All Organisms CH2O + O2 CO2 + H2O + Energy Oxidizable Organic Molecule Cellular Respiration All Organisms CH2O + O2 CO2 + H2O + Energy Oxidizable Organic Molecule Aerobic & Anaerobic Cellular Respiration All Organisms CH2O + O2 CO2 + H2O + Energy Oxidizable Organic Molecule Used Aerobic & Anaerobic Energy Currency: Cellular Respiration All Organisms CH2O + O2 CO2 + H2O + Energy Oxidizable Organic Molecule Aerobic & Anaerobic Energy Currency: ATP Photosynthesis Green Plant Cells Photosynthesis Photoautotrophs C02 + H20 CH2O + O2 + H2O Oxidizable Organic Molecule Made Oxygen Produced Light Dependent CO2 split? Photosynthesis Photoautotrophs C02 + H20 CH2O + O2 + H2O Purple Sulfur Bacteria: CO2 + H2S CH2O + S Photosynthesis Photoautotrophs C02 + H20 CH2O + O2 + H2O Purple Sulfur Bacteria: CO2 + H2S CH2O + S Radioactive Isotopes (Plants): CO2 + H2O CH2O + O2 CO2 + H2O CH2O + O2 Photosynthesis Photoautotrophs C02 + H20 CH2O + O2 + H2O Photosynthesis Photoautotrophs C02 + H20 CH2O + O2 + H2O Chloroplast Chloroplast Structure Chloroplast Development of Chloroplasts (circular DNA) Protoplastid Etioplast Prolamellar body (chromoplasts or leucoplasts) Chloroplast Photosynthesis Photoautotrophs C02 + H20 CH2O + O2 + H2O Light needed to split water Pigment Molecules large complex molecules that can trap light energy Photosyntheically Active Radiation (PAR) Photosynthesis Photoautotrophs C02 + H20 CH2O + O2 + H2O Light needed to split water Pigment Molecules PGAL C3 – 1st Food -> Glucose Starch Lipids Proteins recycled – CO2 acceptor RuBP C5 Photosynthesis Photoautotrophs C02 + H20 CH2O + O2 + H2O Pigment Molecules Chlorophyll a C55H72O5N4Mg Blue-green 4 tetrapyrole rings Chlorophyll a Other Chlorophylls Chl b – Yell/Green Chl c Chl d Absorption Spectrum of Chlorophylls a and b Action Spectrum of Photosynthesis Absorption Spectra (various photosynthetic pigments) Carotenoids (lipids) Xanthophyll – yellow (has oxygen) Carotene – orange/yellow Alpha & Beta (lacks oxygen) Absorption Spectrum of A & B Carotene Phycobilins (straight-chain tetrapyrole group attached to a protein) Phycocyanin (bluish) Phycoerythrin (reddish) Phytochromes Phycocyanin & Phycoerythrin Absorption Spectra Absorption Spectrum of the Phytochromes Accessory Pigments other chlorophylls, xanthophylls, carotenes …….. 1. Absorb light and pass it on to chlorophyll a. 2. Prevents photooxidation of chlorophyll a. Flavinoids (water soluble – all absorb UV light) Anthocyanins red-purple (indicator) Flavones UV light (bee guides) Aurones yellows Betacyanins (water soluble – absorb some UV light) -Contains Nitrogen -Found in plant groups that do not produce anthocyanins: Chenopodiales – goosefoots, cactuses, portulacas. - Red/Yellow (indicator) Chloroplast (Within the thylacoid the pigment molecules are precisely arranged and tightly packed.) Chlorophyll a electron transfer Reaction Center (1 in 300 molecules) Antenna Molecules Accessory Molecules-Photosynthetic Unit Chloroplast (Within the thylacoid the pigment molecules are precisely arranged and tightly packed.) Part of a Photosynthetic Unit Accessory pigments feed Reaction Center Two types of PUs or Photosystems, Structured into the Thylacoid Membrane Photosystem II more chl b Photosystem I 680 nm 700 nm more chl a and carotenoids Need both red wavelengths for enhanced photosynthesis R. Emerson, 1950’s (Each system carries out certain reactions. Link by electron acceptors in Light Phase of Photosynthesis.) Light Phase (If components arranged according to energy levels: Z-Pathway Light Phase Photosystem II Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation Photosystem I Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation Light Phase Products: 1. NADPH2 2. ATP (OXIDIZABLE ORGANIC MOLECULES made in the Dark Phase of Photosynthesis.) Light Phase Light Phase Triazine Herbicide Cyclic Photphosphorylation Cyclic Photophosphorylation Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation PCR, Calvin-Benson Cycle Photosynthetic Carbon Reduction Cycle (PCR) (Ribulose 1, 5 –Bisphosphate Carboxylase – Rubisco – CO2 Trapping enzyme) Oxidative Pentose Phosphate Cycle (Source of NADPH2 for lipid synthesis: RuMP (C5) for Nucleic Acid Production) Enzymes of the Photosynthetic Carbon Reduction Cycle (PCR) only function with light. Electron Flow in the Chloroplast Some Pathways Warburg Effect 1920’s RuBp Oxygenase Reaction (Rubisco) Favored in High Temp or Low CO2, High O2 “Photorespiration” RuBp Oxygenase Reaction (Rubisco) C4 Plants In Mesophyll Cells CO2 + PEP Oxylate (C4) Asparatate & Malate (C4) translocates C4 Plants Bundle Sheath Cells C4 Acids Pyruvate (C3) + CO2 CO2 + RuBP (C5) PCR Cycle The C4 Syndrome Another Way of Assimilating CO2 Krans Leaf Anatomy C- 4 Plants Krans Leaf Anatomy Mesophyll Chloroplasts - have grana Bundle Sheath Chloroplasts - no grana - much starch storage Advantages of C4 Photosynthesis Advantages of C4 Photosynthesis 1. Steeper CO2 Utilization Gradient 2. Decreased Photorespiration 3. Arrangement of Mesophyll/Bundle Sheath Cells favorable to Transport Disadvantages of C4 Photosynthesis Disadvantages of C4 Photosynthesis 1. Extra Biochemical Steps (energy expense) CAM Plants - CAM Plants do not have Krans Leaf Anatomy. - CAM Plants use PEP as a CO2 Trap – as in C4 plants - CO2 Trapping and PCR cycle separated in time. CAM Plants C4 vs CAM Plants Ambient Factors Affecting Photosynthesis Oxygen O2 Ambient Factors Affecting Photosynthesis Oxygen O2 Light Effects of Light (Differences Between C3 and C4 Plants) Effects of Light Light-Saturated Photosynthesis 1/3 full sunlight for most plants (mostly limited by PCR Cycle Reactions) Light-Limited Photosynthesis Only at very low light intensities (Light Compensation point Below CO2 accumulation) Blackman’s Principle of limiting Factors Shade Plants Thinner Leaves More Chlorophylls; Less Carotenoids (Chl a less protected from photooxidation) PSUII:PSUI = 3:1 Lower light compensation point Sun Plants Thicker Leaves Less Chlorophylls; More Carotenoids (Chl a more protected from photooxidation) PSUII:PSUI = 2:1 Higher light compensation point Ambient Factors Affecting Photosynthesis Oxygen O2 Light Temperature Effect of Temperature Effect of Temperature Ambient Factors Affecting Photosynthesis Oxygen O2 Light Temperature CO2 and H2O Stomatal Action “trade off”