Vectors
advertisement

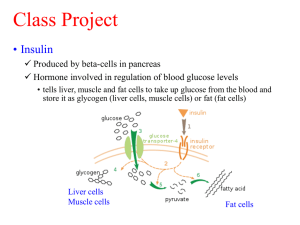
Insulin & human growth hormone by E.coli Edited by Prof. Dr. Sudjadi DAFTAR PUSTAKA BR GLICK & JJ PASTERNAK MOLECULAR BIOTECHNOLOGY DJA CROMMELIN & RD SINDELAR PHARMACEUTICAL BIOTECHNOLOGY Sudjadi, Bioteknologi Kesehatan Overview Part A rDNA Objectives Steps in rDNA Processing Genetic Engineering Advances Part B Genomic library – Plasmid – Restriction enzim, ligase Part C The Use of rDNA to Produce Human Insulin and Human Growth Hormon PART A Genetic engineering plays a very important role, not only in scientific research, but also in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. rDNA is NOT Whole Animal Cloning Recombinant DNA is a tool in understanding the structure, function, and regulation of genes and their products The objectives of Recombinant DNA technology include: – Identifying genes – Isolating genes – Modifying genes – Re-expressing genes in other hosts or organisms These steps permit scientists and clinicians to: – Identify new genes and the proteins they encode – To correct endogenous genetic defects – To manufacture large quantities of specific gene products such as hormones, vaccines, and other biological agents of medical interest Process Example THINK ABOUT THIS ? What is DNA Ligase Used for? What is a Restriction Enzyme? Why Are Plasmid’ Used as Cloning Vectors? Production Human Insulin in E.coli Part B Genomic library Prinsip kloning PEMOTONGAN HpaI PEMOTONGAN EcoRI Cloning Vectors A vector is used to amplify a single molecule of DNA into many copies. A DNA fragment must be inserted into a cloning vector. A cloning vector is a DNA molecule that has an origin of replication and is capable of replicating in a bacterial cell. Most vectors are genetically engineered plasmids or phages. There are also cosmid vectors, bacterial artificial chromosomes, and yeast artificial chromosomes. PENAPISAN KOMPLEMENTASI PELACAK DNA ANTIBODI Genetic engineering has permitted: Isolation of large quantities of pure protein: Insulin, growth hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, as well as other proteins, are now available as recombinant products. Physicians will no longer have to rely on biological products of low purity and specific activity from inconsistent batch preparations to treat their patients. PART C Case Study: The Use of Recombinant DNA to Produce Human Insulin Recombinant human proteins as therapeutic agents Human proteins produce fewer side effects than proteins from other animals (e.g. pork insulin vs. human insulin) -- Hormones or hormone-like compounds -- Enzymes -- Antibodies -- Proteins with vaccine action Replacement therapy of genetic diseases Why synthesize human insulin? Patients’ immune systems do not produce antibodies against human insulin as they do with bovine or porcine insulin Need for a more reliable and sustainable method of obtaining the product Structure of Insulin Two polypeptide chains; one with 21 amino acids and the second with 30 amino acids Chains are linked via a disulfide bond Gene encoding the insulin protein is found on chromosome 11 In reality both chains are present in the same protein www.blc.arizona.edu/.../rick/ biomolecules/protein.html First recombinant human insulin Human gene library was screened and INS gene subcloned into a plasmid expression vector using lac operon to promote transcription Expression in E. coli resulted in inclusion bodies packed full of insulin Isolation of insulin from inclusion bodies is timely and expensive http://www.apsu.edu/reedr/Reed%20Web%20Pages/Chem%204310/Lectures/recomb1.jpg Humilin (Eli Lilly, 1986) – first industrially produced human insulin 24 aa Signal peptide leader was added to 5’ end. secretion of insulin into culture medium instead of its retention inside inclusion bodies (Signal leader detaches as insulin is transported across cell membrane..) A chain synthesized in one E. coli strain B chain synthesized in a different E. coli strain Chains are purified separately then joined together Continuous culture techniques used Human Growth Hormone (HGH) (somatotropin) HGH promotes overall body growth by increasing amino acid uptake by cells, protein synthesis and fat utilization for energy Insufficient production of HGH by the pituitary gland = dwarfism Chubby face “Baby fat” around waist Unusual body properties as an adult ~ 4 feet tall only IQ = Normal HGH helps undersized children reach their normal height and size http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/hmn/F01/photos/36.jpg Pressure to use HGH to stimulate growth in youngsters who have no deficiency but whose parents want them to grow up tall. In the summer of 2003, the U.S. FDA approved the use of human growth hormone (HGH) for boys predicted to grow no taller than 5′3″ and for girls, 4′11″ even though otherwise perfectly healthy. If adult suffers with hypopituitarism, HGH therapy is also available as normally payable under an insurance policy. Pre-recombinant era of HGH production HGH could be purified from cadaver pituitary glands 8 cadavers/year for 8 – 10 years per patient Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease (CJD) is one of the risk of using brain tissue 24 cases reported by 1993 in France from cadaver HGH news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/ health/2136673.stm umed.med.utah.edu/.../lectures/ inf/baringerimg/brain.htm 10_25_cDNA.jpg Making cDNA from mRNA using reverse transcriptase and DNA polymerase Protropin (Genentech) and Humatrope (Eli Lilly) hGH therapy is very expensive, costing anywhere from $800 to $2,500 a month Native human GH contains signal peptide needed to direct nascent polypeptide to RER in eukaryotes Signal peptide is bad for E.coli (it can not synthetize this protein) Signal sequence removed be EcoRI cleavage Coding sequence for first 24 aa also lost in the process of removal 24 amino acids added back by synthetic DNA linker Expressed in E. coli successfully