Affinity Chromatography - Structural Biology Labs
advertisement

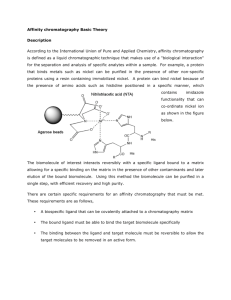
Affinity Chromatography Supervisor: Anton Zavialov By: Elham Barazeghi Mehrafarin Ramezani Affinity Chromatography: Separation of proteins by reversible interaction of proteins and specific ligand in matrix of column Advantages: Selectivity Resolution Suitable for concentrating a protein Some common terms : Matrix Spacer Arm Ligand Binding Elution Wash Ligand coupling Matrix Open and porous structure Inert or non-specific interaction OH group on sugar residues , good anchor for ligand attachment Able to pass liquids through itself rapidly Stable enough in various conditions Sepharose is an ideal matrix! Spacer arm Improve efficiency of binding length How it works? On the matrix: on the chromatogram: Essential components of Affinity Chromatography system: Column type(depending on target protein and the ligand) Buffers: Loading buffer Elution buffer Elution methods: * * * * * pH elution Ionic strength elution Competitive Polarity disturbance Denaturing Step vs. gradient elution Different types of Affinity Chromatography Type of column Enzyme Immunoaffinity Lectin Nucleic acid Hormone, vitamin Glutathione Immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC) Target Substrate analogue, cofactor, inhibitor Antigen, virus,cell Polysaccharides, glyco-proteins, cell surface receptor, cell Complementary base sequence, histones, nucleic acid polymerase, nucleic acid binding protein Receptor, carrier protein Glutathione-S-transferase, GST fusion protein Poly (his)fusion proteins, native proteins with histidine, cystein or tryptophan residues on their surfaces Immuno-affinity chromatography (IAC) A sub category of affinity chromatography A biologically related binding agent is used for the selective purification or analysis of a target compound stationary phase consists of an antibody or antibodyrelated reagent The selective and strong binding of antibodies for their given targets has made them of great interest as immobilized ligands in affinity chromatography Moser A.C., et. Al., Immunoaffinity chromatography: an introduction to applications and recent developments, bioanalysis -2010 ,2(4):769-790 The loading buffer has the ability to promote fast and efficient binding of the target analyte to immobilized antibodies which typically occurs under physiological conditions pH=7 The elution carry out by temporarily lowering the effective strength of antibody binding to the target. Changing the mobile phase pH is the most popular method for eluting retained compounds from IAC columns. This approach is usually conducted by applying an acidic buffer (pH 1–3) to the column An example of competitive elution: http://youtu.be/Hb791WsC78s Thank You