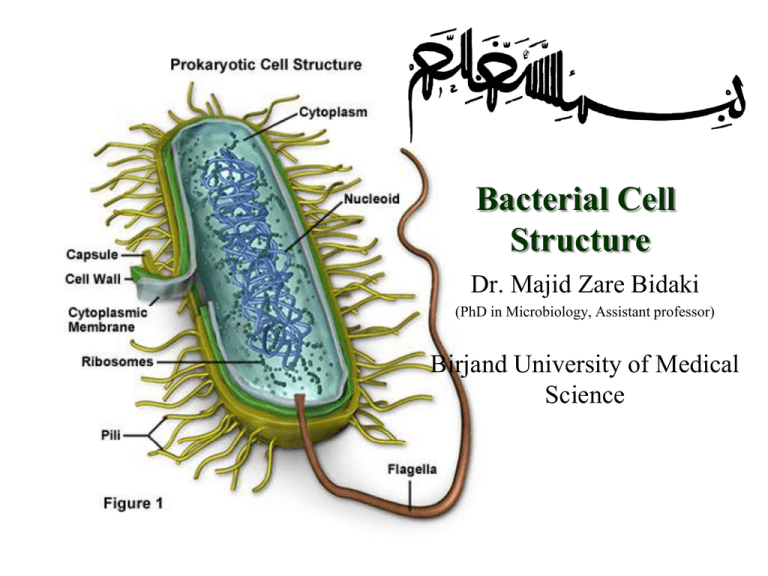
Bacterial Cell
Structure
Dr. Majid Zare Bidaki
(PhD in Microbiology, Assistant professor)
Birjand University of Medical
Science
References
1. Jawetz, Melnick, & Adelberg; Medical Microbiology,
24th ed.
2. Zinsser, Hans, And Joklik, Wolfgang K.; Medical
Microbiology, 17th ed.
3. Baron, Samuel; Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
First to observe living
microbes
his single-lens
magnified up to 300X
(1632-1723)
3
4
Louis Pasteur (1822-1895)
Showed microbes caused
fermentation & spoilage
Disproved spontaneous
generation of microbes
Developed aseptic
techniques.
Developed a rabies vaccine.
5
Robert Koch
Proposed: Germ theory
of disease
Developed: pure culture
methods.
Identified: cause of
anthrax, TB, & Cholera.
(1843-1910)
6
Acellular and cellular Microorganisms
Acellular:
Viruses
Viroids
Prions
Cellular:
Bacteria
fungi
Protista: Protozoa & algae
helminths (worms)
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic
8
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
Size
smaller
Larger
Nucleus
-
+
Organelles
-
+
Chromosomes 1 circular
Multiple, linear
Ribosomes
Larger 80s
smaller 70s
r
In prokaryotes against Eukaryotes, cell membranes lack
sterols (e.g. cholesterol)
Scientific nomenclature
Binomial (scientific) nomenclature
Gives each microbe 2 names
Genus - noun, always capitalized
species - adjective, lowercase
Both italicized or underlined
– Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)
– Escherichia coli
(E. coli)
10
Bacterial shapes
Cytoplasmic membrane
Protoplast
Spheroplast
L forms
Gram positive
Gram negative
Lipopolysaccharide
O-antigen
Highly variable
Core
• Heptoses
• Ketodeoxyoctonic acid
Lipid A
• Glucosamine disaccharide
• Beta hydroxy fatty acids
(Hydroxy myritic Acid)
LPS function
Endotoxins
Exotoxins
Peptidoglycan
Gram positive
Gram negative
4 groups based on cell wall
composition
1. Gram positive cells
2. Gram negative cells
3. Bacteria without cell walls
4. Bacteria with chemically unique cell walls
Gram positive wall
Gram negative cell wall
Lipoteichoic acid
Peptidoglycan-teichoic acid
Cytoplasmic membrane
Cytoplasm
Porin
Outer Membrane
lipoprotein
Inner (cytoplasmic) membrane
Cytoplasm
Lipopolysaccharide
Gram Positive Cell Envelope
Peptidoglycan-teichoic acid
Lipoteichoic acid
r
r
r
Cytoplasmic membrane
r
r
r
r
r
r
r
Bacteria classification based on
cell wall structure
Grasilicutes (Gram Negative)
Firmicutes (Gram Positive)
Tenricutes (with no Cell wall)
Mendosicutes (with no Peptidoglycan in
cell wall)
Major Taxonomic Groups of Bacteria
Gracilicutes – gram-negative cell walls, thinskinned
Firmicutes – gram-positive cell walls, thick
skinned
Tenericutes – lack a cell wall & are soft
Mendosicutes – archaea, primitive procaryotes
with unusual cell walls & nutritional habits
Capsule
2 types
1. Macro capsule - highly organized, tightly
attached
2. Micro capsule, Slime layer or Glycocalyx loosely organized and attached
Functions
attachment
inhibits killing by white blood cells
Receptor (K antigen)
2 Types of Capsule
Biofilms
Flagella
Fimbrea (Pili)
Adhesion to other cells and surfaces
Structure
Pili & Sex pili
Rigid tubular structure made of pielin protein
Found mostly in Gram negative cells
Functions
Adhesion
joins bacterial cells for DNA transfer (Conjugation)
Conjugation
Cytoplasm
dense gelatinous solution of sugars, amino
acids, & salts
70-80% water
serves as solvent for materials used in all
cell functions
Chromosome
single, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule
that contains all the genetic information required by
a cell
DNA is tightly coiled around a protein, aggregated
in a dense area called the nucleoid
plasmids
small circular, double-stranded DNA
free or integrated into the chromosome
duplicated and passed on to offspring
not essential to bacterial growth & metabolism
may encode antibiotic resistance, tolerance to
toxic metals, enzymes & toxins
used in genetic engineering- readily manipulated
& transferred from cell to cell
Ribosomes
made of 60% ribosomal RNA & 40% protein
consist of 2 subunits: large (50 S) & small (30 S)
procaryotic differ from eucaryotic ribosomes in
size & number of proteins
site of protein synthesis
All bacterial cells have ribosomes.
Inclusions, granules
intracellular storage bodies
vary in size, number & content
bacterial cell can use them when
environmental sources are depleted
Examples: glycogen, sulfur and polyphosphate
granules, poly-b-hydroxybutyrate, gas vesicles for
floating.
endospores
Important components in endospore:
Calcium
Dipicolinic Acid
The Endospore structure
Spore structure
Spherical or Oval
Terminal, subterminal or central
Bulging or nobulging
Growth in Bacteria
Temperature
Nutrients
pH
Osmotic pressure
Temperature
Minimum temperature – lowest temperature that
permits a microbe’s growth and metabolism
Maximum temperature – highest temperature
that permits a microbe’s growth and metabolism
Optimum temperature – promotes the fastest
rate of growth and metabolism
3 temperature adaptation groups
Bacterial Metabolism
Phototroph
Photoautotroph (Photolitotroph)
Photoheterotroph (Photoorganotroph)
Chemotroph
Chemoautotroph (Chemolitotroph
Chemoheterotroph (Chemoorganotroph)
Stages of metabolism in
chemoheterotrophic bacteria
Digestion
Absorption (Passive and active transportation)
Preparation for oxidation
Oxidation
Oxidation & Reduction
X
e- & H+
Cytochromes, ….
Y
Oxygen requirements
Bacterial growth
Binary division
G2
G1
G2
G0
G2
G1
G2
Microbial growth calculation
b = a X 2n
G (Generation time) = T / n
(n = The number of generations, T = The total time of growth for the population)
The curve of bacterial growth in a closed
culture
Growth Curve
Bacterial growth in a
continues culture
Continuous Culture, Chemostat
Chemostats are a
means of keeping a
culture in log phase
indefinitely.
Measuring the bacterial growth
• Measuring the mass of bacteria
• Measuring the number of bacteria
Fermentation
Incomplete oxidation of glucose or other
carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen
Uses organic compounds as terminal electron
acceptors
Yields a small amount of ATP
Production of ethyl alcohol by yeasts acting on
glucose
Formation of acid, gas & other products by the
action of various bacteria on pyruvic acid
Fermentation
Methods in bacterial identification
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Microscopic morphology
Macroscopic morphology – colony appearance
Physiological / biochemical characteristics
Chemical analysis
Serological analysis
Genetic & molecular analysis
G + C base composition
DNA analysis using genetic probes
Nucleic acid sequencing & rRNA analysis
Bacterial Colonies
• Standard Bacterial Count
• Colony-Forming Units
• Plaque-Forming Units
•Spread Plate
• Pour Plate
• Soft-Agar Overlay
Medium
Definition
Types based on solidity:
1. Liquid medium (Name broth)
BHI, TSB, SF, NB, …
2. Solid medium (Name agar)
Blood agar, Nutrient agar, chocolate agar,
Columbia agar, EMB
3. Semi-solid medium
SIM
Culture media
General medium
Special medium
Differential medium
Enrichment medium (….. & cold enrichment)
Transport medium (Stwart, Carry Blair, …)
Galleries
Types of culture methods
Isolation culture
Spread culture
Pour plate culture
Colony count culture