SC2 cracking furnace
advertisement
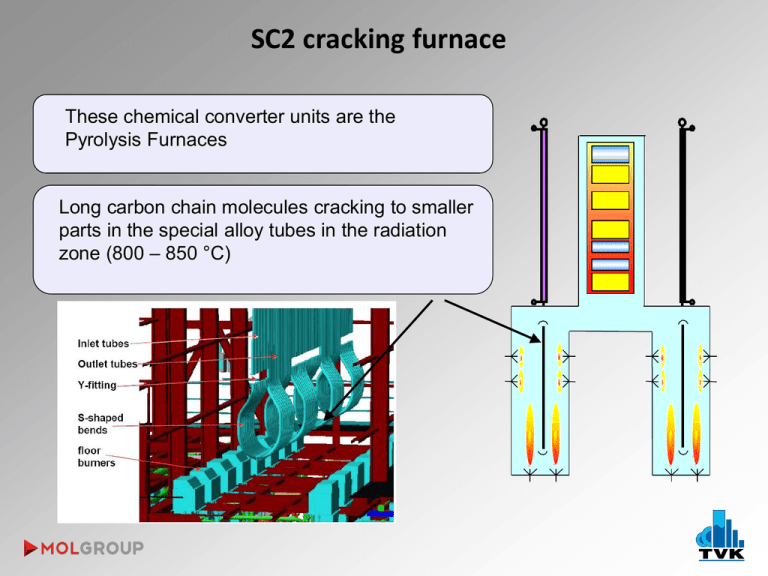
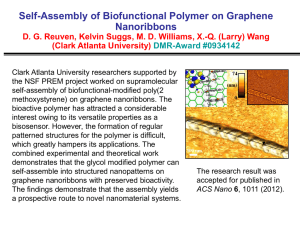
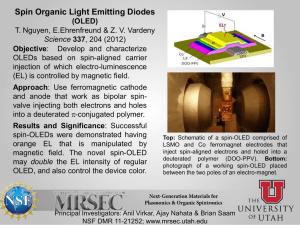
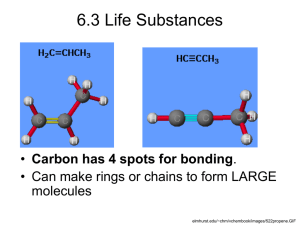
SC2 cracking furnace These chemical converter units are the Pyrolysis Furnaces Long carbon chain molecules cracking to smaller parts in the special alloy tubes in the radiation zone (800 – 850 °C) SC-1 block diagram Information about polymer units of TVK „…locally large, but globally small, …how can we do anymore? „ Basic behavior of polyolefin units Low MI PP4 PP3 Average cycle lenght Op Qu alit y co ntr ol ~31 days 10~11 17~18 24 29 Nr. of transitions/cycle 9~10 16~17 Off-spec. ratio 1,1% 0,1% Transition grade ratio 2,3% 1,7% Final product Production L tic s i og High MI * Transition grades were created in Q4, 2012 PP-4 ~33 days Reactor grades COPO ent lopm Deve HOMO Polymer Units PP-3 TVK’s PP in 2012 Co n Co troll un ing tin / g Sales& Marketing tim izat ion nce a n e nt Mai Cyclical industry with frequent transitions on a dynamic market PE-1/LD2 PE-1/HD1 Average cycle lenght ~24 days ~28 days ~30 days Reactor grades 7 9 7 Final product 11 10~11 10 Nr. of transitions/cycle 6 4/line 6 Off-spec. ratio 5,1% 1,8% 1,07% Transition grade ratio 0,8% 0,2%* 0,3%* TVK’s PE in 2012 PE-2 TVK’s polymer technology review The „troops” that we have PolyPropylene PP: linear polymer built from propylene and in some cases contains also ethylene Tradename: Tipplen (TVK) Three main types: homo PP, random copolymer PP (C2: 0.5-6.5%) and block copolymer PP (C2: 5-25%) Properties: Melt index: 0.2 - 80g/10 min (230oC/2,16 kg) C2 content: 0.5 – 20wt% Melting range: 140 – 165oC Licensors: PP3; PP4: LyondellBasell / Spheripol (loop Rx with monomer as diluent) PP-3 Unit – 100 KTA (1989) PP-4 Unit – 180KTA (1999) Spheripol PP advantage-disadvantage Bulk Loop vs. Gas phase reactor technology Higher CAPEX Easy Temperature Control at Reactors Shorter Grade Transition Time Narrower Product Portfolio (It means lower C2 content random PP, TPO grades) Lower Volatile Content in PP (Just at CR grades) Better Catalyst Activity Low Density Polyethylene LDPE technologies: autoclave/tubular reactor LDPE-2 Plant started in 1991. Annual capacity: 65 kt Product Tradename: Tipolen Density: 0.919 – 0.925 g/cm3 Melt index: 0.2 – 4.6 g/10 min (190oC/2.16 kg) Main application: film blowing Licensor: LyondellBasell tubular autoclave LDPE tubular vs. autoclave Shematic process of LDPE-2 Plant Polymerisation type: free radical monomer: iniciator: growth modificator: comonomer: radical formation starting of chain transmitting radical activity termination plasticity, polarity, shining of the product High/Medium Density Polyethylene HDPE/MDPE: Polyethylene having only short chain branches on the linear main chain Tradename: Tipelin (TVK) Properties: Density: 0.935 – 0.965 g/cm3 Melt index: 0.1 - 50 g/10 min (190 oC/2,16 kg) Melting range: 125 – 135oC Licensor: PE1/ HDPE-1: Chevron Phillips (loop Rx with light diluent) PE2 / HDPE-2: Mitsui Chemicals Inc. (stirred tank Rx with heavy diluent) No of SCB LLDPE MDPE HDPE 0,915 0,926 0,940 0,970 PE-1/HDPE-1 Unit – 200KTA (1986) Loop Reactor (90 – 106°C; 42barg) Flash Tank (60°C; 0,3barg) Flash Gas to recycling system ethylene hexene-1 hydrogen Cyclon e Treaters isobutane Dryer (70°C) Bag Filter HDPE fluff to powder silos Purge Column (75°C) Powder Silos (8pcs) Additives Homogenizer Repellet Scales Dryer HDPE pellets Classifier • Silo farm (28 silos) • Bagging machines (2 lines) • Truck loading facility Continuous Intensive Mixer (CIM) Extruder (210°C) PE-2 / HDPE-2 Unit – 220KTA 2004 Comonomer Centrifuge H2 Daily tank TEAL Dryer / 105°C Mixing silo Pellet Silo Homogenizer VOC: ~33 -> 0,1wt% Powder Silo R1: 85°C/7barg 220°C R2: 75°C/2.5barg Packaging Fresh solvent Termék Solvent tank 2/3 1/3 Low Polymer (LP) Advantages, disadvantages in the HDPE units PE-1/HDPE1 vs. Less rotation maschine - Higher reliability Excellent diluent recovery Broad density range (0,962-0,935) Lower catalyst costs Less steam consumption Lower volatile content (instead of MDPE) MI correction in the extrusion section Higher electricity consumption Just monomodal products Longer transitions Lower flexibility PE-2/HDPE-2 Wider product range (mono and bimodal) Shorter grade transition time High flexibility Lower pressure in the reactor part Start and stop without flaring Lower ESP in the extrusion section Possibility to use C3- instead of purchased co-monomer Higher steam consumption in the diluent recovery section Higher specific diluent consumption Higher volatile content Higher maintenance costs Process Control - Optimization Try to find…. …keep it… …automate it. General process control scheme APC DCS Basic Control level Process – Field level Optimization 3 basic rules: 1 – Safety 2 – Quality 3 – Economic goals The economical situation forces the polymer producers to find „new operating region”, and they would be able to adopt new technics to remained there in every different workpoints. APC the most common tool for optimization The APC is not a „magic weapon”. This is that tool wich can help us to keep the plant near to the optimum continuously if the operators are familiare with that. The two most critical behaviors of a polymer plant: Non-linearity, multivariable Thank you for your kind attention!