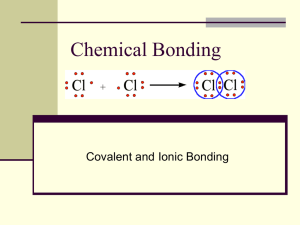
U2 Ionic and Covalent Bonding Notes
advertisement

Objectives • I can compare the properties of ionic and covalent compounds with a Venn diagram. • I can practice drawing Lewis Dot Diagrams of molecules by completing a worksheet. • I can investigate the relationship between electronegativity and chemical bonding by sorting compounds by electronegativity data. Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds • Bond Strength = the energy needed to break the bonds between atoms in a compound. Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds Atoms in ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds. Atoms in covalent or molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds. Ionic bonds are stronger (more bond strength) Covalent bonds are weaker (less bond strength) Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds Formed by Transfer of electrons Formed by Sharing of electrons Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds Structure: Crystal Lattice Structure: Molecules Water (H2O) molecules Lithium Chloride (LiCl) crystal lattice Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds Consist of Metal and nonmetal Consist of Nonmetal and nonmetal Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds State of matter: Solid at room temp. State of matter: Solid, Liquid or Gas at room temp. Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds Conductivity? Conducts Conductivity: Does not electricity when conduct electricity when dissolved. dissolved. Ionic vs. Covalent • Think, Pair, Share: With a partner, fill in the middle overlapping portion of the Venn diagram. What do ionic and covalent compounds have in common? • Possible answers: – types of compounds, formed by chemical bonds, include more than one atom, involve electrons, are formed and broken by chemical reaction Chemistry of Life All organisms (living things) are made of macromolecules. Macromolecules are large covalent compounds. The atoms in proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are all connected by covalent bonds. 3 Types of Bonding **IONIC How are ELECTRONS are Bonds transferred Formed? between ions (1 Type of Bond Formed Who’s Involved ? *COVALENT METALLIC Electrons are shared between atoms. steals, 1 gives) Solid Crystals with Usually liquid or repeating patterns solid of (+) and (-) ions METAL + NONMETAL Special When dissolves in Properties H20, conducts electricity “Sea of Electrons” Spread all over between atoms of the same element. Solid metal NON-METAL + NON-METAL METAL AND METAL Does not conduct electricity Very good conductors of electricity on their own!