Deammonification and Humboldt
advertisement

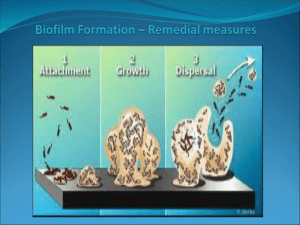
Deammonification and Humboldt Treatment Process Sidestreams Sidestream Characteristics 1. Concentrated Nutrient Loads constituting 15-25% of TN. Ammonia: 500-1500mg/L 2. Low Alkalinity: Typically contains 50% alkalinity needed for nitrification of ammonia 3. Relatively low BOD/COD 4. Small Flows – often intermittent and resulting in high peak load to the mainstream process. 5. Can change characteristics of influent impacting sensitive biological processes and varying demand for chemical dose. Why consider sidestream treatment? • A plant can often reuse existing infrastructure to reduce project costs. • Treatment is usually economical when sidestreams contribute greater than 15% of TN load. Treatment Alternatives Available Biological Bioaugmentation Physico-Chemical Coagulant Aided Precipitation In-Nitri BABE Struvite Precipitation NYC at 3 Ostara Maureen MFH Nitritation/Denitritation Procorp/DHV SHARON Paques Deammonification ANAMMOX Ammonia Stripping DEMON CLEAR Green ANITA-Mox Ion Exchange Deammonification Benefits of Deammonification vs Conventional Nitrification/Denitrification • Aeration energy savings from 55-60% • 100% Savings BOD/COD. i.e. No carbon needed for nitrogen removal • Net consumer of CO2vs release of CO2 with conventional • Alkalinity demand reduced by 45% (no additional alkalinity required) • Reduction in solids production Deammonification-unusual metabolism Type of Bacteria Common Reaction Name Carbon Source Electron Donor (substrate oxidized) Electron Accepter Products Aerobic Heterotroph ic Aerobic oxidation Organic compounds Organic compounds Oxygen CO2, H2O Aerobic autotrophic Nitrification CO2 NH4+, NO2- Oxygen NO2-, NO3- Facultative Heterotroph ic Denitrificati on/anoxic reaction Organic compounds Organic Compounds NO2-, NO3- N2, CO2, H2O Obligate Chemolitho autotrophic Anammox/d eammonific ation CO2 NH4+ NO2- N2, NO3-, H2O What is Deammonification • Conventional Nitrification/Denitrification NH4-N is oxidized under aerobic conditions to NO2-N or NO3-N by autotrophic bacteria, and then the NO2-N or NO3-N is reduced to N2 under anoxic conditions, with the consumption of organic substances by heterotrophic bacteria. Deammonification Deammonification Deammonification Deammonification Anammox granules Anammox granules vs biofilm Deammonification Technologies DEMON™ ANITA Mox™ Cleargreen™ Reactor Configuration SBR with Hydrocyclone MBBR SBR Biomass characteristic Floc Biofilm Floc Control Parameters pH, NH4 Loading Ph, NH4 Loading NH4 Loading, aeration Power Consumption (kWh/kg N) Design Loading (kg N/m3-d) Technology Provider 1.16 1.45-1.75 0.7-0.8 1.2-2.0 World Water Works Veolia/Kruger Degremont ANAMMOXTM granular Paques ANNAMOXTM vs Conventional Conventional Treatment ANAMMOX 3-5 1-2 kWh/kg N Methanol 2.5-3 0 kg/kg N Sludge Production 0.5-1 0.1 kg VSS/kg N CO2 Emissions >4.7 0.7 kg/kg N Total Costs 4-6 1-3 $/kg N Power Deammonification Characteristics Slow growth rate: Double every 10-11 days Growth Rate Population after 11 days Anammox 11 days 1.0*21=2 Nitrobacter 13 hours 1.0 *220=1,050,000 Nitrosomomas 7 hours 1.4*238=138,000,000,000 E. Coli 17 minutes 1.0*2931 Deammonification Characteristics Requirements to favor growth of deammonifiers: - Maintain long SRT. Retain the right bacteria (selective wasting) - Temperature control - pH control - DO Control - Free ammonia control - Limit available carbon (BOD) Process Configurations DEMON (World Water Works) Sequencing Batch Reactor: - Acronym for DEamMONification -Includes a hydrocyclone to separate granual anammox bacteria from the floc-forming AOBs and NOBs -The heavier anammox are returned to the reactor, the flocs are separated and wasted. -This allows the system to control the accumulation of NOBs and stabilize performance. Anammox Floc Granules DEMON DEMON Hydrocyclone Moving Bed BioFilm Reactors (MBBR) Biofilm grown on media. Moving Bed Biofilm Media AOB and anammox bacteria are established within the biofilm. The biofilm tends to locate in protected regions of the support media. Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors Media in Reactor AnitaMox A single stage deammonification MBBR by Veolia. Media with protected surface area for biofilm growth of 1,200 m2/m3 Volumetric ammonium-N removal rate of up to 1.2kg-N/m3.day with a 40% media fill and temperature range of 27-300C Summary • Deammonification has been found to be: - Technically and economically feasible - Several technology options have been tested and commercialized - More than 50 Full size deammonification units have been constructed since first full scale in 2001. Deammonification and Humboldt Candidates: Cities of Fortuna, Eureka, Arcata. Compelling Factors: Regulatory: Fortuna: Surface Discharge facing stringent nutrient removal Eureka, Arcata: Ocean and Bay discharge. No current nutrient regulations. Future regulation? Example JWPCB of the LACSD Cost: Evaluation of cost/benefits of collaboration? JWPCP Joint Water Pollution Control Plant -One of the largest wwtp in the world -Permitted capacity 400 mgd -Population served approx 3.5 mm -Discharge outfalls 1.5 miles off Palos Verdes peninsula to depth of 200ft. Aeration Basin Decant Gravity Belt Thickener Anaerobic Digester Digester Mixing Pumps Heat Exhanger Belt Filter Press Dewatered BFP Sludge Sidestream Basin Anammox – Bench Scale Anammox –Bench Scale Anammox-Bench Scale Thank You