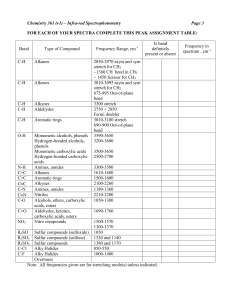
FTIR Spectroscopy of Polymers: Lab Report Analysis
advertisement

Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Mohammed Alzayer, Chris Clay, Xinhang Shen Mat E 453, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Iowa State University, Ames, IA 50011 Introduction Polystyrene PS showed an O-H peak at approximately 3400 cm -1, an aromatic C-H stretch at 3050 cm -1, and an aliphatic C-H stretch at 2950 cm -1. The O-H bond may result from the water in the sample. [4] Results FTIR spectroscopy is a method that uses absorption of IR radiation by polar molecules to undergo vibration and rotational transitions.[1] Vibrations, in the form of bond stretching or bending, within polymeric structure will be observed after excitation by IR radiation. Certain frequencies of IR can interact with the dipole moments of various functional groups of the polymer. These frequencies are dependent on the bond strength, length, and the mass of the atoms in the bonds. IR spectral transmittance of an unknown polymer can be collected and correlated to known values to determine the functional groups present within the polymer. Poly(methyl methacrylate) PMMA showed an O-H peak at approximately 3400 cm -1, a C-H stretch at 3050 cm -1, C=O stretch at 1700 cm -1 , and a C-O stretch at 1100 cm -1.[5] Conclusions Fig 2. PEG spectral and reference graph Fig 3. PVC spectral and reference graph Testing Procedures Four polymer samples were tested: 1. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) 2. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) 3. Polystyrene (PS) 4. Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) 10-50 mg of each polymer was dissolved in approximately 1 mL of THF. A few drops of this solution were placed in a KBr plate. A minute or so was allowed for the THF to evaporate. An FTIR spectrum was taken of a clean KBr plate and used as a background. Afterwards, the FTIR spectrum of the four polymer samples were taken with the following parameters: Scan Range: 400-4600 cm -1 Scan Resolution: 4 cm -1 Scan Number: 20 Fig 1. Inner chamber of FTIR8000 and the sample holder[1] FTIR is a valuable tool to assess the functional groups present in an organic compound or polymer. Experimental results were consistent with reference spectra, with the exception of the 2300 cm-1 peak in PVC. It is important to keep the IR samples as dry as possible, as water is IR absorbent and can affect results. KBr plate is used instead of a typical glass plate as glass is IR opaque (IR light cannot penetrate glass) THF is a good choice of solvent as it can dissolve all the polymers we tested and volatilizes easily. Acknowledgments Fig 4. PS spectral and reference graph Fig 5. PMMA spectral and reference graph Polyethylene Glycol PEG showed an O-H peak at approximately 3400 cm -1, a C-H stretch at 2850 cm -1, and a C-O-C stretch at 1100 cm -1, all of which agreed with the reference spectrum. [2] Polyvinyl Chloride PVC showed an O-H peak at approximately 3400 cm -1, a C-H stretch at 2850 cm -1 which both of agreed with the reference spectrum [3]. It also showed a peak at 2300 cm -1, which corresponds to an impurity of some kind. This laboratory report utilized data from an actual laboratory performed by our group and Steven Kmiec , Chenhao Ren, and Khalid Alamri, supervised by Nathan Podjenski at Iowa State University. References [1].Mendoza, J. D. Lab 3: FTIR, Iowa State University [2] National Institute of Science and Technology, Polyethylene Glycol, 2009 [3] ISU MatE 453/MSE 553 – Lab 3-FTIR [4] Leon-Bermudez, A, and Salazar, R, Synthesis and Characterization of the polystyrene, UIS. 2008. [5] Duan G, Zhang C, Li A, Yang X, Lu L, Wang X, Preparation and Characterization of Mesoporous Zirconia Made by Using a Poly (methyl methacrylate) Template. 2008