Absolute Dating

Absolute Dating
J F M A M J J A S O N D J
Earth
Forms
Earth
Cools
First
Life
Abundant
Oxygen
Multicellular
Organisms
Dinos
15-25
Humans
11:20 pm
Plants and
Animals
1 second
1/ 31,556,925.974 of the year 1900
9,192,631,770 flips of the magnetic field of a cesium atom
What is Absolute/Numerical Dating?
• The age of an earth material or event in years
Relative age
3 rd
2 nd
1 st youngest
Absolute
12 kya
95 mya
1.7 bya
8 kya
Estimating Earth's Age -
Early (failed) Attempt
Bishop Usher – Biblical Interpretation
4004 BC – before the birth of Christ
October 21
9:00 in the morning
Estimating Earth's Age -
Early (failed) Attempt
Sedimentation rates - 3 my – 500 my
Halley/Joly - Ocean Salinity – 100 my
Lord Kelvin – Rate of Cooling – 30 my
Radioactive Revolution around 1900
•
Radioactive decay - spontaneous transformation of an element to another isotope of the same element or another element.
Pieces of an Element
•
Protons - positively charged
•
Neutrons - no charge
•
Electrons - negatively charged e
N
P
P e
Isotope - element with different number of neutrons in the nucleus.
Hydrogen - stable Tritium - unstable e
P e
N
P
N
Tritium
(parent)
Radioactive Decay
Helium 3
(daughter) e
N
P
N unstable nuclear decay e
N
P
P e stable
Radioactive Decay
Alpha Decay – loss of a positively charged He ion
Beta Decay – neutron splits into proton and electron
Alpha Decay
238
92
U
234
Th +
90
4
2
He ( 2protons + 2 Neutrons)
Beta Decay
234
90
Th
234
91
Pa + e-
Neutron splits into a proton and an electron
Half-life
The fixed period of time during which half the parent atoms present in a closed system decay to form daughter atoms
Half-Life
1 2 3 4 5
Half-life
Half-lifes Potassium 40 / Argon 40
0 12 grams / 0 grams
1 6 / 6
2
3
3 / 9
1.5 / 10.5
Half-Life Exercise
Sample: 1024 grams
Isotope A
Parent
64 grams
10,000
1 st
512 / 512
(10 k) half-life
20,000
2 nd
256 / 768
Isotope B
Daughter
960 grams
30,000
3 rd
128 / 896
40,000
4 th
64 / 960
Parent/Daughter Half Life (yrs) Range (yrs)
238 U/ 206 Pb 4.5 billion
10 million to
4.5 billion
14 C 5730 100 to 70,000
3 H/ 3 He 12.3
1 to 50
Parent/Daughter
238 U/ 206 Pb
14 C
Material Dated
Igneous and
Metamorphic rocks
Organic material
3 H/ 3 He Water
Uranium (U) - Thorium (Th) - Lead (Pb)
238U decays to 206Pb (4.5 billion)
235U decays to 207Pb (713 million)
232Th decays to 208Pb (14.1 billion)
>Rocks containing Uranium provide three possible techniques.
>Because all three occur together, it allows a method to cross-check the dates.
>Uses zircons, uraninite and uranium ores
Potassium (K) - Argon (Ar) Dating
>Potassium (K) is an extremely common element.
>Half-life (t1/2) is 1.3 billion years.
>Range is 100,000 to 4.6 billion years.
>Useful for relatively young and very old rocks.
>Found in muscovite, biotite, orthoclase and glauconite.
>Used to date volcanic rocks.
Carbon 14 / Carbon 12
>Cosmic rays hit Nitrogen 14 changing it to
Carbon 14.
>Carbon 14 is taken in by organisms.
>When organism dies, amount of C-14 decreases.
Magnetic Polarity Dating
Dating techniques that can be used on this geologic column:
• absolute dating
• paleomagnetism
• superposition
• fossil correlation
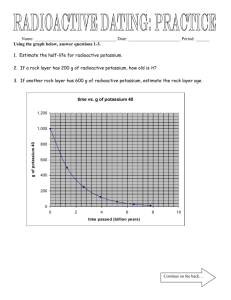
What is the Parent / Daughter ratio of a sample of radiogenic material if the original sample was 200g. and 3 half-lifes have passed.
If the half-life is 20,000 years, how old is the sample?
What is the half-life of an isotopic pair if the sample is 2 million years old and contains 625g of parent and 9375g of daughter isotope?