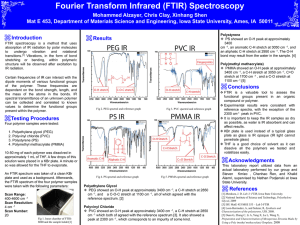
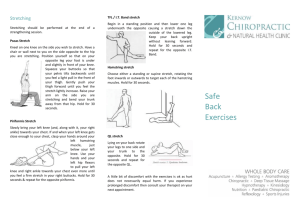
C=O stretch
advertisement

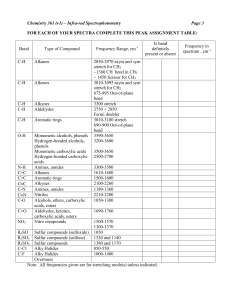
FREQUENCY cm-1 3650 - 3584 VIBRATION TYPE FUNCTIONAL GROUP STRENGTH (WIDTH) COMMENT O-H stretch free N-H stretch alcohols, phenols, water M-W (sharp) amines, amides M (broad) Rare; found in dilute solutions, or when multiple OH are present Characteristic N–H stretching absorptions 3300 to 3500 cm1. NH2 group shows an irregular doublet, NH - weak multiple bands. Ammonium ions show N-H at 2600 cm1. Amine absorption bands are sharper and less intense than hydroxyl bands. alcohols, phenols, water S (very broad) 3300 O-H stretch H-bonded C-H stretch alkynes S (sharp) 3080 - 3010 C-H stretch alkenes S-M (sharp) 3050 C-H stretch aromatic: phenyl ring M-W Usually multiple bands are found 3000 - 2800 carboxylic acids S (very broad) Irregular band, slanted up to lower frequencies 2830 - 2690 O-H stretch H-bonded C-H stretch aldehydes M-W 2980 - 2800 C-H stretch alkanes, alkyl groups S (sharp) 2260 - 2215 C-N stretch triple bond C-C stretch triple bond nitriles S (sharp) alkynes variable very S (rel. broad) very S (rel. broad) very S (rel. broad) very S (rel. broad) Usually 2 bands are observed. The higher frequency band is often obscured by aliphatic C-H Asymmetric bands are at higher frequencies and are stronger than symmetric. 3° absorption is weak Conjugation with another double bond or phenyl ring causes absorption at the lower end of frequency range Strong in monosubstituted alkynes, very small or non-existent in symmetrical or nearly symmetrical alkynes Lowered by conjugation with another double bond or phenyl ring Lowered by conjugation with another double bond or phenyl ring Lowered by conjugation with another double bond or phenyl ring Lowered by conjugation with another double bond or phenyl ring 3400 - 3200 3550 - 3200 2150 - 2100 1750 - 1735 C=O stretch esters 1725 - 1705 C=O stretch aldehyde or ketone 1700 C=O stretch carboxylic acids 1690 - 1600 C=O stretch amide or lactam Weak in large molecules FREQUENCY cm-1 1680 - 1600 VIBRATION TYPE FUNCTIONAL GROUP STRENGTH (WIDTH) COMMENT C=C stretch alkene S-M-W 1650 - 1590 amines 1660 - 1500 1600 NH2 deformation band C=C stretch NH2 bend aromatic rings amides and amines S (broad) M-W S-M Strong in cis-alkenes or conjugated alkenes conjugated alkenes are at the lower end of frequencies 1o amines only 1540 NH bend amides M-W 1520, 1350 NO2 stretch nitro compounds S 1450, 1375 1410 1330 - 1260 CH3 C-H bend CH2 C-H bend C-N stretching S variable S-M (broad) 1240 - 1170 C-N stretching alkanes, alkyl groups alkanes, alkyl groups amines o 3 amines show no C-N vibrations amines 1140 - 1080 C-N stretching amines 1090 - 1068 C-N stretching amines 1205 - 1124 C-O stretch alcohols, ethers, esters Variable intensity, usually a number of bands is seen A good supporting band for the NH2 stretch The so-called Amide II band. A good supporting band for the NH stretch In aromatic amines S-M (broad) S-M (broad) S-M (broad) S Saturated 3°, symmetrical 2° alcohols; NH at a 3o carbon NH at a 2o carbon NH at a 1o a carbon 1124 - 1087 C-O stretch alcohols, ethers S Esters usually show two bands at 1270 and 1170 cm-1 Saturated 2°, -unsaturated, cyclic 3° 1087 - 1050 990, 910 C-O stretch =C-H bend alcohols, ethers alkenes S S -unsaturated 2°, 2° in a 5- or 6-membered rings Monosubstituted terminal vinyl group FREQUENCY cm-1 980 - 960 VIBRATION TYPE FUNCTIONAL GROUP STRENGTH (WIDTH) COMMENT =C-H bend alkenes S In trans-1,2-disubstituted ethylenes 895 - 885 =C-H bend alkenes S In a disubstituted terminal vinyl group 730 - 665 =C-H bend alkenes S In cis-1,2-disubstituted ethylenes 850 - 750 N-H wagging amines 825 - 690 =C-H bend substituted benzenes S (broad) VS 720 CH2 C-H bend alkanes, alkyl groups S Strong, broad, multiple bands. These are weak in aromatic amines Appearance and exact position of these bands depends on the substitution pattern Only visible when more then 4 connected CH2 groups are present 800 - 600 C-Cl stretch chloroalkanes S 700 - 500 C-Br stretch bromoalkanes S 600 - 400 C-I stretch iodoalkanes S CHARACTERISTIC PROTON CHEMICAL SHIFTS Type of Proton Structure Chemical Shift, ppm Cyclopropane C3H6 0.2 Primary R-CH3 0.9 Secondary R2-CH2 1.3 Tertiary R3-C-H 1.5 Vinylic C=C-H 4.6-5.9 Acetylenic triple bond,CC-H 2-3 Aromatic Ar-H 6-8.5 Benzylic Ar-C-H 2.2-3 Allylic C=C-CH3 1.7 Fluorides H-C-F 4-4.5 Chlorides H-C-Cl 3-4 Bromides H-C-Br 2.5-4 Iodides H-C-I 2-4 Alcohols H-C-OH 3.4-4 Ethers H-C-OR 3.3-4 Esters RCOO-C-H 3.7-4.1 Esters H-C-COOR 2-2.2 Acids H-C-COOH 2-2.6 Carbonyl Compounds H-C-C=O 2-2.7 Aldehydic R-(H-)C=O 9-10 Hydroxylic R-C-OH 1-5.5 Phenolic Ar-OH 4-12 Enolic C=C-OH 15-17 Carboxylic RCOOH 10.5-12 Amino RNH2 1-5