Carbohydrates (PowerPoint)
advertisement
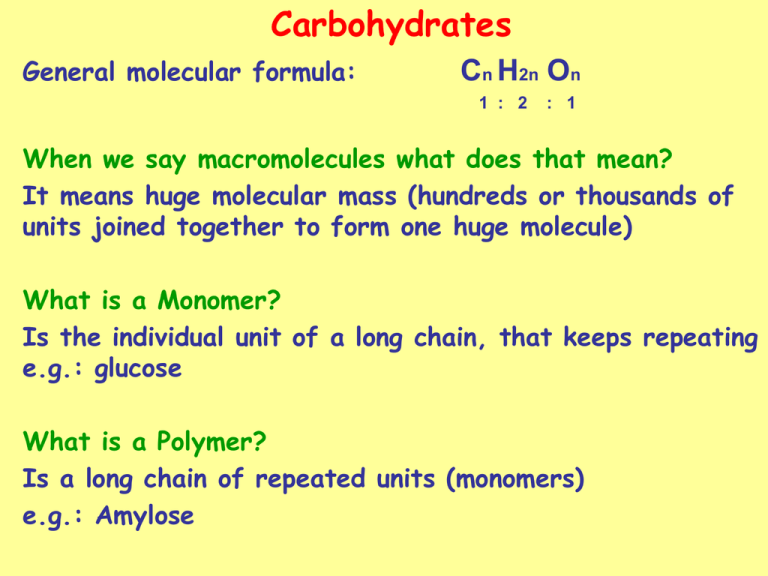
Carbohydrates General molecular formula: Cn H2n On 1 : 2 : 1 When we say macromolecules what does that mean? It means huge molecular mass (hundreds or thousands of units joined together to form one huge molecule) What is a Monomer? Is the individual unit of a long chain, that keeps repeating e.g.: glucose What is a Polymer? Is a long chain of repeated units (monomers) e.g.: Amylose Monosaccharides C6 H12 O6 α- glucose 6 5 1 4 3 2 α- glucose β-glucose 6 5 1 4 3 2 β-glucose What are the Functions (importance) of glucose? 1. Through glycolysis and cellular respiration, glucose is oxidized to eventually form CO2 and water yielding energy mostly in the form of ATP. C6H12O6 + 6 O2 2. → 6 CO 2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP) Enters in the formation of disaccharides (maltose, lactose and sucrose), It is also the monomer in the formation of starch, glycogen and chitin, as well as the precursor of vitamin C. Monosaccharides Galactose Is a monosaccharide hexose sugar, also called brain sugar. Found in dairy products, in sugar beets and other gums. Monosaccharides Fructose Is a monosaccharide hexose sugar (six carbon atoms). Found in Honey, tree fruits, berries, melons, and some root vegetables, such as beets, sweet potatoes, and onions. Monosaccharides End CH2OH l O OH l l OH l l OH l OH l OH Disaccharides C12H22O11 Maltose Found in barley (malt) and is used in the production of malt drinks and brewing beer. Disaccharides Lactose Found in milk and dairy products. Disaccharides Sucrose (α1-2 glycosidic linkage) Table sugar is Found in sugar cane, sugar beets, and sugar maple trees. Disaccharides Maltose = Glucose + Glucose Lactose = Glucose + Galactose Sucrose = Glucose + Fructose Disaccharides End Polysaccharides (C6H10O5)n + H2O Amylose (straight chain, coiled) (H2O insoluble) α1-4 glycosidic linkage *The angle at which the α 1-4 glycosidic linkage forms, results in the coiling of the polymers Polysaccharides Amylopectin (Branched) (H2O insoluble) α1-4 glycosidic linkage (the main chain) α1-6 glycosidic linkage (at the branch points) Polysaccharides Starch is a mixture of both Amylose and Amylopectin (H2O insoluble) i.e.: Amylose + Amylopectin = Starch *plants store excess glucose as starch in chloroplasts, amyloplasts and other plastids. *Starch is found in plants like potatoes, rice, wheat, and corn which constitute a major source of starch in the human diet. Polysaccharides Glycogen (highly branched) (H2O insoluble) α1-4 glycosidic linkage (the main chain) α1-6 glycosidic linkage (at the branch points) Glycogen has the same structure as amylopectin, however it is more branched. *Animals store excess glucose as glycogen *Glycogen is broken back down into glucose when energy is needed (a process called glycogenolysis). Polysaccharides Cellulose (straight chain) (H2O insoluble) β1-4 glycosidic linkage *The hydroxyl groups at the 1-4 positions in β glucose cause every other monomer to be inverted for the glycosidic linkage to form, this results in the straightness of the polymer, which allows hydroxyl groups of parallel molecules to form many hydrogen bonds , producing tight bundles called microfibriles. Polysaccharides Chitin (H2O insoluble) Is a cellulose-like polymer, the monomer is a glucose molecule to which a nitrogen-containing group is attached to the second carbon atom. *Chitin forms the exoskeleton of crustaceans, such as crabs, lobsters and the cell wall of some fungi. What are the main two functions of polysaccharides? 1. Energy storage: Starch is stored in the chloroplasts, amyloplasts and other plastids of plants. Glycogen is stored in muscle cells and liver cells, and enzymes in these tissues hydrolyze glycogen into single glucose molecules that are used for energy. 2. Structural support: Cellulose microfibrils interlace and form a meshwork that supports plant cells (the cell wall). Chitin forms the exoskeleton of crustaceans, such as crabs, lobsters and the cell wall of some fungi. The cellulose cell wall & the chitin exoskeleton Cell wall Exoskeleton Polysaccharides End