Fibre types
advertisement

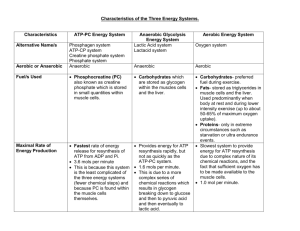
Energy Systems 3 Systems 3 groups of energy nutrients Muscle fibre types Three Energy Systems • ATP – PC (anaerobic alactic) – No oxygen • Glycolysis (anaerobic lactic) – No oxygen • Aerobic System – oxygen needed Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) • ATP – It is re-synthesized in two ways: • • Aerobically in the mitochondria = 36 ATP or Anaerobically in the cytoplasm = 1or 2ATP 1 molecule of PC gives 1 molecule of ATP 1 molecule of glucose gives 2 ATP + Lactate The Three Energy Nutrients • Carbohydrates – glucose and glycogen • Proteins – amino acids • Fats – fatty acids ATP – PC system • • • • Anaerobic alactic – no lactic acid is produced Lasts 10 -15 seconds Uses stored ATP and creatine phosphate No by-products, just the product ATP Glycolysis • Anaerobic Lactic system • Lasts 15 seconds – 3 minutes • Uses glucose and glycogen to make ATP • By – product is lactic acid Aerobic System • • • • • Occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria Needs oxygen to produce all 36 ATP Lasts as long as you are alive Uses glucose, glycogen, fats, and proteins to make ATP By-products are carbon dioxide and water Muscle Fibre types • Type I – slow twitch (aerobic) • Type IIA – Fast twitch ( Fast twitch oxidative or FOG) • Type IIB – Fast twitch (anaerobic) Type I • Slow contractions but can go a long time • Red (dark) in colour • Predominantly used in aerobic activities • High concentration of myoglobin – muscle can store oxygen for regeneration of ATP Type II A • In between fast and slow twitch • Faster, stronger contraction than Type I but can be sustained longer than Type IIB • Redish/white in colour • Moderate myoglobin concentration • Predominantly used in anaerobic activities Type II B • Fast twitch • White in colour • Fastest contraction speed of all muscle fibres • Low myoglobin concentrations • Predominantly used in anaerobic alactic activities – explosive lift or jump Approximate Distribution of muscle fibre types Sport % slow twitch % fast twitch Cycling 61 39 Middle – 59 distance runner Sprinter 26 41 Untrained person 58 42 74