The Dynamic Cell Energy and Transport note sheet
advertisement
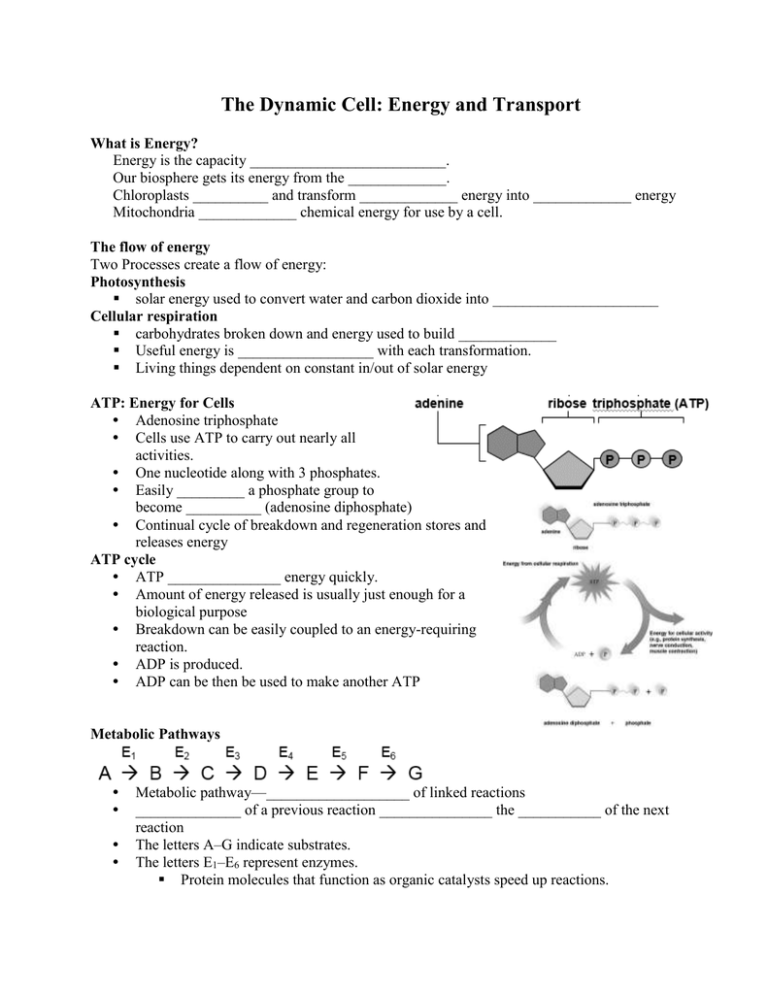
The Dynamic Cell: Energy and Transport What is Energy? Energy is the capacity __________________________. Our biosphere gets its energy from the _____________. Chloroplasts __________ and transform _____________ energy into _____________ energy Mitochondria _____________ chemical energy for use by a cell. The flow of energy Two Processes create a flow of energy: Photosynthesis solar energy used to convert water and carbon dioxide into ______________________ Cellular respiration carbohydrates broken down and energy used to build _____________ Useful energy is __________________ with each transformation. Living things dependent on constant in/out of solar energy ATP: Energy for Cells • Adenosine triphosphate • Cells use ATP to carry out nearly all activities. • One nucleotide along with 3 phosphates. • Easily _________ a phosphate group to become __________ (adenosine diphosphate) • Continual cycle of breakdown and regeneration stores and releases energy ATP cycle • ATP _______________ energy quickly. • Amount of energy released is usually just enough for a biological purpose • Breakdown can be easily coupled to an energy-requiring reaction. • ADP is produced. • ADP can be then be used to make another ATP Metabolic Pathways • • • • Metabolic pathway—___________________ of linked reactions ______________ of a previous reaction _______________ the ___________ of the next reaction The letters A–G indicate substrates. The letters E1–E6 represent enzymes. Protein molecules that function as organic catalysts speed up reactions. Cellular Aerobic Respiration • Chemical pathway that ________________________________ molecules • Requires ________________________, produces ___________________________ as wastes • Also uses _____________________ NAD+ and FAD+ to transfer electrons Four phases of Aerobic Respiration • Glycolysis occurs outside the mitochondria in the cytoplasm. • The preparatory reaction, citric acid cycle and electron transport chain occur inside the mitochondria. Outside the Mitochondria: Glycolysis • In eukaryotes, takes place in the ________________ • Glucose is broken down into two molecules of ________________________ (3 carbons) • Two phases… – Energy-investment steps – Energy-harvesting steps Energy-investment steps ________ ATP molecules are used to make the first break and activate the reactions Energy-harvesting steps ATP synthesis produces _________ATP • Net gain of ________ATP 2 NADH made from NAD+ Two 3-carbon molecules of ___________________ are formed Outside the Mitochondria: Fermentation • Fermentation—_________________ breakdown of glucose • Occurs if _________________________________ available – no more ATP will be produced – only the two from glycolysis • Lactic Acid Fermentation – Animal and bacteria cells – __________________ formed (muscle cells) • Alcohol Fermentation – Microorganisms – bacteria and yeast – ________________ and ____________________________ produced • Yeast—carbon dioxide makes bread rise, ethanol made in wine and beer Inside the Mitochondria Other 3 phases take place inside the mitochondria only _________________________________ Inside the Mitochondria: Matrix Preparatory Reaction • prepares ________________ molecules for the citric acid cycle • Each pyruvate is broken into carbon dioxide and a 2-carbon acetyl molecule • The acetyl molecule is attached to a coenzyme A molecule • NADH is produced from NAD+ Citric Acid Cycle • __________________ the breakdown of the original glucose molecule • Acetyl group is oxidized to carbon dioxide • NAD+ → NADH and FAD → FADH2 • ________ ATP produced Inside the Mitochondria: Cristae Electron Transport Chain Located in _______________ (inner folded membrane) of mitochondria NADH and FADH2 ___________________________ from previous reactions Series of carriers pass electrons along the membrane from one to the other Energy is _____________ and _________________________________ __________________ ATP produced Final acceptor of electron is oxygen, forming water A total of _________________ molecules are made from one glucose molecule C6H12O6 + 6O2 + ADP 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP Using other foods for energy Cells use other energy sources Fatty acids have longer carbon chains—________________ ATP Intermediates can also be used to make other products Extra food made into fat for ____________________ Cell Transport Plasma membrane ___________________ traffic in and out of cell Selectively ____________________—some substances pass freely, some transported, some prohibited Three ways to enter: Passive transport—substances move from _______________________________ concentration, ____________________________________________ required Active transport—substances move from ________________________________ concentration, additional energy ___________________________ Bulk transport—movement ___________________________________, additional energy required Passive Transport - Includes diffusion, Facilitated diffusion and Osmosis Diffusion Molecules move from higher to lower concentrations (_______________ their concentration gradient) until equilibrium is reached. __________energy required Cell does not expend additional energy because molecules already in motion ________________, __________________________ molecules (carbon dioxide, methane, oxygen, water, small lipids) can slip between membrane phospholipids. Large or charged molecules cannot diffuse through the membrane Facilitated diffusion ____________________ proteins in the cell membrane are used to transport some molecules ____________________ protein is specific to one molecule Water uses _____________________—explains faster than expected transport rate Glucose has several transport proteins Osmosis Diffusion of ___________ across a selectively permeable ________________ Can be simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion If solutes cannot diffuse through the membrane, water moves to equalize the concentrations Net movement of water is from beaker with the ______________________ concentration to the tube with the _____________________________ concentration (with gradient) Effect of osmosis on cells ____________________ solution Cell neither gains nor loses water _____________________________________________ on both sides of the membrane 0.9% saline isotonic to red blood cells _____________________ solution Concentration _____________________________________________ than inside cell Cell _____________ water Animal cells may lyse or burst Plant cells use this to remain turgid _____________________ solution • Concentration of ____________________________________ than inside cell • Cell ___________ water • Animal cells shrink • Plant cells undergo plasmolysis and may wilt Active Transport Movement of molecules _________________________________ gradient (from low to high) Cells expend __________________ Requires ________________ protein _____________________________________ important in maintaining gradient of ions used in nerve impulse conduction Bulk Transport Movement of _______________________ too large to be moved by transport proteins. Vesicle formation takes them in or out of cell. Exocytosis—movement ______________ of cell Endocytosis—movement ________________ cell Phagocytosis—cell surrounds, ________________, and digests particle Pinocytosis—vesicle forms around __________________________________ particles Receptor-mediated endocytosis—___________________ for particular substances found in coated pit—selective and more ___________________