Meiosis and Gametogenesis
advertisement

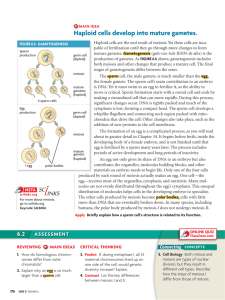
2 Meiosis and Gametogenesis Chapter 1 Thompson and Thompson Somatic and Germline cells • Development of a fertilized egg into an adult results in two distinct types of cells – Somatic cells • These create all tissues and organs of the adult except for cells destined to become sperm or egg • They can only undergo mitosis – Germline cells • The final differentiated form of these cells are mature gametes: the sperm and egg • These cells undergo mitosis until gametogenesis – They then undergo meiosis Meiosis Meiosis is required for gametogenesis Meiosis I Somatic cells Germline Cells Interphase I and Prophase I Leptotene Prophase I Zygotene Prophase I Pachytene Prophase I Diplotene Recombination And on the molecular level Metaphase I and anaphase I Meiosis I is the reduction division Non-disjunction Telophase I Cytokinesis sperm formation oocyte formation Meiosis II A comparison of meiosis and mitosis Mitosis Maintains Meiosis Reduces 1 2 Cells resulting 2 4 Cells involved Somatic Germline Chromosome number Nuclear Divisions And now, Meiotic “Titanic” Relationship to Gametogenesis Sperm and Egg formation Gametogenesis • Entry of a single sperm into an egg prevents entry of other sperm • The DNA of sperm and egg are initially kept separate in “pronuclei” of the zygote • Timing of a pregnancy extends from the “last menstrual period” (LMP) rather than the time of fertilization Fertilization Mitotic Non-disjunction