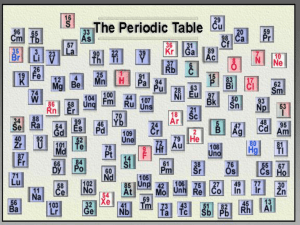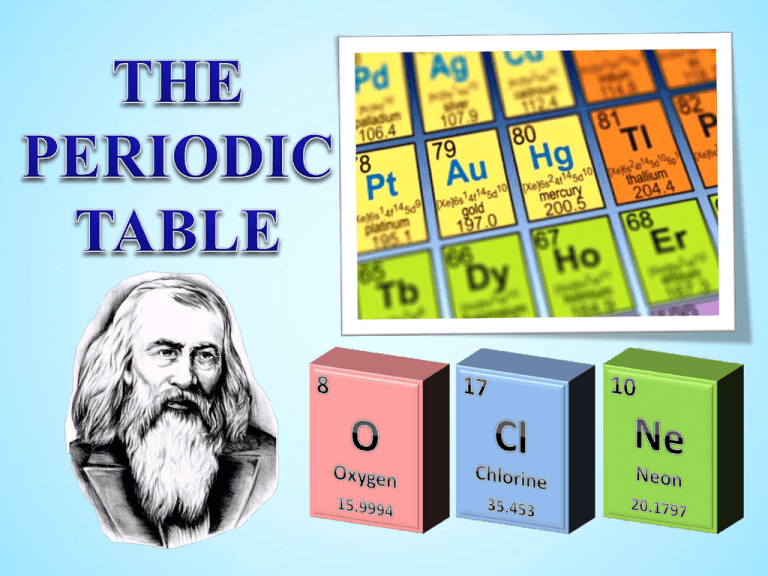
INTRODUCING THE PERIODIC TABLE
Periodic Table: It is a chart that
organizes elements
________ according to
increasing atomic numbers
their _______________________
and their ___________________
chemical and physical
properties
_________.
When was the Periodic Table
developed and who created it?
•
1869 by a man named ________________
Dmitri Mendeleev
It was developed in _____
who was a Russian chemist and inventor.
INTRODUCING THE PERIODIC TABLE
•
In his time, there were only ___________
60 elements discovered, but his
future discoveries
predicted and left room for the ________________
periodic table _________
of elements
___________.
Maybe there
are more
elements?
INTRODUCING THE PERIODIC TABLE
•
Each element on the periodic table is represented within an
element
box which contains the following basic information.
___________
atomic number (A whole number with no decimals.)
2+
oxidation number (It has a + or – sign.)
element symbol (Only the first letter is capitalized.)
element name
atomic mass
a) Draw the box
for the element
that has an
atomic mass of
107.87.
1+
(It is larger than atomic number
and always has decimals.)
b) Draw the box
for the element
that has the
element symbol
Pt.
4++
2
ORGANIZATION OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
•
The periodic table is arranged in columns and rows.
− Each column on the periodic table is called a ______.
group
− There are ___
18 groups on the periodic table.
How many groups
are there on the
periodic table?
ORGANIZATION OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
•
The periodic table is arranged in columns and rows.
− Each column on the periodic table is called a ______.
group
− There are ___
18 groups on the periodic table.
period
− Each row on the periodic table is called a ________.
7 periods on the periodic table.
− There are __
How many periods
are there on the
periodic table?
ORGANIZATION OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
•
There is a zigzag that separates the periodic table into two
sides. This zigzag is also called the staircase
________.
− To the left of the staircase you will find all the metals
______.
non-metals
− To the right of the staircase you will find all the __________,
hydrogen , which is a non-metal
except for the element _________
found on the left side.
non-metals
metals
Can you find the
zigzag on the
periodic table?
ORGANIZATION OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
•
Directly to either side of the staircase you will find elements
8 of these types of elements.
metalloids . There are __
called _________
metalloids
METALS, NON-METALS & METALLOIDS
Metals: •
•
All metals are solids
_____ at room temperature except for
mercury which is a liquid
________
_____ .
Many metals are lustrous
_______ and silvery
______ in
ductile , _________
malleable , __________
conductive
color, ______
and some are magnetic
________.
METALS, NON-METALS & METALLOIDS
Non-Metals:
gases , except for ________
bromine
• Most non-metals are _____
which is a liquid
_____ , and five non-metals which
______ , phosphorus
__________ ,
are solids
_____ . These ones are: carbon
sulfur
iodine
_____ , selenium
________ , and ______.
•
colors
Non-metal elements are either colorless
________ or have various
____________.
malleable , __________
not ductile , ______
brittle when solid,
They are not
____________
nonmagnetic
poor
conductors and ____________.
______________
METALS, NON-METALS & METALLOIDS
Metalloids:
all solids at room temperature.
• Metalloids are ________
• They have some properties of both
____ metals and non-metals.
− They are mostly metallic
_______ in appearance but they are
fair electrical conductors.
brittle They are ___
______.
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Chemical Family: Is a group (column) that contains elements with
similar _________
properties .
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Chemical Family: Is a group (column) that contains elements with
similar _________
properties .
Group 1: Alkali Metals
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Group 1: Alkali Metals
• This group of elements are all
•
soft and _____-colored
silver
solids
____
_____ .
most reactive of all the metals because…
They are the _____
one valence electron.
they only have ____
Li
Na
K
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Group 1: Alkali Metals
• This group of elements are all
•
soft and _____-colored
silver
solids
____
_____ .
most reactive of all the metals because…
They are the _____
one valence electron.
they only have ____
bond with other elements
They each very readily _____
by transferring
__________ their valence electron
Sodium Atom
Chlorine Atom
Na
Cl
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Group 1: Alkali Metals
• This group of elements are all
•
soft and _____-colored
silver
solids
____
_____ .
most reactive of all the metals because…
They are the _____
one valence electron.
they only have ____
bond with other elements
They each very readily _____
by transferring
__________ their valence electron to each become
ion meaning they have a ___
full outer orbital.
a stable ___,
The bond
Chlorine Ion
Atom
Atom
Sodium Ion
between the
ions creates
new
a ____
Cl
Na
substance
called a
NaCl
_________.
compound
table salt
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Group 1: Alkali Metals
• They are all reactive with water
_____.
•
water vapor
To prevent contact with ___________in
oil
the air, they are stored in mineral
_________.
more reactive as you go
Elements get _____
down
_____ the group.
Francium
________ is the most reactive. ...and it’s…
water
mineral oil
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Chemical Family: Is a group (column) that contains elements with
similar _________
properties .
Group 1: Alkali Metals
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
• These elements are also all silver
_____-colored solids
_____ .
less so than
• They are also reactive with water
_____ but ____
group 1 elements
They each have two
___ valence electrons.
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
• These elements are also all silver
_____-colored solids
_____ .
less so than
• They are also reactive with water
_____ but ____
group 1 elements
They each have two
___ valence electrons.
Be
Mg
Ca
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
• These elements are also all silver
_____-colored solids
_____ .
less so than
• They are also reactive with water
_____ but ____
group 1 elements.
•
They each have two
___ valence electrons.
Similar to group 1 elements, they readily bond
with other elements. However, in this case they
two valence electrons to become
transfer their ____
stable ions with full outer orbitals.
more reactive as you go down
Elements get _____
_____ the group.
Radium is the most reactive.
_______
...and it’s also…
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Chemical Family: Is a group (column) that contains elements with
similar _________
properties .
Group 1: Alkali Metals
Groups 17: Halogens
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Groups 17: Halogens
• This group of elements are all __________
non-metals
and are found in all _____
three states.
gas • They are the _____
most reactive of the non-metals
seven valence electrons.
Because they have _____
1 electron short of a full outer orbital.
They readily combine with other elements
liquid
take one valence electron from them to
to ________
become stable ions (with full outer shells).
solid
F
Cl
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Groups 17: Halogens
• This group of elements are all __________
non-metals
and are found in all _____
three states.
gas • They are the _____
most reactive of the non-metals
seven valence electrons.
Because they have _____
1 electron short of a full outer orbital.
They readily combine with other elements
liquid
take one valence electron from them to
to ________
become stable ions (with full outer shells).
Sodium Ion
Chlorine Ion
Na
Cl
solid
Recall:
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Groups 17: Halogens
•
gas
liquid
solid
Halogens become more reactive
up the group.
as you move ___
Fluorine
_______ is the most reactive.
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Chemical Family: Is a group (column) that contains elements with
similar _________
properties .
Group 1: Alkali Metals
Groups 17: Halogens
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
Groups 18: Noble
Gases
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Groups 18: Noble Gases
•
These non-metal elements
are non-reactive
___________ gases.
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Groups 18: Noble Gases
•
do not bond with other elements
They ______
because they have full
___ outer orbitals.
He
•
Ne
Ar
Since they don’t react with other elements, they
do not form __________.
compounds
______
inert gases
Noble gases are also described as __________.
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Chemical Family: Is a group (column) that contains elements with
similar _________
properties .
Group 1: Alkali Metals
Groups 17: Halogens
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
Groups 3-12: Transition Metals Groups 18: Noble
Gases
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Groups 3-12: Transition Metals
• These groups contain metals that have the usual properties of
•
metals. (Lustrous, malleable, ductile, electrically conductive, etc.)
These metals are all found in the solid state except for mercury
_______
which is a liquid
_____ at room temperature and pressure.
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Groups 3-12: Transition Metals
• The transition metals contain some of the most
commonly known metals.
platinum
ring
iron skillet
titanium
aircraft
silver
goblet
copper
pipes
copper
penny
tungsten
light bulb
gold necklace
mercury
thermometer
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Chemical Family: Is a group (column) that contains elements with
similar properties.
Group 1: Alkali Metals
Groups 17: Halogens
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
Groups 3-12: Transition Metals Groups 18: Noble
Gases
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
CHEMICAL FAMILIES ON THE PERIODIC TABLE
Lanthanides: Elements 57-71
metals that have been
• They are all ______
misleadingly labeled
earth metals in the past.
“ rare
_______________”
Actinides: Elements 89-103
radioactive
• They are metals
______ that are __________.
combust
They will spontaneously ________
in the air.
Created by Anh-Thi Tang – Tangstar Science
Copyright © April 2013 Anh-Thi Tang (a.k.a. Tangstar Science)
All rights reserved by author.
This document is for personal classroom use only.
This entire document, or any parts within, may not be
electronically distributed or posted to any website.