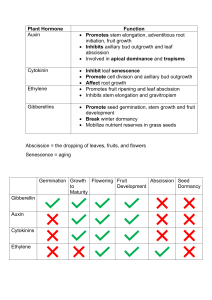
PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT Growth: an irreversible permanent increase in size of an organ or its parts. Plants retain capacity of unlimited growth due to presence of meristems. Primary Growth: elongation of plants along axis. Secondary Growth: increase in girth due to activity of lateral meristem, vascular cambium and cork cambium. Growth Rates: (i) Arithmetic: only one continue to divide while other differentiate and matures (1 1 + 1 1+1+1 1+1+1+1..) Mathematically, Lt= L0 +rt (ii) Geometrical: initial growth is slow(lag phase),and it increases rapidly thereafter exponentially (log or exponential phase), the slows down(stationary phase). Sigmoid Curve. Mathematically, W1= W0 e^rt Differentiation: Cells derived from root apical and shoot apical meristems and cambium mature to perform specific functions. This act leading to maturation is called Differentiation. Eg to form tracheary elements, cells lose protoplasm. Dedifferentiation: the living differentiated cells that lost the capacity to divide can regain the capacity of division under certain conditions. Eg formation of intrafascicular cambium and cork cambium from fully differentiated parenchyma cells. Redifferentiation: dedefferentiated cell again lose meristematic capacity and mature to perform specific functions. Development: all changes than an organism goes through its life cycle. Plasticity: form different kind of structure in response to different environments. Eg heterophylly in cotton, coriander and larkspur. PLANT GROWTH REGULATOR: indole-3-acetic acid(IAA); Adenine derivatives (N⁶ furfurylamino purine,kinetin); derivatives of carotenoids (abscisic acid,ABA) ; Terpenes(Gibberlellic acid, GA3 ) or Gases(ethylene, C2H4) Charles Darwin and Francis Darwin discovered phototropism(bending towards light) in coleoptile of Canary Grass. FW Went : isolated Auxin from tip of coleoptile of oat seed. E. Kurosawa reported 'bakanae'(foolish seedling) of rice caused by fungi Gibberella fujikuroi. Treated by using gibberellic acid. First identified Three inhibitors: inhibitor-B, abscission II and dormin. Later it was proved that they are chemically identical ie Abscisic acid. H.H. Cousins(1910) : Ethylene from ripened orange hastened ripening of unripened Banana. AUXINS: first isolated from human urine. Produced by growing apices. Synthetic Auxin: NAA(napthalene acetic acid) and 2,4-D(2,4- dichlorophenoxyacetic) Initiates rooting in stem cutting; promote Flowering in Pineapples. Prevent early fruit and leaf drop . promote abscission in older leaves and fruits. Induce parthenocarpy in tomato. 2,4-D kills dicot weeds. Helps in cell division,xylem differentiation. Apical dominance: growing of apical bud inhibits growth of lateral/auxiliary bud. GIBBERELLINS: ALL GA are acidic. Increase length of axis such as in grape stalks; fruits like apple elongates; delay senescence; GA3 speed up the malting process in brewing industry. Spraying Gibberellin in sugarcane increases stem length this increase yield by 20 tonnes per acre. Spraying Gibberellin on juvenile conifers hasten the maturity period thus early seed production ; bolting(elongation of stem) in beet, cabbage. CYTOKININS: first discovered as kinetin from autoclaved herring sperm . Influence in Cytokinesis. Natural CYTOKININS are synthesized in region where rapid cell division occur such as root apices,shoot buds,young fruits.helps produce leaves, chloroplast in leaves, lateral shoot growth and adventitious root formation. Helps overcome apical dominance. Promote nutrients mobilisation thus delaying leaf senescence. ETHYLENE: gaseous PGR. Produced by tissues undergoing senescence and ripening fruits. Promote senescence and abscission of leaves and flowers. Breaks seed dormancy, initiate Germination in potato tubers, peanut seeds. Helps upper part/leaves remain above water. Promote root hair formation, root growth. Most widely used source of ethylene is Ethephon. Promote female flowers in cucumber. Hasten fruit ripening in tomato and apples. ABSCISIC ACID: growth inhibition. Inhibits seed germination. Stimulates closer of stomata. Increases tolerance to stress. STRESS HORMONES. Induce dormancy. ABA acts as an antagonist to Gas. PHOTOPERIODISM: Periodic exposer of light for Flowering. Long day plant: require exposure of light for e period exceeding a well defined critical duration for Flowering. Short Day plant: exposure of light for a period less than a well defined critical duration for Flowering . Day neutral plants: no relation between light exposure duration and Flowering. Site of perception of light duration are the Leaves. VERNALISATION: Flowering depends quantitatively or qualitatively on duration of low temperature. Eg wheat , barley. It Prevents precocious reproductive development. Vernalisation is seen in Biennial plants monocarpic plants normally flowers and die in second season. Eg Sugarbeet, cabbage, carrots. SEED DORMANCY: impermeable seed coat, Abscisic acid, phenolic acid, para- ascorbic acid and immature embryo causes seed dormancy. Effect of inhibitory substance can be removed by applying chilling condition or gibberellic acid and nitrates.