CarbonylClassificationTests
advertisement

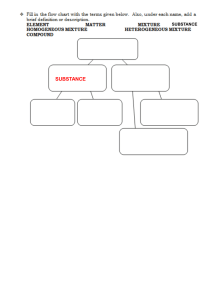
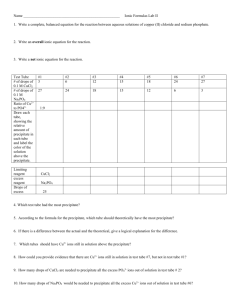
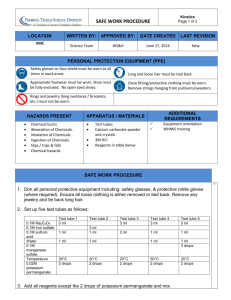
Carbonyl Classification Tests The samples to be tested in each of the following tests are: .Your Sample .Cyclohexanol .Cyclohexanone .Benzaldehyde .Acetophenone 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine* Test OH R2C=O + H2NNH-C6H4(NO2)2* R2C-NH-NH-C6H4(NO2)2 R2C=N-NH-C6H4(NO2)2 + H2O 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone 1. Dissolve 1 - 2 drops of sample to be tested in 10 drops of 95% ethanol. 2. Add this solution to 10 drops of 2,4-DNPH reagent. 3. Shake the mixture vigorously, and if no precipitate forms almost immediately, allow the mixture to stand for 15 minutes. A positive test is indicated by the presence of a precipitate the 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone of your compound. Dispose of test tube contents into the Recovered Organic Solvent Bottle. Tollens' Test RCHO + Ag(NH3)2 + 2 OH 2 Ag + RCO2NH + H2O + 3NH3 1. Place 3 drops of sample into a test tube, followed by 10 drops Tollens' reagent. The formation of a silver mirror, or a black precipitate constitutes a positive test. 2. If no reaction occurs at room temperature, warm the solution in a beaker of warm tap water from one of the hot water faucets at the front of the lab. Dispose of contents into the sink and clean tubes CAREFULLY. Chromic acid test See Alcohol Classification Tests Pg. 29. H2CrO4 Primary alcohols and aldehydes: RCH2OH ------------> RCO2H H2CrO4 Secondary alcohols: R2CHOH ------------> R2CO Ketones: no visible reaction Tertiary alcohols: R3COH do not react with H2CrO4 1. To a test tube, add 20 drops acetone, 1 drop of sample, and 1 drop of chromic acid reagent. 2. Shake the contents of the tube. A positive test is indicated by the disappearance of the orange color of the chromic acid reagent and the formation of a green or blue-green precipitate or emulsion. Primary and secondary alcohols and aliphatic aldehydes give a positive test within 5 minutes, while aromatic aldehydes require up to 45 minutes. Dispose of test tube contents into the Recovered Organic Solvent bottle. Iodoform Test When an aldehyde or ketone that has -hydrogens is treated with a halogen in basic medium, halogenation occurs at the -carbon: R1 O X2, NOOH R1 O R2 - C - C - R(H) -----------> R2 - C - C - R(H) H X If R1 and R2 = H, AND X = I H O 3I2,4NaOH X O I O HC-C-R(H)--------> X-C-C(H) ---> X-C-H(s) + Na+ -O-C-R(H)+3NaI H H2O X I 1. To a test tube, add 10 drops dioxane, 2-3 drops of sample, and 10 drops 3M NaOH. 2. To the tube now slowly add 15 drops of Iodine solution. A positive test is evidenced by the disappearance of the brown iodine color and the separation of the yellow iodoform. Dispose of test tube contents into the Recovered Organic Solvent bottle. Pour the remainder of your product , if any, into the cyclohexanone recovery bottle at the front of the lab. Laboratory Report. Write the name of each compound & the observation after mixing it with the reagent. B. Mechanism of Halogenation Using H for R1 & R2 and I for X. HO HO H OHC-C-R(H) + NaOH- ---> H2O + HC-C-R(H) H-C=C-R(H) +Na+ H HO H O HC-C-R(H) + I2 ---> HC-C-R(H) + NaI I HO - O OHC-C-R(H) + NaOH ---> HC-C-R(H) HC=C-R(H) + H2O + Na+ I I I - O I O HC-C-R(H) + I2 ----> HC-C-R(H) + NaI I I Repeat this last step again to get I I-C-C-R(H) + NaI I Sum is H O I O HC-C-R(H) + 3NaOH ---> I-C-C-R(H) + 3NaI H I Now I O I OI O I-C-C-R(H) + NaOH ---> I-C-C-R(H) --> I-C- + HOCR(H) + Na+ I I OH I I I I-C- + H2O ---> I-CH(s) + OHI I O O Na+ + OH- + HO-C-R(H) ---> Na+ C-R(H) + H2O O O Net Eq. CH3-C-R(H) + 4NaOH + 3I2 ---> I3CH + Na+ -OCR(H) + 3NaI + OHEXERCISE: Write the equation of a positive test for test performed. Tell what you observed that constituted a positive test.