powerpoint
advertisement

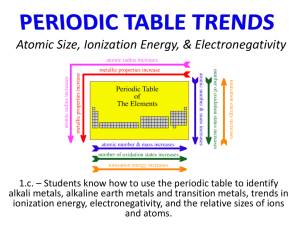
#24 Why did Mendeleev leave spaces in his periodic table? He could tell from the elements surrounding the “holes” in his table that they must exist. #25 What effect did the discovery of gallium have on the acceptance of Mendeleev’s table? His ability to predict the properties and existence of unknown elements made his table much more believable #26 What pattern is revealed when the elements are arranged in a periodic table in order of increasing atomic number? Many trends are revealed such as electronegativity, atomic and ionic radii, #27 Based on their locations in the periodic table, would you expect carbon and silicon to have similar properties? Yes, they are in the same group #28 Identify each property below as more characteristic of a metal or aof non-metal, think non-metal. oxygen gas a. gas at room temp. #28 Identify each property below as non-metal, think more characteristic of a metal or aof a piece of lead in non-metal. your pencil--Carbon b. brittle #28 Identify each property below as more characteristic of a metal or a non-metal. metal: think of c. malleable. pounding a piece of gold into leaf with a mallet. think of howbelow well as #28non-metal: Identify each property metal conducts electricity. more characteristic of a metal ie. or a a wire. non-metal. d. poor conductor of electric current. #28 Identify each property below as more characteristic of a metal or a non-metal. metal: think of a shiny e. shiny. piece of silver or gold. Metalloids have properties that are #29 In general, how are metalloids similar to both different frommetals metalsand andnon-metals. nonmetals? How a metalloid behaves depends on the conditions. #30 Where are the alkali metals, the alkaline earth metals, the halogens, and the noble gases? #31 Which of the following are symbols for representative elements: Na Mg Fe Ni Cl #32 Which noble gas does not have eight electrons in its highest occupied energy level? Helium; it only has two all others have 8 valence electrons #33 Which of these metals isn’t a transition metal? a. aluminum b. silver c. iron d. zirconium Transition metals are light blue in this table #34 Use figure 6.12 to write the electron configuration of these elements. a. B b. As c. F d. Zn e. Al #35 Write the electron configurations of these elements: a. the noble gas in period 3 Ar: 1s22s22p63s23p6 b. the metalloid in 22s22p63s23p2 Si: 1s period 3 Na: 1s22s22p63s1 c. the alkali metal in period 3 #36 Which element in each pair has atoms with a larger atomic radius? a. sodium, lithium #36 Which element in each pair has atoms with a larger atomic radius? b. strontium magnesium #36 Which element in each pair has atoms with a larger atomic radius? c. carbon germanium #36 Which element in each pair has atoms with a larger atomic radius? d. selenium oxygen #37Explain the difference between the first and second ionization energy of an element. First ionization energy is the energy required to remove the FIRST electron Second ionization energy is the energy required to remove the SECOND electron. It is always GREATER THAN the first ionization energy #38 Which element in each pair has a greater first ionization energy? a. lithium boron Boron #38 Which element in each pair has a greater first ionization energy? a. magnesium strontium Magnesium #38 Which element in each pair has a greater first ionization energy? a. cesium aluminum Aluminum #39 Arrange the following groups of elements in order of increasing ionization energy. Sr Mg Be #39 Arrange the following groups of elements in order of increasing ionization energy. Cs Ba Bi #39 Arrange the following groups of elements in order of increasing ionization energy. Na Al S Atomic Radius as compared to IONIC radius Atoms in elemental form (same # of electrons as protons) Ions 1 1 1 1 1