Electrochemical Cells Lab: Daniell Cell & Reactivity Series
advertisement

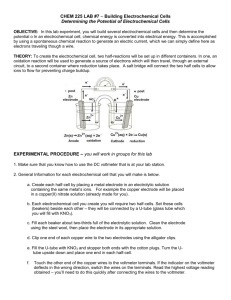
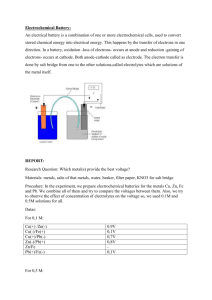
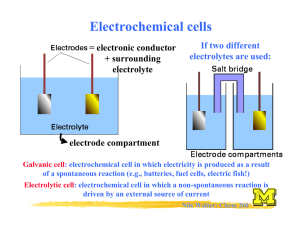
LLG Paris–Abu Dhabi Advanced Math and Science Pilot Class Academic year 2014-2015 Lab work– Chemistry Electrochemical cells Purpose: ● Building electrochemical cells by associating two half cells Metallic ion / Metal : Mn+ / M ● Measuring the voltage of the cell and identifying positive and negative terminals ● Deducing the reaction occurring at each electrodes and writing the corresponding half equations ● Writing the redox reaction associated with an electrochemical cell ● Classifying the different reducers studied by their relative strength Equipment: Metallic plate: copper Cu, zinc Zn, aluminum Al, iron Fe and a graphite inert electrode: C Solutions of metallic ions: (Cu2+,SO42-), (Zn2+,SO42-), (2Al3+, 3SO42-), (Fe2+, 2 Cl-) at 0.1mol.L-1 Hydrochloric acid solution: H+, ClBeakers, salt bridges, wires, voltmeter I. Complete study of the Daniell cell ( Cu2+/Cu and Zn2+/Zn cell) E1.Using the equipment available on your table, create an electrochemical cell following the drawing below. E2. Study the cell in open circuit, with a voltmeter. Measure the difference of potentials (or electromotive force: emf) Q3. Specify the polarity of the electrodes. Q4. Write the equation of the reactions taking place at the electrodes and the reaction of equation associated with the transformation taking place in the cell when it delivers a current. Note: the electrode where the oxidation takes place is named the ANODE the electrode where the reduction takes place is the CATHODE Q5. Explain the role of the salt bridge. Q6. Represent the direction of the electrons and the ions in the solution and in the salt bridge in closed circuit. II. Emf of other cells E7:build cells, identify the negative terminals (anode). Collect your data in the table: Cells anode Cu2+/Cu Zn2+/Zn Al3+/Al Fe3+/Fe H+/H2 Cu2+/Cu Zn2+/Zn Zn - 1.1V Al3+/Al Fe3+/Fe H+/H2 III. Classification of metal reducers : Reactivity series Q8: Use the results from the previous experiment to classify the half-call according to their ability to be the negative electrode. Then, classify the reducer studied by increasing strength (ability to give electron = to be the negative electrode). IV. Study of a real battery: Zn/MnO2 (manganese oxide) /C DATA: Redox pair involved: Zn2+/Zn and MnO2 /Mn2O3 Q9: Write the reaction occurring when this cell is delivering electricity. Q10: What is the use of the carbon electrode? Of NH4Cl? (MnO2(s) + NH4Cl paste) Q11: In “alkaline” battery, NH4Cl is replaced by KOH. How is this affecting the final redox equation occurring in the battery? LLG Paris–Abu Dhabi Advanced Math and Science Pilot Class Equipment: Students: • filtration device • 6 test tubes • wash bottle of distilled water • sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol / L) • 6 beakers 100 mL + Voltmeter Teacher: • 1 L of solution (Cu2+ + SO 24 ) at 0.1 mol/L • steel wool • iron powder • iron(III) chloride solution (Fe3++3Cl-) at 0.1 mol/L • spatulas Academic year 2014-2015 Lab work– Chemistry