Periodic table
advertisement
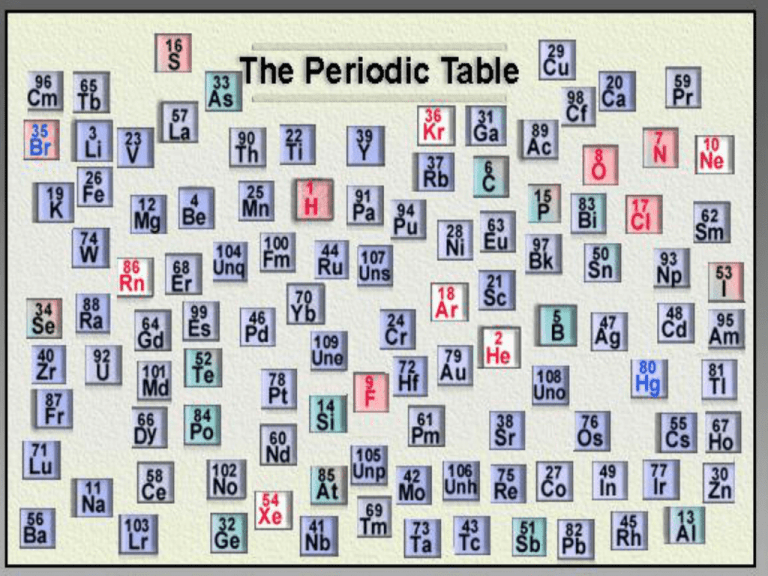
“FIND THE "MISSING ELEMENTS" Part I: Paint Chip Periodic Table In this activity, you will be creating your own incomplete periodic table using paint strips. You will be using "color" as a guide. As you start to arrange your periodic table, you will notice 'holes' or missing colors. Your task will be to arrange your periodic table, so that you will be able to determine the missing elements/colors. You will then determine the missing element's color, shade and location. When you get your materials (1 baggie with 32 color strips): 1. Arrange the color strips by color, left to right, in the order of the rainbow (ROY G BIV). 2. Arrange the shades of each color, top to bottom, from light to dark. 3. Now you will notice the 'holes' in your periodic table. 4. Using colored pencils, sketch or give a name to the colors and locations of the paint strips that are missing colors to form a COMPLETE periodic table. 5. Answer the conclusion questions in complete sentences. Questions: (1) Explain how you arranged your chips to form a periodic table with rows (periods) and columns (groups). (2) a) Describe the properties of the missing paint chips. b) Ask your teacher for the envelope containing the "missing elements" for your set. Were you able to predict the properties (color and shade) of the three elements not yet discovered? Why or why not? (3) Explain the value of your periodic table in predicting properties of paint chips, and explain how chemists used the Periodic Table to predict the existence of unknown elements. The atomic number is one and the atomic mass (weight) is 1.00794 amu. The number of neutrons in the most common isotope is 0 and the number of electrons is one. Hydrogen has three common isotopes. The simplest isotope, called protium, is just ordinary hydrogen. The second, a stable isotope called deuterium, was discovered in 1932. The third isotope, tritium, was discovered in 1934. It has one electron. Melting Point:13.81 K (-259.34°C or -434.81°F)Boiling Point:20.28 K (252.87°C or -423.17°F)Density:0.00008988 grams per cubic centimeter Hydrogen is a colourless, odourless gas that burns and can form an explosive mixture with air. The element, Hydrogen that was discovered by Henry Cavendish. The name was derived from the Greek ‘Hydro genes” meaning water forming. It is found in mines, oils, and gas wells and is manufactured from methane gas and by electrolysis of water aqueous . Hydrogen is used for mental refining, balloons, fertilizers, plastics, salts, and pharmaceuticals. It’s also used for Ammonia, cyclopean, and methanol. http://www.chemsoc.org/viselements/pages/hyd rogen.html http://chemicalelements.com/ http://www.bayerus.com/msms/fun/pages/perio dic/i_table.html NAME 1 Hydrogen 2 Sodium SYMBOL NAME 3 4 Nitrogen C 9 Calcium 10 11 Neon 5 6 Sulfur 7 Iodine O2 12 13 Boron He 14 15 Chlorine SYMBOL Al Hg 8 Si 16 Lithium http://www.funbrain. com/periodic/ In the element key for Carbon, 6 is the atomic number (number of protons) C is the symbol 12.011 is the atomic mass (average mass of all the isotopes) The isotopes of carbon can have mass numbers of 12, 13, or 14 (looking at the atomic mass – which do you think occurs most frequently in nature?) Atomic number Atomic Mass Protons Neutrons Electrons Isotopes Elements and the Periodic Table Using the Periodic Table Alkali Metals Halogens Alkali Earth Metals Noble Gases C6 (2.4) Transition metals Label the first 18 elements with the chemical symbol, atomic number, and electronic configuration Label the groups and periods Identify the names of the different families/groups Find a way to distinguish between metals and non-metals Label the groups with the number of electrons in the outer energy level PERIODIC TABLE The Periodic Table is my idea! Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) Periodic table • Table of elements arranged according to repeated pattern of properties. GROUPS vertical columns are called groups or families with same number of valence electrons. similar chemical properties has 8 groups plus a block of transition metals 1 Alkali Metals 2 Alkaline Earth Metals 3-12 Transition Metals 17 Halogens 18 Inert or Noble Gases PERIODS horizontal rows numbered 1 to 7 going down 1 only hydrogen and helium 2 Lithium to Neon 3 Sodium to Argon … Zig-Zag line separates metals (left) from non-metals (right) From left to right across a period, Most Metallic (Grp 1) to Most Non-Metallic (Grp VII) Hmmm... The number system varies Most metallic - bottom and left Metal Heroes Most nonmetallic – top and right (not group 8) White