Energy Systems Unit 1 P7
advertisement

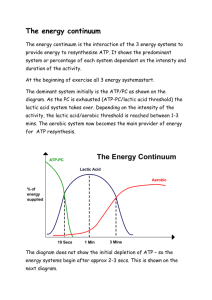
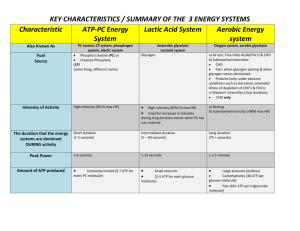
Unit 1 P7 Know the different types of energy systems • All movement requires energy. • The methods by which your body generates energy is determined by the intensity and duration of the activity being undertaken. • Activities that require short bursts effort like sprinting or jumping require the body to produce large amounts of energy over a short period of time. • Marathon running or cycling require the body to provide continued energy production over a longer period and at a slower rate. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5G 8cVpXpsL8 Phosphocreatine energy system ATP and Creatine phosphate make up the ATP-PC system. It is the immediate energy system. When exercise intensity is high, or energy needs are instantaneous, Creatine phosphate stored in the muscle is broken down to provide energy to make ATP. When the high energy bond in PC is broken, the energy it releases is used to resynthesise ATP. Explosive work can be achieved but only for up to 10 seconds at maximum intensity. For example 100metre runner. Lactic acid energy system This is the short term energy system. To meet energy requirements of higher intensity over a longer period, such as during a 400 metre race, ATP can be made by the partial breakdown of glucose and glycogen. This is an aerobic process that does not require oxygen and is therefore not sustainable over a long duration. Aerobic energy system This is the long term energy system. If plenty of oxygen is available, as it is during everyday movements and light exercise, glycogen and fatty acids break down to yield large amounts of ATP. Phosphocreatine ENERGY SYSTEMS O2 Required Speed of energy supply Fuel Source Amount of ATP Production By Products Duration Cause of fatigue Activity ATP/PC SYSTEM ANAEROBIC GLYCOLYSIS (Lactic acid system) AEROBIC ENERGY SYSTEM No No Yes Very fast Fast Slow Creatine Phosphate Carbohydrates Carbohydrates &fats (protein in extremes) Limited Limited Unlimited None Lactic acid CO2 ,H2O & Heat 0-10sec Up to 2min Forever Limited supply ATP/PC Lactic acid production Unlimited Power based activities Sprint endurance Long duration Energy contribution ATP/PC SYSTEM •Main source of energy in first 10 sec •Peaks in output at approx 5sec •Fatigues quickly due to depletion ATP/PC AEROBIC ENERGY SYSTEM •Main source of energy from 30sec + (point when oxygen supply has increased sufficiently to contribute ATP) •Unlimited capacity to work unless insufficient fuel supply (food) LACTIC ACID SYSTEM •Main source of energy from 10- 30 sec •Peaks in output at approx 20sec •Fatigues due to build up of lactic acid •Provides energy for up to 2min 10s 20s 30s 60s Time 2min 4min+ ENERGY SYSTEM INTERPLAY