File
advertisement

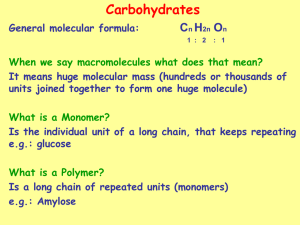
Carbohydrates Dr. Nasim AP Biochem Dr. Nasim 1 Monosaccharides (Single sugar residue) 3 C: 4 C: 5 C: 6 C: 6 C: Trioses Tetroses Pentoses Hexoses Hexoses Dr. Nasim 2 Monosaccharides (Single sugar residue) (Aldose) (ketose) Glyceraldehydes Erythrose Ribose Xylose Glucose DHA 3C Erthrulose - 4 C Ribulose - 5 C Xylulose 5C Fructose - 6 C Dr. Nasim 3 Monosaccharides Aldoses: Those Monosaccharides which contain Aldehyde group. (H-C=O) Ketose: Those Monosaccharides which contain keto group. (C=O) Dr. Nasim 4 Monosaccharides Anomeric carbon: Aldoses & Ketose may cyclize to produce an Anomeric carbon. Anomeric carbon contain reactive hydroxyl group. Dr. Nasim 5 Monosaccharides If the Reactive hydroxyl group is free (Not attached to any other molecule) then the sugar is known as reducing sugars. Reactive hydroxyl group may attached covalently to another molecule. N-Glycosidic linkage: If the Reactive hydroxyl group is attached to–NH2 group. Dr. Nasim 6 Monosaccharides O-Glycosidic linkage: If the Reactive hydroxyl group is attached to–OH group. ISOMERS: If 2 compound have the same chemical formula. E.g. Fructose & glucose are isomers of each other. Dr. Nasim 7 Monosaccharides Epimers: If 2 compound have the same chemical formula but the differ in configuration around 1 specific C atom. Galactose & glucose are C 4 Epimers of each other. Mannose & glucose are C 2 Epimers of each other. Dr. Nasim 8 Monosaccharides Enantiomers: If 2 compound are mirror image of each others. E.g. L - Glucose & D – Glucose. The configuration of asymmetric carbon atom farthest from the aldehyde or keto group (with reference to D or L glyceraldehydes) determines whether a monosaccharide is of D or L series. In D form OH gp is on right side & vice versa in left side. Dr. Nasim 9 Disaccharides (2 Monosaccharides units) Sucrose = Glucose + Fructose (α1-2 linkage) Lactose = Glucose + Galactose (β1-4 linkage) Maltose = Glucose + Glucose (α1-4 linkage) Iso-malotose = Glucose + Glucose (α1-6) Dr. Nasim 10 Oligosaccharides (3-10 Monosaccharides) E.g. Maltotriose: Compose of 3 Glucose residues. Dr. Nasim 11 Polysaccharides (>10 Monosaccharides units) Homo Polysaccharides (contain same type of monosaccharides) Glycogen which is also known as animal starch. Dextrin Dextran Cellulose Dr. Nasim 12 Polysaccharides Hetero Polysaccharides (contain same type of monosaccharides or different monosaccharides along with prosthetic groups) Muco Polysaccharides Mucilages Hemicellulose Dr. Nasim 13 Polysaccharides Hetero Polysaccharides Muco Polysaccharides Hyaluronic acid Heparin Chondroitin sulphate Blood group Polysaccharides. Serum mucoids Dr. Nasim 14 Polysaccharides Hetero Polysaccharides Mucilages Agar Vegetable Pectin Dr. Nasim 15 Monosaccharides Glyceraldehydes: Reference sugar All sugars are derived from it D & L forms are refer to it DHA Produced from glucose in glycolysis & also from glycerol which is produced in break down of fats Dr. Nasim 16 Monosaccharides Erythrose & Erthrulose Produced from glucose in HMP shunt Can be converted to glucose Ribose Produced from glucose in HMP shunt Ribose component of RNA Deoxy-Ribose component of RNA Dr. Nasim 17 Monosaccharides Ribulose, Xylose & Xylulose Produced from glucose in HMP shunt Dr. Nasim 18 Monosaccharides Glucose Grape sugar Dextrose Dextro-rotation Most common source sucrose which is table sugar Main source of energy for body & specially brain. Dr. Nasim 19 Monosaccharides Glucose (Cont.) FBS 60 – 100 mg/dl RBS 100 – 160 mg/dl On reduction glucose forms alcohol e.g. Sorbitol On oxidation sugar acids Gluconic acid If oxidation of C1 of glucose Dr. Nasim 20 Monosaccharides Glucose (Cont.) Glucuronic acid If oxidation of C6 of glucose Glucaric acid If oxidation of C1& C6 of glucose Glucuronic acid is used for detoxification of various toxic substances Dr. Nasim 21 Monosaccharides Galactose Main source Lactose which is milk sugar C 4 epimer of glucose Mannose Can be converted to glucose On reduction forms Mannitol Dr. Nasim 22 Monosaccharides Fructose Levulose. Levo-rotation. Sweetest among all sugars. Most common source Sucrose (table sugar). Pure honey = Fructose only. Fructose Glucose. Entry into cells is independent of Insulin. Source of energy for sperms. Dr. Nasim 23 Disaccharides Maltose = Glucose + Glucose (α1-4) Fruit sugar Reducing sugar Produced from starch by hydrolysis due to salivary & pancreatic amylase. Hydrolyzed by Maltase Dr. Nasim 24 Disaccharides Lactose = Glucose+ Galactose (β1-4) Milk sugar Reducing sugar Hydrolyzed by Lactase Dr. Nasim 25 Disaccharides Sucrose = Glucose + Fructose (α1-2) Cane sugar Table sugar Non-reducing sugar Invert sugar Hydrolyzed by Sucrase (Invertase) Dr. Nasim 26 Polysaccharides Homo Polysaccharides Glycogen Store from of Glucose Present mostly in Liver & Muscles. Animal starch Branched structure (Tree like) Less then 12 glucose residues Dr. Nasim 27 Polysaccharides Homo Polysaccharides Glycogen (Cont.1) Within a chain (α1-4) broken by Phosphorylase enzyme. At branch point (α1-6) broken by debranching enzyme. Blood glucose levels are usually maintained by Liver glycogen stores. Dr. Nasim 28 Polysaccharides Homo Polysaccharides Starch Most of dietary carbohydrates are in this form. 2 types Amylose (Straight chain) Amylopectin (Branched structure) more then 12 residues in each chain. Dr. Nasim 29 Polysaccharides Homo Polysaccharides Starch (Cont.) Hydrolyzed by salivary & Pancreatic amylase into Maltose, Maltotriose & dextrins. Dr. Nasim 30 Polysaccharides Homo Polysaccharides Dextrins Intermediate product of hydrolysis of starch. E.g. Amylodextrins, Erythrodextrins & Achrodextrins. Dr. Nasim 31 Polysaccharides Homo Polysaccharides Dextrans Highly viscous. Polysaccharides Plasma expander. Cellulose Can’t be digested. Increase bulk of stool. Dr. Nasim 32 Polysaccharides Hetero Polysaccharides Muco Polysaccharides Animal origin Mucoprotein & Mucin (when in combination with proteins) Dr. Nasim 33 Polysaccharides Hetero Polysaccharides Muco Polysaccharides Subtypes Hyaluronic Acid Chondroitin sulphate Heparin Blood group Polysaccharides Serum mucoids Dr. Nasim 34 Polysaccharides Muco Polysaccharides Hyaluronic Acid (Cementing agent) Present in skin, synovial fluid, seminal fluid & vitreous humor. Functions Prevents penetration of bacteria into skin Lubrication of the joints Helps in fertilization Hydrolyzed by Hyaluronidase Dr. Nasim 35 Polysaccharides Muco Polysaccharides Chondroitin sulphate Dr. Nasim 36 Polysaccharides Muco Polysaccharides Heparin Dr. Nasim 37 Polysaccharides Muco Polysaccharides Blood group Polysaccharides Dr. Nasim 38 Polysaccharides Muco Polysaccharides Serum mucoids Dr. Nasim 39 Polysaccharides Mucilages Plant origin Agar Non-digestible Laxative Culture media Dr. Nasim 40 Polysaccharides Vegetable gums Used in pharmaceutical industry Pectins For making jellies Hemicellulose Dr. Nasim 41 Asymmetric carbon atom Asymmetric carbon atom: The carbon atom to which 4 different chemical groups are attached & it can rotate plain polarized light to the right or to the left. E.g. Open chain formula of Glucose contains 4 Asymmetric carbon atoms. (C2, 3, 4 & 5). E.g. Close chain formula of Glucose contains 5 Asymmetric carbon atoms. (C1, 2, 3, 4 & 5). Dr. Nasim 42 Optical Isomers Those sugars which rotates plain polarized light to right are (d) sugars & which to left are (l) sugars. Racemic Mixture: Such a solution which contains equal amount of Levo & dextro-rotatory then rotation of light will be equal but in opposite direction. Dr. Nasim 43 Ring Structure Hemiacetal ring: if the ring is formed by aldehyde gp. Hemiketal ring: if the ring is formed by keto gp. Pyranose Ring: 6 sided ring. O2 bridge b/w C1 & C5. Furanose Ring: 5 sided ring. O2 bridge b/w C1 & C4. Dr. Nasim 44 Anomeric carbon C of Aldehyde or keto gp forming hemiacetal or Hemiketal rings. C1 in Aldo-sugars. E.g. glucose C2 in keto sugars. E.g. fructose Dr. Nasim 45 Mutarotation The direction of plain polarized light in a freshly prepared glucose solution goes on changing for some time before settling to specific direction. Reason: unfolding of ring structure to striaght chain in order to maintain equilibrium b/w α & β forms of sugars. Dr. Nasim 46 Phenomenon of Inversion Dr. Nasim 47