Introduction

Experiment 2
DISTILLATION AND
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
OF ALKANES
Objectives
Explore the relationship between molecular structure, intermolecular forces and boiling points of various types of compounds.
Learn techniques of simple distillation and gas chromatography (GC).
You will use these techniques to separate and identify compounds in an unknown mixture.
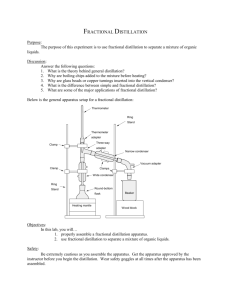
Distillation
Separates components of a mixture based on their boiling points.
Common purification method.
Boiling point can be used to determine the identity and purity of a substance.
Pure substance : characteristic sharp bp (<1 o C range)
Impure substance : broader and lower bp range.
to voltage regulator
Heating Mantle iron ring water out
Distillation
Involves vaporization, condensation, and collection of the condensate (distillate).
The temperature of the distillate is measured by a thermometer placed in the path of the vapor.
water in
Simple Distillation
Simple distillation is most effective when the mixture contains only one volatile component.
More than one ….most effective if the boiling points of the components differ by at least 70 ºC.
Gas Chromatography
Used to determine the composition of a mixture: qualitatively (what is present) and quantitatively (how much of each component is present).
Today, we will use gas chromatography to analyze the purity of our samples.
A single peak , other than the solvent peak, in a GC chromatogram indicates a pure compound.
He
Carrier Gas
Capillary Tube
Liquid Stationary Phase
A A B
A
B
A
B
B
B
He Carrier gas
A
A
A B
B
B
A
Immediately after injection
Gas Chromatography
Oven
Injection port
Column
Detector
Recordercomputer
Lower boiling component
Higher boiling component
He Carrier gas
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
After several minutes
B A
0
Time
Resulting chromatogram
•The individual fractions collected are analyzed by GC during the course of the distillation. Based on peak size, it is evident that as the distillation proceeds, the later fractions contain mainly the higher boiling component of the mixture.
•The individual fractions collected are analyzed by GC during the course of the distillation. Based on peak size, it is evident that as the distillation proceeds, the later fractions contain mainly the higher boiling component of the mixture.
Component
#2
Product Analysis
(Quantification of Components)
Adjusted area %
Most often you will dissolve your compound or mixture in a low boiling solvent for GC analysis. The relative areas of the components of interest must therefore be adjusted, to exclude the large % area of the solvent peak.
In general, to calculate the adjusted area percent , the area of each peak of interest is divided by the sum of the areas of all peaks of interest (excluding the solvent peak) and that value is multiplied by
100%. Refer to page 37 for further explanation.
Adjusted area % = area % of peak of interest sum of area % of ALL peaks of interest
*omit area % of solvent peak
X 100
Product Analysis
(GC Analysis)
• Have your SECOND and FOURTH fractions analyzed by GC. ( 5 drops of your sample in a vial, containing 1.0 mL of pentane from the dispenser in balance room.)
• Be sure to record your GC vial slot # in your laboratory notebook. GC chromatographic results will be returned during the following lab meeting.
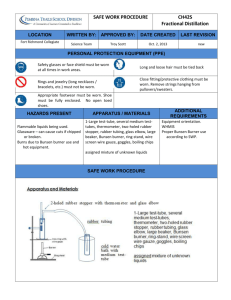
SAFETY CONCERNS
All compounds used in today’s experiment are extremely flammable .
Wear safety goggles at all times and use extreme caution!
WASTE MANAGEMENT
Place all fractions and the residue remaining in the flask in the containers labeled “Organic Waste
(Distillation)” in the waste hood.
Clean all ground glass joint distillation glassware with a small amount of wash acetone , and leave in your hood for instructor inspection.
Rinse all other glassware from your drawer with soap and water, and follow with a quick wash acetone rinse. Glassware must be COMPLETELY
DRY before returning to drawers!