Protein Synthesis Overview
advertisement

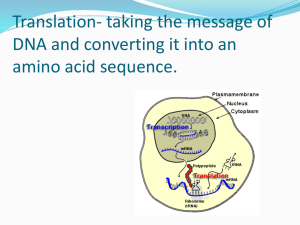
Bell Ringer Compare and Contrast: DNA and RNA Bell Ringer • What organelle is responsible for protein synthesis (making proteins)? • What types of cells have this organelle? • Where in the cell can this organelle be found? Bell Ringer (1) •What are the 3 types of RNA? •What is the function of each type? Protein Synthesis: An Overview Day 5 Unit 5 Goal: Students will be able to describe the processes of transcription and translation. Protein Synthesis Foldable Transcription Translation 1. Where? 2. What molecules are involved? 3. What is produced? 4. Where does it go? 5. What happens? 1. Where? 2. What molecules are involved? 3. What is produced? 4. Where does it go? 5. What happens? Back of Foldable • Central Dogma • Amino Acids & Nucleotides • Codons • Types of RNA – Start = – Stop = Structure of RNA copyright cmassengale 7 Pathway to Making a Protein DNA mRNA tRNA (ribosomes) Protein copyright cmassengale 8 DNA RNA Protein Nuclear membrane DNA Transcription Eukaryotic Cell Pre-mRNA RNA Processing mRNA Ribosome Translation Protein copyright cmassengale 9 Types of RNA • Messenger RNA (mRNA) makes a copy of DNA • Transfer RNA (tRNA) decodes mRNA and transfers amino acids to the ribosome • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) build the protein by bonding amino acids together. Ribosomes are made of rRNA. Protein Synthesis • Protein synthesis uses the information in genes to make proteins. • 2 Steps –Transcription –Translation Transcription: Where? • mRNA is made in the NUCLEUS • mRNA will leave the nucleus through the pores in the nuclear membrane • (DNA does NOT leave the nucleus) Transcription: Involved Molecules • DNA (instructions for making the protein) • mRNA (copy of the instructions) • RNA polymerase (enzyme that builds mRNA) RNA Polymerase = The Enzyme responsible for Transcription copyright cmassengale 14 Transcription: Produces? • mRNA (messenger RNA) • Long Straight chain of Nucleotides • Made in the Nucleus • Copies DNA & leaves through nuclear pores • Contains the Nitrogen Bases A, G, C, U ( no T ) copyright cmassengale 15 Transcription: Goes to? •mRNA leaves the nucleus through the pores in the nuclear membrane and goes to the ribosomes copyright cmassengale 16 Transcription: What Happens? Big Idea: DNA is copied into a complementary sequence of mRNA. 1.RNA polymerase is the enzyme that is responsible for transcription 2.RNA polymerase reads the gene and adds the correct complementary RNA base to make a new strand of RNA. – DNA = GCCATT – mRNA = CGGUAA Remember the Complementary Bases On DNA: A-T C-G On RNA: A-U C-G copyright cmassengale 18 Transcription 3. The mRNA gets processed (edited and packaged) 1. Introns (interrupting sequences) removed 2. Exons spliced together 3. G3 Cap and PolyA Tail attached 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the cytoplasm. The mRNA is then TRANSLATED by tRNA at the RIBOSOME (made of rRNA). mRNA processing Adenine (DNA and RNA) Cystosine (DNA and RNA) Guanine(DNA and RNA) Thymine (DNA only) Uracil (RNA only) RNA polymerase DNA RNA The Genetic Code • Each gene on a strand of DNA is read in 3 base sequences called codons • A codon designates an amino acid • An amino acid may have more than one codon • There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons • Some codons tell the ribosome to stop translating copyright cmassengale 22 The Genetic Code •Use the code by reading from the center to the outside •Example: AUG codes for Methionine copyright cmassengale 23 Name the Amino Acids • • • • • GGG? UCA? CAU? GCA? AAA? copyright cmassengale 24 Start/Stop Codons • There will always be a “Start” codon (AUG) at the beginning. It is like capitalizing the 1st letter of a sentence. • There will always be a “Stop” codon (UGA, UAA, UAG) at the end. It is like a period at the end of a sentence. Translation Translation: Where? • Ribosome –Free floating ribosome in cytoplasm (makes proteins for that cell) OR –attached ribosome on the Rough ER (makes proteins to be exported to other cells) Translation: Involved Molecules • mRNA (copy of the instructions) • tRNA (translates the instructions) • rRNA (builds the protein) Transfer RNA amino acid attachment site • Decodes (translates) the mRNA • Transfers amino acids to the ribosome U A C anticodon copyright cmassengale 30 Codons and Anticodons • The 3 bases of an anticodon are complementary to the 3 bases of a codon • Ex: Anticodon UGA • Codon ACU copyright cmassengale UGA ACU 31 Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • rRNA is a single strand 100 to 3000 nucleotides long • Globular in shape • Made inside the nucleus (nucleolus) of a cell • Associates with proteins to form ribosomes • Site of protein Synthesis copyright cmassengale 32 Translation: Produces? • Chain of amino acids • Polypeptide (protein) Translation: Where does it go? The protein will do one of 2 things • Stay inside the cell to carry out functions for that cell OR • Be exported to other cells – Rough ER Golgi Exocytosis Translation: What Happens? • Big Idea: The mRNA is then TRANSLATED by tRNA at the RIBOSOME (made of rRNA). The RIBOSOME then BUILDS the protein by bonding amino acids together. Translation: What Happens? 1. tRNA translates the mRNA using “anticodons.” (complementary to the codon) – Each tRNA molecule has an anticodon on one end and an amino acid on the other. 2. tRNA transfers the amino acids to the ribosome in the correct sequence. 3. rRNA forms peptide bonds between the amino acids. This links them together to build the protein. Nucleus Messenger RNA Messenger RNA is transcribed in the nucleus. Phenylalanine tRNA mRNA Transfer RNA Methionine The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that binds methionine. The ribosome also binds the next codon and its anticodon. Ribosome mRNA Lysine Start codon The Polypeptide “Assembly Line” The ribosome joins the two amino acids— methionine and phenylalanine—and breaks the bond between methionine and its tRNA. The tRNA floats away, allowing the ribosome to bind to another tRNA. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, binding new tRNA molecules and amino acids. Lysine Growing polypeptide chain Ribosome tRNA tRNA mRNA Completing the Polypeptide mRNA Translation direction Ribosome The process continues until the ribosome reaches one of the three stop codons. The result is a growing polypeptide chain. Protein Synthesis Activity • Step 1: Transcription – Copy the “gene” into the complementary sequence of mRNA. – This must be done in the “Nucleus.” • Step 2: Translation – Translate the mRNA using the “tRNA cards” posted around the room. The codon should match up with a word. – If you have done this correctly, your sentence should make sense!!! – Don’t forget the punctuation (Start/Stop codons)!! QOD (1) •What happens during transcription? •What happens during translation?