Cell Introduction Powerpoint
advertisement

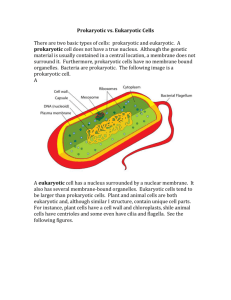
Biology 30 - Unit 2 Cells Cells An Introduction Animal Cell Cells Alive – Interactive Cell http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.ht m Plant Cell Cells Alive – Interactive Plant Cell http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.ht m Similarities and Differences Refer back to the diagram of a plant and an animal cell in your duotang. Compare and Contrast: Cell Info Cells are made of: 90% Water 10% (includes 50% Protein, 15% CHO, 15% Nucleic Acid, 10% Lipid, 10% other) Cell Info Continued . . . The Elements of a Cell: 60% Hydrogen 25% Oxygen 10% Carbon 5% Nitrogen What’s in a Gene?? GENOME SIZE: stated as the total number of base pairs the human genome = 3 billion base pairs Each DNA Molecule contains many genes (the basic physical and functional unit of heredity). a gene is a sequence of nucleotides bases, who carry the info required for constructing proteins, which carry the structural components of cells, tissue, and enzymes. The Human Genome has about one hundred thousand genes. human genes vary in length (average size = thousands of bases) humans can synthesize approx. 100 000 different kinds of proteins THE GENETIC CODE: is a series of codons that specify which amino acids are required to make up specific proteins. the three billion base pairs are organized into 23 units called chromosomes (1 set of chromosomes comes from each parent - Total of 46 chromosomes) Chromosomal DNA contains an average of 150 million bases Cell History Please refer to the cell history handout in your duotang. Types of Cells Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Eukaryotic are larger and more Cellupedia complex Different Types of Cells have a nuclear - Eukaryotic Cells membrane - Examples have membrane bound organelles (where isolated biochemical reactions occur) DNA more complex Examples: Plant and Animal cells Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Prokaryotic smaller simpler lack nuclear membrane have no membrane bound organelles oldest known forms of life hereditary info is spread throughout the nucleus reactions occur on the inner membranes Example: Bacteria, Blue-green Algae University of Arizona Prokaryotic Tutorial Info Cellupedia Prokaryotic Images Overview of Cell Structure Cells vary in shape, size and function Cell Parts: Basic cell parts include: Cell Membrane: phospholipid bilayer; function - to hold all contents in place and regulate the movement of molecules in and out of the cell; receptor sites located in the membrane control what enters Cell Parts Cytoplasm: nutrients are absorbed, transported and processed; wastes will accumulate here; Nucleus: cell’s control centre all info is encoded in the DNA Video of Animal Cells http://www.howe.k12.ok.us/~jimaskew/bvid4a.mov Video of Plant Cells http://www.howe.k12.ok.us/~jimaskew/bvid4b.mov Review Site: http://www.howe.k12.ok.us/~jimaskew/unit4.htm Cell Structure Handout: You will create a handout that highlights the following parts of the cell. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomes, Chloroplasts, Microtubules (Microfilaments, Cytoskeleton), Mitochondria, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosome, Centriole, Vacuole, Cell Wall, etc. Use the websites listed online to help you out Biology in the Classroom: Cells: Cell parts http://wblrd.sk.ca/~bio2030sp/bio30/unit2/plantandanimalcells/page1. htm