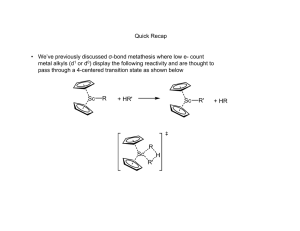
class14_carbene_metathesis
advertisement
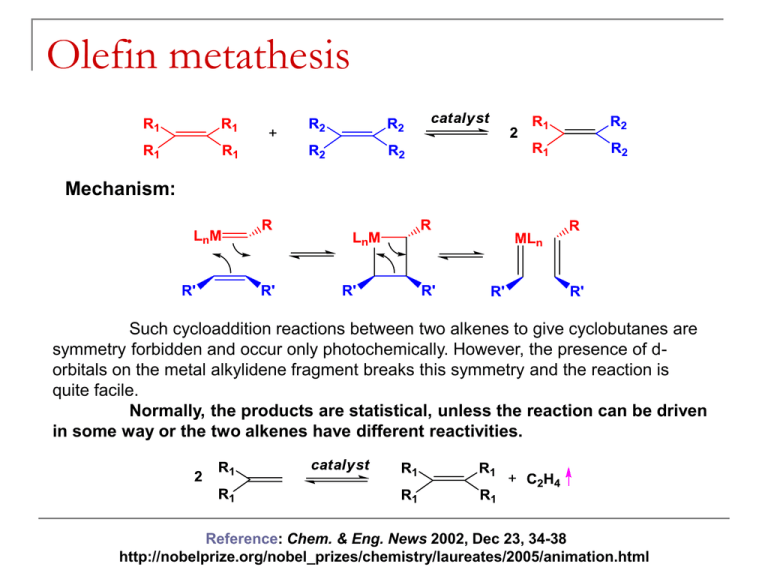
Olefin metathesis Mechanism: Such cycloaddition reactions between two alkenes to give cyclobutanes are symmetry forbidden and occur only photochemically. However, the presence of dorbitals on the metal alkylidene fragment breaks this symmetry and the reaction is quite facile. Normally, the products are statistical, unless the reaction can be driven in some way or the two alkenes have different reactivities. Reference: Chem. & Eng. News 2002, Dec 23, 34-38 http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/2005/animation.html Timeline Reaction overview Large-scale applications of OM PHILIPS process (ARCO, Texas): SHOP (Shell): C8 and C16 internal olefins are metathesized in the course of a multi-step process (ethylene oligomerization, isomerization, metathesis, hydroformylation) leading to C11 – C15 primary alcohols (detergents). Neo-hexene (musk scent for perfume industry) synthesis: Mechanism: pair-wise vs. non pair-wise Mechanism: sticky olefin A system in which the metathesis products do not themselves metathesize is needed such that the initial products are those detected. The results of this reverse double cross experiment showed a 1:2:1 mixture of d0, d2, and d4 isotopomers of the resulting ethylene. Schrock catalysts: history Reference: Schrock, R. R. J. Mol. Cat. A: Chem. 2004, 213, 21 Schrock catalysts Stereogenic-at-Mo catalysts for Z-selective metathesis R. Schrock, A. Hoveyda, et al. Nature 2011, 471, 461-466, and Nature 2008, 456, 933-937 Grubbs catalysts Reference: Trnka, T. M.; Grubbs, R. H. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 18 Mechanism with Grubbs catalysts Ruthenium catalysts for Z-selective olefin metathesis Published in: Benjamin K. Keitz; Koji Endo; Paresma R. Patel; Myles B. Herbert; Robert H. Grubbs; J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 693699. DOI: 10.1021/ja210225e Copyright © 2011 American Chemical Society ROMP: Observations ROMP: strained cyclic olefins – driving force is the relief of ring strain. It is difficult to ROMP tri- and tetrasubstituted olefins. Norbornene monomers can be synthesized from the Diels-Alder reaction of cyclopentene. Living polymerization: block copolymers RCM: Observations The ring to be formed cannot have appreciable strain. Reaction is intramolecular most of the times (low dilution). Asymmetric version: Schrock-Hoveyda catalyst Comparison of catalysts Schrock catalysts Grubbs catalysts Less functional group tolerant More functional group tolerant, but nitriles and amines are still a problem More reactive, higher rates Less reactive, slower rates Asymmetric RCM works very well Asymmetric RCM does not work as well Perform ene-yne metathesis Not known Counterparts for alkyne metathesis Not known (yet) Alkyne metathesis Although there are two types of metal carbynes, only Mo/W compounds were found to be active for alkyne metathesis. Alkyne metathesis is not applied commercially because acetylenes are made by other cheap and easy methods and side reactions cannot be avoided during alkyne metathesis. Reactions related to olefin metathesis Polymerization of acetylenes Metathesis of enynes: intermolecular mechanism Fine Chemicals Manufacture Homogeneous catalysis and fine chemicals manufacture Reaction Catalyst Product Use Cross-coupling Hydroformylation Pd Rh Diflunisal Vitamin A Pharmaceutical Pharmaceutical Hydrocaboxylation Hydrogenation Pd Rh/DIPAMP Ibuprofen L-dopa L-phenylalanine Pharmaceutical Food additive Aroma chemical Isomerization Epoxidation Rh/BINAP Ti(OiPr)4/tBuOOH di-iPr tartrate L-menthol Disparlure Glycidol Insect attractant Intermediate Pharmaceutical Cyclopropanation Cu/chiral Schiff base cilastatin Diflunisal: cross-coupling Giordano et al. Eur. Pat. Appl. 1992, 494419 Vitamin A: hydroformylation High regioselectivity in the production of the branched aldehyde in the hydroformylation step is key to the formation of the C5 building block in the synthesis of vitamin A. Ibuprofen and naproxen: asymmetric hydrogenation L-dopa Hydrogenation – L-dopa L-menthol: asymmetric isomerization (+)-Disparlure: asymmetric epoxidation Cilastatin: cyclopropanation cilastatin renal enzyme inhibitor Cu and Ru-enantioselective cyclopropanation Outstanding levels of enantioselectivity have been achieved with Cu/C2 symmetric ligands and Rh2L*4. Cu catalyst is Cu(I). Other Cu reagents generate Cu(I) in situ. Ru catalysts give lower ee and yields than Cu or Rh, but they may offer some advantages. Mechanistic considerations for Cu/Ru Metallacyclobutane intermediate is more likely for Ru (same as olefin metathesis intermediate). Reference: Kirmse, W. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 1088