File
advertisement

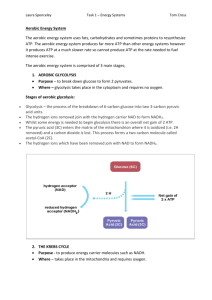
BTEC LEVEL 2 SPORT UNIT 4 – THE SPORTS PERFORMER IN ACTION Aerobic and Anaerobic Energy Systems D Nicholls OBJECTIVES To identify what we mean by the aerobic and the anaerobic energy systems. To consider specific sports that use each system. IMPORTANT All tasks on this PPT should be completed on your website unless otherwise stated. Make sure you put appropriate information on appropriate pages as and where required – this means you may have to create more pages! TASK 1: KEY TERMS First off – some definitions! You need to demonstrate an understanding of the following terms: Alactic Acid Glycolysis Lactic Acid Creatine Phosphate TASK 2: WHAT IS MEANT BY… Next up – following on from our first task, EXPLAIN what is meant by: The Aerobic Energy System The Anaerobic Energy System Remember – Explain means IN YOUR OWN WORDS! AEROBIC VS ANAEROBIC TASK 3: THE ENERGY SYSTEMS IN ACTION So – now that we’ve explained what we mean by each of the key terms, you now need to find out when we use these energy systems. Task: Using YouTube, find 2 videos that demonstrate the Aerobic Energy System being used in a sport, and 2 videos that demonstrate the Anaerobic Energy System being used. Embed the videos onto your website. For each video, explain WHY they are using that energy system. SO…ANAEROBIC…ATP-CP What this means is: Reliance on stored adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (the molecule that produces the energy in all living things), energy supplied by ATP (up to four seconds) Another stored molecule, creatine phosphate (CP) helps restore ATP CP is restored aerobically (with oxygen) Energy is supplied by ATP and CP (four to 20 seconds) When this system runs out of ATP-PC stores, glycolysis takes place. ANAEROBIC…GLYCOLYSIS/LACTIC ACID ATP is made from glucose stored in the liver and muscles Energy is supplied by ATP, CP and muscle glycogen (20 to 45 seconds) Energy is supplied by muscle glycogen (45 to 240 seconds) Waste product is lactic acid When this system is unable to maintain energy requirements, the aerobic system starts to produce energy Sports that use this system to provide energy are moderate to high intensity, i.e. short bursts of exercise lasting a few minutes, e.g. running 400 m, 800 m, and 1500 m distances. SO…IF WE SUMMARISE… The anaerobic energy system relies on stored adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which is responsible for producing energy. Creatine Phosphate (CP) helps restore ATP. CP is restored AEROBICALLY The energy you use in the first 4-20 seconds is supplied through these – Glycolysis occurs when this energy is used up. ATP is made from glucose stored in both the liver and muscles, so the energy supplied by ATP, CP and muscle glycogen is responsible for 20-45 seconds, then the muscle glycogen for 45 – 240 seconds. As a result, a waste product; Lactic Acid; is produced. When the body reaches the limit of the above – we shift over to Aerobic Energy. TASK 4: ANAEROBIC ENERGY You need to explain what we’ve just looked at IN YOUR OWN WORDS. This means you should explain it as if you were giving a talk to a class, or explaining it to a friend who doesn’t understand it. You can use diagrams to back up your information as and where required. AEROBIC ENERGY For example during longer periods of exercise/activity; sustained energy relies on this system. Sports that mainly use this system to provide energy used for sustained activity are longdistance events such as marathon running, long-distance swimming, long-distance cycling. Energy supplied by muscle glycogen and fatty acids (240 to 600 seconds) Uses oxygen as a means of making energy (re-synthesising ATP) Low to moderate intensity (beyond 90 seconds). SO WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? Simply put – the following: Aerobic exercise, is submaximal exercise which gets your heart rate and breathing rate up, over a sustained period. For example, jogging, swimming, cycling. Aerobic exercise is excellent for the health of your heart and lungs. TASK 5: AEROBIC EXERCISE Explain what we mean by what we have just looked at – making sure you are clear about WHY we call it aerobic exercise and WHAT happens. LONG TERM ADAPTATIONS TO AEROBIC EXERCISE Make sure you note these down! Makes more red blood cells so more Oxygen can be transported in the blood Your arteries become wider and more elastic so that your blood pressure falls Your heart grows bigger (hypertrophies) and the walls become thicker so it can pump more blood with each beat. This means it doesn't have to beat so fast! More capillaries grow within your muscles so that more O2 can get there quicker Your heart rate returns to normal more quickly following exercise More capillaries also grow around the alveoli in your lungs so more O2 is taken into the blood and more CO2 is released Your diaphragm and intercostal muscles become stronger so they can make your chest cavity bigger meaning you can breathe in more air with each breathe TASK 6: ADAPTATIONS Explain how the body adapts to aerobic exercise over a long period of time, making sure you are specific and clear in your explanation. TASK 7: A HAND OUT. Your next task is to create a hand out that can be given to students who are investigating the energy systems and how they work. You should consult the help PPT on DJN’s website and summarise slides 1-10 in a hand out form. Make sure you include and EXPLAIN the graphs included. Make sure the information is in YOUR OWN WORDS. Make sure you use appropriate illustrations. TASK 8: COMPARISON Now that you’ve found out all of the key information – you need to draw some comparisons between the sports that use the different energy systems. To do this, you should complete the following: DESCRIBE how the body uses the different energy systems – be VERY CLEAR! Compare how the different energy systems are used in sports with different demands: What is similar? What is different? Why is this? Make sure you use specific examples! TASK 9: 2 ATHLETES Now then – you need to chose 2 athletes: 1 from a sport that uses the Aerobic Energy System 1 from a sport that uses the Anaerobic Energy System You should conduct some research into them, so research: Their training methods The demands of their sport A bit of history about their achievements Why their sport is Aerobic or Anaerobic You should make sure you embed video of them in action with your work by way of further evidence.