AQA organic mechanisms VERSION 4
advertisement

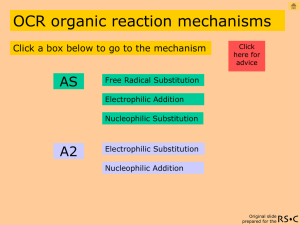
AQA organic reaction mechanisms Click a box below to go to the mechanism AS Free Radical Substitution Click here for advice Electrophilic Addition Nucleophilic Substitution (nitrile hydrolysis reaction) Elimination of HX from haloalkanes Elimination of water from alcohols A2 Electrophilic Substitution Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Acylation Nucleophilic Addition Nucleophilic Addition Elimination Original slide prepared for the Free radical substitution chlorination of methane i.e. homolytic breaking of covalent bonds Overall reaction equation CH4 + Cl2 CH3Cl + HCl Conditions ultra violet light excess methane to reduce further substitution Original slide prepared for the Free radical substitution mechanism ultra-violet Cl2 Cl + Cl initiation step two propagation steps CH4 + Cl CH3 + HCl CH3 + Cl2 CH3Cl + Cl CH3 + Cl CH3Cl termination step CH3 + CH3CH3 minor termination step CH3 Original slide prepared for the Further free radical substitutions Overall reaction equations CH3Cl + Cl2 CH2Cl2 + HCl CH2Cl2 + Cl2 CHCl3 + HCl CHCl3 + Cl2 CCl4 + HCl Conditions ultra-violet light excess chlorine Original slide prepared for the Electrophilic addition bromine with propene CH3CH=CH2 + Br2 mechanism CH3CHBrCH2Br 1,2-dibromopropane hydrogen bromide with but-2-ene CH3CH=CHCH3+ HBr mechanism CH3CH2CHBrCH3 2-bromobutane concentrated sulphuric acid with but-2-ene CH3CH=CHCH3+ HOSO3H mech CH3CH2CH(OSO3H)CH3 2-butylhydrogensulphate Original slide prepared for the Electrophilic addition mechanism bromine with propene H reaction equation H C C CH3 H + Br Br - H H carbocation CH3 C + C H BrBr Br H H CH3 C C Br 1,2-dibromopropane Br H Br Original slide prepared for the Electrophilic addition mechanism hydrogen bromide with trans but-2-ene reaction equation CH3 H C C CH3 H H + Br - H H carbocation CH3 C + C CH3 Br- H H H CH3 C C Br H CH3 2-bromobutane Original slide prepared for the Electrophilic addition mechanism concentrated H2SO4 with cis but-2-ene H H C C CH3 CH3 H + reaction equation H CH3 C H H carbocation C CH3 + OSO3H OSO3H - H H CH3 C C 2-butylhydrogensulphate H CH3 OSO3H Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic substitution hydroxide ion with bromoethane CH3CH2Br + OH- (aqueous) CH3CH2OH + Brethanol cyanide ion with iodoethane CH3CH2I (ethanol) + CN-(aq) ammonia with bromoethane CH3CH2Br + 2 NH3 mechanism mechanism CH3CH2CN + Ipropanenitrile mechanism CH3CH2NH2 + NH4+Braminoethane Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic substitution mechanism hydroxide ion with bromoethane H + CH3 C H OH- Br H CH3 C OH H Br ethanol reaction equation Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic substitution mechanism cyanide ion with iodoethane H + CH3 C H CN- Br H CH3 C CN H Br propanenitrile reaction equation Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic substitution mechanism ammonia with bromoethane H + CH3 C H Br H CH3 C H - Br + NH2 H NH3 NH3 H CH3 C aminoethane H NH2 reaction equation H NH3+Br Original slide prepared for the Nitrile hydrolysis Acid hydrolysis of nitriles: CH3CH2CN +2 H2O + H+ Reflux with strong acid CH3CH2COOH + NH4+ propanoic acid eg HCl (aq) Original slide prepared for the Elimination of HX from haloalkanes Elimination of HBr from 2-bromopropane CH3CHBrCH3 + OHCH3CH=CH2 + H2O + Br(in ethanol) H H CH3 C C Br H H H H C CH3 OH - propene C H Br - H OH acting as a base Original slide prepared for the Haloalkanes and hydroxide ions nucleophilic substitution alcohol RCH3CH2OH + Br- + OH- (aqueous) hydroxide acts as a nucleophile RCH2CH2X + OH- (ethanol) elimination hydroxide acts as a base RCH=CH2 + H2O + Xalkene Original slide prepared for the Elimination of water from alcohols Elimination of H2O from propan-1-ol CH3CH2CH2OH CH3CH=CH2 + H2O Heat with concentrated H2SO4 Original slide prepared for the Elimination mechanism – water from propan-1-ol H H CH3 C C H H H CH3 C H + H H OH H CH3 C H C OH + H H protonated alcohol OH C+ H H C H carbocation H H + H C CH3 reaction equation H H OH propene Original slide prepared for the Electrophilic Substitution Nitration of benzene C6H6 + HNO3 C6H5NO2 + H2O Conditions / Reagents concentrated HNO3 and concentrated H2SO4 50oC mechanism Original slide prepared for the electrophilic substitution mechanism (nitration) + 1. Formation of NO2 the nitronium ion + HNO3 + 2H2SO4 NO2 + 2HSO4- + H3O+ 2. Electrophilic attack on benzene + NO2 + NO2 H - O SO3H 3. Forming the product and re-forming the catalyst reaction equation NO2 H O SO3H Original slide prepared for the Friedel-Crafts alkylation Where an H atom attached to an aromatic ring is replaced by a C atom Alkylation of benzene C6H6 + RCl electrophilic substitution C6H5R + HCl R = alkyl group Conditions / Reagents RCl (haloakane) 0 - 25oC and anhydrous AlCl3 to prevent further substitution Original slide prepared for the Alkylation example With chloroethane C6H6 + CH3CH2Cl overall reaction equation C6H5CH2CH3 + HCl Three steps in electrophilic substitution mechanism 1. Formation of the electrophile (a carbocation) CH3CH2 Cl AlCl3 + CH3CH2 Cl - AlCl3 Original slide prepared for the Alkylation electrophilic substitution mechanism 2 2. Electrophilic attack on benzene + CH3CH2 CH3CH2 H + - Cl AlCl3 3. Forming the product and re-forming the catalyst CH3CH2 H AlCl3 Cl ethylbenzene Original slide prepared for the Friedel-Crafts acylation An H atom attached to an aromatic ring is replaced by a C atom where C is part of C=O Acylation of benzene C6H6 + RCOCl electrophilic substitution C6H5COR + HCl Conditions / Reagents RCOCl (acyl chloride) and anhydrous AlCl3 50 oC Original slide prepared for the Acylation example With ethanoyl chloride overall reaction equation C6H6 + CH3COCl C6H5COCH3 + HCl Three steps in electrophilic substitution mechanism 1. Formation of the electrophile (an acylium ion) O CH3C Cl + CH3C O AlCl3 Cl - AlCl3 Original slide prepared for the Acylation electrophilic substitution mechanism 2 2. Electrophilic attack on benzene O + CH3C O CH3C + H Cl 3. Forming the product and re-forming the catalyst O CH3C - AlCl3 H Cl AlCl3 phenylethanone Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic Addition Reduction of carbonyls RCHO RCOR + 2[H] + 2[H] RCH2OH RCH(OH)R primary alcohol secondary alcohol Conditions / Reagents NaBH4 and H2SO4(aq) Room temperature and pressure Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic Addition Mechanism RCOR + 2[H] RCH(OH)R alcohol reduction of propanone NaBH4 is a source of hydride ions H + CH3 C O - CH3 H H+ from H2SO4 (aq) H+ O CH3 C CH3 H O H CH3 C H CH3 propan-2-ol Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic Addition addition of hydrogen cyanide to carbonyls to form hydroxynitriles RCOR + HCN RCHO + HCN RC(OH)(CN)R RCH(OH)CN Conditions / Reagents NaCN (aq) and H2SO4(aq) supplies H+ supplies the CN- nucleophile Room temperature and pressure Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic Addition Mechanism hydrogen cyanide with propanone CH3COCH3 + HCN CH3C(OH)(CN)CH3 NaCN (aq) is a source of cyanide ions + CH3 C O - CH3 CN H+ from H2SO4 (aq) + H O CH3 C CH3 CN C N O CH3 C H CN CH3 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic Addition Elimination Acylation of water to give carboxylic acids RCOCl + H2O RCOOH + HCl carboxylic acid RC Conditions O OH room temperature and pressure Original slide prepared for the Formation of ethanoic acid ethanoyl chloride CH3COCl + H 2O CH3COOH + HCl ethanoic acid O CH3 C OH mechanism Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic Addition Elimination Mechanism + O CH3 C nucleophilic addition O CH3 C + OH Cl H Cl OH elimination H CH3 O C CH3 O C + OH H OH H Cl Cl reaction equation Original slide prepared for the Acylation of primary amines to N-alkyl amides RCOCl + 2 R’NH2 RCONHR’ + R’NH3+ClN-alkylamide RC Conditions O NHR’ room temperature and pressure N-propylethanamide CH3 C O NHCH2CH2CH3 Original slide prepared for the Formation of N-propyl ethanamide from ethanoyl chloride CH3COCl 1-aminopropane + 2 CH3CH2CH2NH2 CH3CONHCH2CH2CH3 + CH3CH2CH2NH3+Cl- N-propylethanamide mechanism Original slide prepared for the Nucleophilic Addition Elimination Mechanism nucleophilic O O + + addition CH3 C CH3 C NHCH2CH2CH3 Cl Cl H NHCH2CH2CH3 elimination H CH3 H O C CH3 NHCH2CH2CH3 Cl + NH2CH2CH2CH3 O C + NHCH2CH2CH3 H Cl NH2CH2CH2CH3 reaction equation Original slide prepared for the Advice To get back to the mechanism links page from anywhere in the presentation, click the button at the top right corner of the screen. This version provides the organic mechanisms specified (2002/3) by the AQA exam board. Each stage of a reaction equation, its conditions and mechanism are revealed in turn on a mouse click or keyboard stroke. Note that there is another version available where each reaction and mechanism play automatically after an initiating click or key stroke. The number of ways of navigating through this presentation may depend on the version of PowerPoint being used and how it is configured. Some possible ways of advancing: left mouse click or return key or right arrow key or up arrow key. Some possible ways of reversing: backspace key or left arrow key or down arrow key. Original slide prepared for the References Steve Lewis for the Royal Society of Chemistry Original slide prepared for the