7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Parts Powerpoint
advertisement
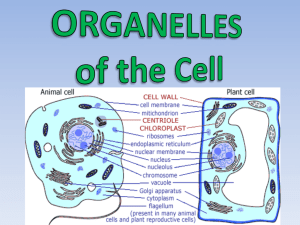
Eukaryotic Cell Structures 7-2 In some respects, the eukaryotic cell is like a factory It contains several tiny specialized structures called organelles Biologists divide the cell into 2 parts: the cytoplasm and the nucleus The cytoplasm is the portion of the cell outside the nucleus It contains the organelles and is where some cellular processes take place Nucleus Contains nearly all of the cell’s DNA and instructions for making proteins & other molecules It is surrounded by a nuclear envelope, which is made up of 2 membranes Contains 1000’s of tiny pores which allow material (RNA & proteins) to move into and out of nucleus Nucleus contains chromatin, which is DNA bound to proteins Condenses to form chromosomes during cell division May also contain a nucleolus, which is where ribosomes are made Ribosomes Site where proteins are assembled Composed of RNA & proteins Found in the cytoplasm or on other organelles Produce proteins based on coded instructions from the nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) It is an internal membrane system that synthesizes and exports materials Site where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled Exports proteins and other material for the cell There are 2 types of ER: smooth and rough Rough ER is involved in protein synthesis Contains ribosomes on its surface Proteins leave ribosomes and enter ER to be modified Smooth ER lacks ribosomes Contains enzymes the synthesize lipid membranes & detoxify drugs Large amounts are found in liver Golgi Apparatus Named after Italian scientist Camillo Golgi Accepts proteins modified in the rough ER Function is to modify, sort, and package proteins & other materials from the ER Lysosomes Small organelles filled with enzymes that act like “clean-up crew” in the cell Functions to digest, or breakdown lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small molecules Breaks down old & worn out organelles Vacuoles Saclike structure that stores cellular materials like water, salts, proteins and carbs Plants contain a large vacuole filled with water, which enables plants to support the weight of flowers and leaves Single-celled organisms contain a contractile vacuole, Used to pump out excess water from cell Helps to maintain homeostasis Mitochondria & Chloroplasts Mitochondria are found in plant & animal cells Functions as the cell’s “powerhouse” by converting energy stored in glucose to the cellular energy ATP Composed of 2 membranes: inner & outer The inner membrane is folded to increase surface area Chloroplasts are found in plant cells and in a few other organisms Contains chlorophyll, which is used to capture the energy during photosynthesis Also composed of 2 membranes Organelle DNA Chloroplasts and mitochondria contain their own DNA Biologist Lynn Margulis believes they are descendents from prokaryotic cells Developed from symbiotic relationships Cytoskeleton Functions as support structure for cell Consists of a network of protein filaments that help the cell maintain its shape Two types of protein filaments: microfilaments and microtubules Microfilaments are made of actin and their assembly and disassembly allow cytoplasmic movement Microtubules are hollow structures made of tubulin They are important in cell reproduction because they form the mitotic spindle which separates chromosomes They are also responsible for the formation of cilia and flagella, which allow some cells to move Centrioles are also made of tubulin and help to organize cell division