Document
advertisement

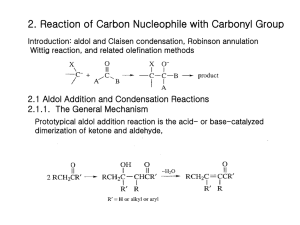
14.3 Aldol Reaction and Claisen Condensation in Biology Main Menu Enol – Keto Tautomerization Aldol Reaction Claisen Condensation Enol – Keto Tautomerization a-H is required to have keto-enol tautomerization. In acidic condition a Keto + H+ Enol - H+ In basic condition Enolate 2 Examples of Enol – Keto Tautomerization a a a 3 Enol – Keto Tautomerization in Carbohydrates Keto-enol tautomerization can lead to structural isomerization between aldose and ketose. Keto Enol Keto D-glucose D-fructose (an aldose) (a ketose) 4 Enol – Keto Tautomerization in Glycolysis Keto-enol tautomerization catalyzed by phosphoglucoisomerase phosphoglucoisomerase Reaction 2 Glucose-6phosphate (an aldose) Fructose-6phosphate (a ketose) 5 Isomerization of Glucose-6phosphate 1 Glucose-6phosphate Cyclic hemiacetal form 1 Opened form glucose-6phosphate 2 1 Enol 1 2 Opened form fructose-6phosphate Keto Fructose-6phosphate Cyclic hemiketal form 1 2 6 Enol – Keto Tautomerization in Glycolysis Keto-enol tautomerization catalyzed by Triosephosphate isomerase Triosephosphate isomerase Keto Keto Reaction 5 Dihydroxyacetone phosphate Glyceraldehyde3-phosphate (a ketose) (an aldose) Enol 7 Learning Check 1. What represent the correct enol-keto tautomerization for the following ketone or aldehyde? I (a) I, II (b) I, II, III II (c) II, III, IV (d) II, IV III (e) None of the above IV 8 Aldol Reaction Formation of new C-C bond by combining keto and enol (enolate) b + Enol In acidic condition Keto The product contains an aldehyde and an alcohol functional groups: Aldol reaction. The product may have two new stereocenters. The product contains a b-hydroxycarbonyl motif. Aldol reaction can be reversible. 9 Electron Flow in Aldol Reaction Aldol reaction: Formation of new C-C bond a + Enol b In acidic condition Keto Retro-Aldol reaction: Breaking of C-C bond between a and b carbons a b + Enol Keto 10 Electron Flow in Aldol Reaction Aldol reaction: Formation of new C-C bond In basic condition H+ + a b Keto Enolate Retro-Aldol reaction: Breaking of C-C bond between a and b carbons a + b Enolate Keto 11 Retro-Aldol Reaction in Glycolysis Retro-Aldol catalyzed by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase + Reaction 4 Fructose-1,6bisphosphate Glyceraldehyde- Dihydroxyacetone phosphate 3-phosphate 12 How does Retro-Aldol Reaction Generate Two 3-Carbon Sugars? Equilibrium between cyclic hemiketal and opened form 1 b Fructose-1,6bisphosphate H+ + 2 Opened form Cyclic hemiketal form 1 : Retro-aldol reaction 2 : Keto-enol tautomerization 13 Aldol Reaction in Citric Acid Cycle Citrate synthesis catalyzed by citrate synthase Citrate synthase + Reaction 1 acetyl CoA Citrate oxaloacetate 2 HS-CoA 1 oxaloacetate H2O 1 : Aldol reaction 2 : Hyrolysis of thioester 14 Learning Check 1. What represent the correct aldol reactions? I (a) I, III, IV (b) I, II, III II (c) I, II, IV (d) II, IV III (e) None of the above IV 15 Claisen Condensation Formation of new C-C bond by combining carboxyl and enol (enolate) b + Enol Carboxyl (Acetyl CoA) (Ester) + ROH Forging two carboxyl functional groups and removal of a small molecule: Claisen condensation. The electron flow is similar to that of an aldol raction. The product contains a b-ketocarbonyl motif that can undergo decarboxylation spontaneously. Claisen condensation can be reversible. 16 Electron Flow in Claisen Condensation Claisen condensation: Formation of new C-C bond + Enol Keto (Acetyl CoA) (Acetyl CoA) b a HSCoA Reaction in ketogenesis! b-ketocarbonyl 17 Electron Flow in Retro-Claisen Condensation Retro-Claisen condensation: Breaking of a C-C bond HSCoA b a 1 + 2 1 : Similar to the formation of hemiketal 2 : Keto-enol tautomerization The 4th reaction in the repeated cycle of b-oxidation. 18 Carboxylation and Claisen Condensation Synthesis of malonyl CoA catalyzed by acetyl CoA carboxylase Acetyl CoA Carboxylase + Bicarbonate ATP ADP + Pi Malonyl CoA (for lipogenesis) Bicarbonate: water soluble form of carbon dioxide Carbonate + H+ + H+ - H+ - H+ Bicarbonate CO2 + Carbonic acid H2O 19 Mechanism in the Synthesis of Malonyl CoA Acetyl CoA carboxylase contains biotin as the carboxyl group carrier. 1 ATP 1 Pi + 2 H+ ADP Biotin-enzyme 2 Acetyl CoA Biotinenzyme 1 : Similar to transacylation Malonyl CoA 2 : Claisen condensation 20 Decarboxylation Is Similar to a Retro-Claisen Reaction a-ketoglutarate synthesis catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase isocitrate dehydrogenase + CO2 Reaction 3 a-ketoglutarate isocitrate 2 1 NAD+ NADH intermediate 1 : Oxidation 2 : Decarboxylation 21 Electron Flow in Decarboxylation The molecule contains b-ketocarbonyl motif can undergo decarboxylation spontaneously. H+ CO2 b enolate a-ketoglutarate 22 Claisen Condensation in Lipogenesis Reaction catalyzed by b-ketoacyl ACP synthase b-ketoacyl ACP synthase + CO2 + ACP-SH CO2 2 1 ACP-S- + H+ ACP-SH 2 1 2 : Decarboxylation : Claisen condensation 23 Carboxylation in Calvin Cycle and Claisen Condensation Synthesis of 2-carboxy-3-keto-D-arabinitol-1,5-bisphosphate catalyzed by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) Ribulose-1,5bisphosphate carboxylase + Carbamate ribulose-1,5bisphosphate - H+ CO2 2-carboxy-3-keto-Darabinitol-1,5bisphosphate 24 Mechanism in Carbon Dioxide Fixation Synthesis of 2-carboxy-3-keto-D-arabinitol-1,5-bisphosphate catalyzed by Rubisco 1 ribulose-1,5bisphosphate 2 Enol intermediate 1 : Keto-enol tautomerization 2 : Claisen condensation 2-carboxy-3-keto-Darabinitol-1,5bisphosphate 25 Retro-Claisen Condensation in Calvin Cycle Synthesis of two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate catalyzed by Rubisco H2O H+ 1 2 2-carboxy-3-keto-Darabinitol-1,5bisphosphate hydrated (ketal) intermediate 1 : Hydration of ketone 2 : Retro-Claisen condensation two molecules of 3phosphoglycerate 26 Electron Flow in the Synthesis of 3Phosphoglycerate H+ + H+ hydrated (ketal) intermediate two molecules of 3phosphoglycerate 27 Main Menu Learning Check 1. What represent the correct Claisen condensations? (a) I, III, IV I (b) I, II, III II (c) I, II, IV (d) II, IV III (e) None of the above IV 28