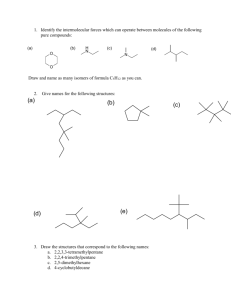
Isomers
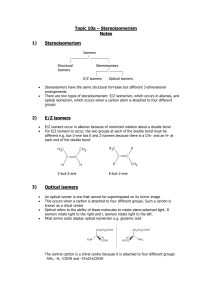
advertisement

Isomers Larry J Scheffler Lincoln High School IB Chemistry 3-4 1 Structural Isomers Structural isomers have the same molecular formulas but they differ in their structural formulas. 2 Stereoisomers Stereo isomers have the same structural formulas but they differ in their spatial arrangements. There are two types of stereoisomerism 1. 2. Geometrical isomerism Optical isomerism 3 Geometrical isomers Geometrical isomers occur in organic molecules where rotation around a bond is restricted This occurs most often around C=C The most common cases are around asymmetric non-cyclic alkenes 4 Geometrical isomers Carbon to carbon double bonds are made up of a s and a p bond. The p bond is formed from the combination of two p orbitals, one from each of the two carbon atoms The two p orbitals must be in the same plane to combine 5 Geometric Isomers in alkenes A cis isomer is one in which the substituents are on the same side of the C=C A trans isomer is one in which the substituents are on the opposite sides of the C=C 6 Geometric Isomers in Cycloalkanes Ring structures like C=C restrict rotation and therefore can result in cis and trans isomers 7 Properties of Geometrical Isomers The chemical properties of geometrical isomers tend to be similar but their physical properties are different 8 Properties of Geometrical Isomers The trans isomer has a much higher melting point. Unlike the cis isomer there is little intra-molecular hydrogen bonding 9 Optical Isomers Optical isomerism is present in all compounds that contain at least one asymmetric (chiral) carbon atom An asymmetric carbon atom has four different atoms or groups attached In this case there are two different ways to arrange the four groups around the chiral carbon atom (shown in red) 10 Optical Isomers While these structures may look identical, in three dimensions they are mirror images of each other. Such molecules are called enantiomers. 11 Distinguishing Enantiomers Optical isomers can be distinguished by the way they interact with plane polarized light Polarized light Polarized light is light that has been passed through a polarizing prism or filter. As a result the light vibrates in a single plane. Distinguishing Enantiomers Optical isomers can be distinguished by the way they interact with plane polarized light. One enantiomer will rotate polarized light to the right, the other to the left. Properties of Optical Isomers Apart from their optical activity enantiomers generally have similar physical and chemical properties. The chemical properties may be significantly different when the enantiomers interact with other optically active compounds. Thalidomide has two optical isomers. One is a tranquilizer, the other is a Powerful teratogen.