Chemical Reaction PowerPoint
advertisement

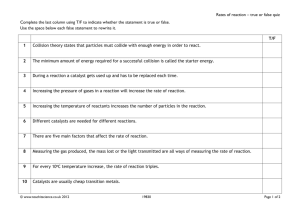
“Reaction Rates” Review of Alka Seltzer Lab Collision Theory Reactions can occur: fast – such as a firecracker Very slow – such as the time it took for dead plants to make coal Very A “rate” is a measure of the speed of any change that occurs within an interval of time Collision Model •Key Idea: Molecules must collide to react. Factors Affecting Rate 1) Temperature Increasing temperature always increases the rate of a reaction. 2) Surface Area Increasing surface area increases the rate of a reaction 3) Concentration Increasing concentration USUALLY increases the rate of a reaction 4) Presence of Catalysts: 5)Pressure Increasing the pressure increases the rate of the reaction. Catalysts Catalyst: A substance that speeds up a reaction, without being consumed itself in the reaction – interfere with the action of a catalyst; reactions slow or even stop Inhibitors Evidence of a Chemical Reaction: color change odor change temperature change bubbles or gas production solid formation http://player.discoveryeducation.c om/index.cfm?guidAssetId=E73F FA0F-977F-4574-8688DC1CB551ECD9&blnFromSearch =1&productcode=US http://player.discoveryeducation. com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=373 BFC67-1589-46B0-9E458E6EA5304C91&blnFromSearch =1&productcode=US