Stoichiometry - Madison Public Schools
advertisement

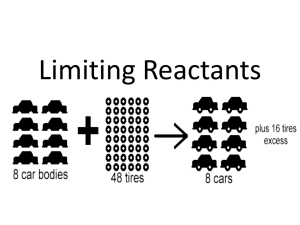
Stoichiometry Introduction Introduction to Stoichiometry Stoichiometry – study of the mass relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g) Mole Ratio 2 Al2O3(l) → 4 Al(s) + 3 O2 (g) 2 m ol Al2O3 4 m ol Al or 4 m ol Al 2 m ol Al2O3 2 m ol Al2O3 3 m olO2 or 3 m olO2 2 m ol Al2O3 4 m ol Al 3 m ol O2 or 3 m ol O2 4 m ol Al Mole Ratio How many moles of Aluminum can be produced from 13.0 moles of aluminum oxide? 4 m ol Al 26.0 m ol Al 13.0 m ol Al2O3 2 m ol Al2O3 Practice 2 Al2O3(l) → 4 Al(s) + 3 O2 (g) 1. If 26.0 moles of aluminum are produced in a reaction, how many moles of oxygen will also be produced? 2. How many moles of aluminum oxide are required to produce 18.1 moles of aluminum? 3. If 23.0 moles of aluminum oxide react, how many grams of Aluminum will be produced? Limiting Reactants Objective: 1. Identify the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction 2. Use the limiting reactant to calculate the maximum amount of product formed or the excess reactant in a reaction. Limiting Reactant – reactant that limits the amount of products that can form in a chemical reaction. Excess Reactant – substance that is not completely used up in a reaction Limiting Reactants N2 + 3 H2 2 NH3 Which is the limiting reactant? Finding the Limiting Reactant N2H4 (l) + 2 H2O2 (l) N2 (g) + 4 H2O(l) Which is the limiting reactant when 0.750 mol of N2H4 is mixed with 0.500 mol of H2O2? • A given amount of a reactant is used to determine the required amount of the other reactant. That amount is then compared to the actual amount. 2 m olH 2O2 1.50 m olH 2O2 0.750m olN 2 H 4 1 m ol N 2 H 4 Finding the Limiting Reactant N2H4 (l) + 2 H2O2 (l) N2 (g) + 4 H2O(l) How much of the excess reactant, in moles remains unchanged? 1 m ol N 2 H 4 0.250m ol N 2 H 4 0.500m olH 2O2 2 m olH 2O2 0.750molN 2 H 4 0.250molN 2 H 4 0.500molN 2 H 4 How much of each product forms? 0.250 mol N2 & 1.00 mol H2O Amount of product in a Limiting Reactant Problem What mass of barium nitride is produced from the reaction between 22.6 g barium and 4.2 g nitrogen gas? Percent Yield actual yield percent yield 100% theoretical yield Theoretical yield – maximum amount of product that can be produced as determined by a stoichiometric calculation and based on the law of conservation of matter Actual Yield-amount obtained in a reaction Percent Yield Methanol can be produced through the reaction of CO and H2 in the presence of a catalyst. If 75.0 g of CO reacts to produce 68.4 g CH3OH, what is the percent yield?