Physical and Chemical Changes
advertisement

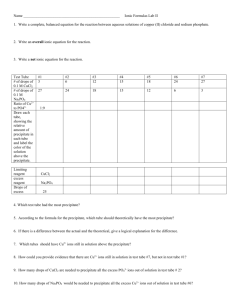
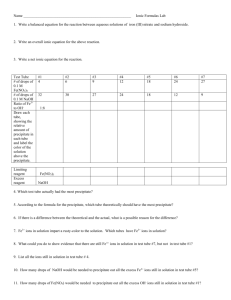
SUBSTANCE SUBSTANCE MATTER SUBSTANCE ELEMENT COMPOUND MIXTURE HETEROGENEOUS HOMOGENEOUS Characteristics of matter that can be measured and observed without changing the makeup of the substance. Ability of a substance to undergo or resist a chemical change. A change in which the appearance of matter changes but its properties and makeup remain the same. A change that produces one or more kinds of matter that are different from those present before the change. A law that states that mass cannot be created or destroyed. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES Physical and Chemical Changes A. Physical change - the form or appearance of matter changes, but composition stays the same. 1.Shape can change, but substance does not. 2. Dissolving a solid into a liquid is a physical change. 3. Changing states through vaporization, condensation, sublimation, or deposition does not change the composition of the matter. B. Chemical change results in a change in the substance’s composition. 1. Color can change as a chemical reaction occurs. 2. Energy may be gained or release during a chemical change. 3. Odor can change when a chemical change occurs. 4. A gas forming can indicate a chemical change. 5. A precipitate (a solid from a liquid) can indicate a chemical change. 5. Chemical changes are not easily reversed. C. Chemical changes alter the composition of the substance, physical changes do no alter the composition of substances. 1. Water freezes or evaporates-amount of matter stays the same (physical change) 2. Wood burns-ashes, smoke, and gases still total the same amount of matter (chemical change) D. Law of Conservation of Mass- particles of matter are not created or destroyed as th result of physical or chemical changes. Physical changes include: Wadding up a piece of paper. Chopping a piece of wood in half with an ax. Tearing a piece of cloth. Cutting a hamburger with a knife. Biting into an apple. Flattening a lump of clay with your fist. Hitting a baseball with a bat. Sitting on a balloon and popping it. Chemical changes include: Digesting your dinner. Removing grease with soap. Cooking an egg in a hot pan. Milk that has gone sour. Lighting the wood you chopped in half with an ax. Making cookie batter and baking it. Exercising and using sugars and fats stored in your body. Chemical vs. Physical Changes In a physical change, the substances are not altered chemically, but merely changed to another phase (i.e. gas, liquid, solid) or separated or combined. In a chemical change, the substances are altered chemically and display different physical and chemical properties after the change. Chemical Changes…. Are changes that cause a NEW material to form. The original material cannot easily be recovered. There is a chemical reaction. SIGNS OF A CHEMICAL REACTION: Unexpected color change Bubbling or fizzing (which means a gas is forming) Light Smoke Temperature change A precipitate may form when two liquids are mixed An odor may occur Physical Changes….. Do not change the identity of the substance or material. May cause the substance to look different after the change. Examples: Breaking something into pieces Changes of state (melting, boiling, condensing, sublimating) Dissolving one substance in another Heating without burning You can usually get the original material back through easy methods such as with separation or distillation. Read the article on physical and chemical changes, complete the questions. pgs 73 - 76 article is also online Complete the worksheet on P-C changes. Read, understand, highlight lab sheet for tomorrow. STUDY FOR NEXT Tuesday'S TEST! when pulled D C A B Identify 1 - 5 and A-D. Tell what the plateaus mean. D C A B 1. Solid 2. Solid to liquid 3. Liquid 4. LIquid to Gas 5. Gas A. Freezing B. Melting C.Condensation D. Evaporation Physical - Chemical Change Lab Students will complete six different experiments and make observations for each experiment. Read the procedure carefully, and make sure you know what to do before you begin each experiment. Watch carefully, and make careful observations. Data table needs to be filled out completely, and questions answered. 1. This is a demonstration. Pay attention and fill out the table. 2. Place a 50ml beaker on your balance and find its mass. Add 0.5 g to that mass by moving the slider. Add colored Powder A to your beaker until it balances again. Add 30ml of water and stir. 3. Carefully, pass a piece of COPPER over a lit burner until a change is observed. Hold the copper with forceps. You will not need your burner after this experiment, so carefully put the flame out and cap it. 4. Put 20 drops of HCl (hydrochloric acid) into a small test tube. Observe changes during and after to the zinc. Add a pinch of zinc metal. 5. Put copper sulfate solution into a small test tube until it is half full. Add a small piece of fine steel wool, and let it sit for 3 minutes. Check carefully for a temperature change by touching the outside of the tube. Tap out the solid onto a paper towel and observe it for changes. 6. Put 20 drops of solution A into a small test tube. Add 20 drops of solution B. Observe changes after 5 minutes. 7. Put 10 drops of solution C into a small test tube. Add 10 drops of solution D. Observe changes for 1 minute. What are the signs of a chemical change? Chemical change results in a change in the substance’s composition. 1. Color can change as a chemical reaction occurs. 2. Energy may be gained or release during a chemical change. 3. Odor can change when a chemical change occurs. 4. A gas or a precipitate can indicate a chemical change. 5. Chemical changes are not easily reversed. procedure 1 Iodine crystals over heat 2 .5 g powder A in 30 mL of H2O 3 4 5 6 7 observation before observation during and after change physical/chem change? QUESTIONS: List three physical properties of many solids. ______________ _____________ _____________ 2. Name a physical property of liquids. __________________________ 3. What are some “signals” that a chemical change is occurring? 4. What kind of change is happening when ice melts? _________________________ 5. When a candle is burning, name both a physical change and a chemical change. EXPERIMENT 2 EXPERIMENT 3 EXPERIMENT 4 EXPERIMENT 2 5 EXPERIMENT 6 EXPERIMENT 7 Physical and Chem Changes Video.docx Matter_and_Its_Properties__Changes_in_Matter.asf _____1) physical change _____2) boiling point _____3) homogeneous mixture _____4) malleable _____5) adhesion _____6) brittle _____7) viscosity _____8) tensile strength _____9) water _____10)melting point _____11)heterogeneous mixture _____12)density _____13)chemical change _____14) cohesion _____1) physical change _____2) boiling point _____3) homogeneous mixture _____4) malleable _____5) adhesion _____6) brittle _____7) viscosity _____8) tensile strength _____9) water _____10)melting point _____11)heterogeneous mixture _____12)density _____13)chemical change _____14) cohesion Attachments Physical and Chem Changes Video.docx Matter_and_Its_Properties__Changes_in_Matter.asf