Per 6 PPT
advertisement
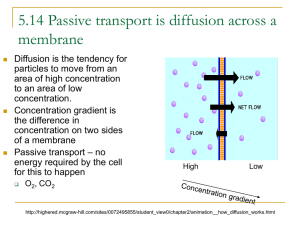
Bellwork: Staple Current Events: • • • • Rubric Written Analysis Article MLA Cite Reference 1. Explain concentration gradient and diffusion with a picture or diagram.. Also write a real-life example of diffusion Concentration Gradient Concentration gradient is when the substance stays in one area more, than in another area. Diffusion Diffusion Diffusion An everyday example of diffusion is Kool-Aid mixing with water. The high concentration of the Kool-Aid powder moves to the areas of the powder where it is in low concentration. 2. Discuss the similarities and differences between diffusion and osmosis. Question #2: Discuss the similarities and differences between diffusion and osmosis. Osmosis vs. Diffusion Diffusion! Diffusion is the movement of particles or substances from an area that is crowded and concentrated to an area that is not in order to reach an equilibrium. Different from…. Osmosis! ….which is when water molecules go through a semi-permeable membrane (plasma membrane) from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Different! But how? Diffusion is the movement of any substance from a higher to lower concentration while osmosis is the movement of water Diffusion does not always move through a semi-permeable membrane (example: food coloring dropped into water) while osmosis does (example: water traveling through the plasma membrane) Similar too! Both move particles from high to low concentration 3. • What would happen to a cell if placed in the following solutions (describe and illustrate). – Isotonic solution: – Hypotonic solution: – Hypertonic solution: 4. • Use pictures to illustrate and arrows to show the direction of osmosis for each of the conditions below. Assume the membrane is not permeable to sucrose. • Intravenous solutions must be prepared so that they are isotonic to red blood cells. A 0.9 % salt solution is isotonic to red blood cells. – Explain what will happen to a red blood cell placed in a solution of 99.3% water and 0.7% salt. – Explain what would happen to a red blood cell placed in a solution of 90% water and 10% salt. Osmosis/Tonicity Vince, Ally, Katelin, and Christian. Hypertonic • The water in the red blood cell leaves the cell. • This happens because the concentration of the solution is higher than the concentration in the cell. The cells are fine because the water stays in the cell. The blood cells are shriveling up because the water is leaving the cell. Hypotonic • The water stays in the cell because the concentration of the solution is higher inside the actual cell. • The cell will possibly burst because the water is flowing in the cell. • Water always moves from low to high. 5. • Draw and describe a plant cell in a hypotonic solution. How will a plant cell respond differently than an animal cell? Why? 5. Hypotonic Solution More water is entering the cell than leaving the cell. Causes the cell to expand. Two different things will happen depending on the type of cell. Plant Cell Water will fill the cell. It will NOT explode. The cell wall prevents the plant cell from rupturing. Animal Cell Water will fill the cell. It will explode if it gets too full. Animal cells do not have the structure that the cell wall provides. 6. • For the most part, plants and animal live in either a salt water environment or a fresh water environment, not both. Explain this using the principles of diffusion. Fresh and Salt Water Conner Hayes, Mariana Corpus Isaac Kerny Certain fish and plants can live in the salt water because they can tolerate large quantities of salt. Other fish can’t live in the salt water because the have low salt tolerance. Fish that can live in both environments come from places like the mouth of a delta. The fresh water diffuses across the salt water and the fish slowly become accustomed too a dualwater environment. 7. • What is required for active transport to occur? #7 What is required for active transport to occur? Ben Baker, Darion Denniston, and Kiersten Henderson(: In order for active transport to occur, you first must have energy (ATP) from the cell. In active transport, a substance in the transport must bind with a carrier protein; this carrier protein usually matches the shape of the molecule, due to chemical energy changing the shape. The carrier protein releases the molecule on the other side of the membrane. Then the protein goes back to it regular shape, after being released from the carrier cell. This is necessary to for homeostasis. 8. • What if there is a large food particle or organism that a predatory cell – like an amoeba – wants to eat? It must use a process called exocytosis. Draw a diagram showing how this process works. Give two examples of substances that a cell might export this way. 0/chapter5/animation_quiz_-_endocytosis_and_exocytosis.html Click for diagram Cells sometimes export proteins that are to big for active transport that are to be used in the plasma membrane. Cells will also export extra cellular fluids for other cells to use. Cell Transport • Active • Passive • Diffusion – Facilitated Diffusion • Osmosis • Isotonic • Hypertonic • Hypotonic • Endocytosis Osmosis: Diffusion of Water • The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. Real- World Applications • Plant Cells: Cellular Respiration • Preserving Fruit and Meat • Medicine – IV – Storage of Red Blood Cells When comparing two solutions to one another, we define: A. Hypotonic solution has a lower solute concentration B. Hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentrations Isotonic – solutions with equal concentration. Osmosis Simulation