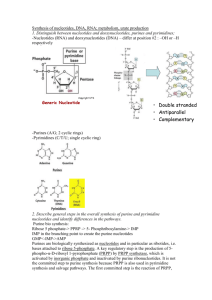
Nucleotide
advertisement

Chapter 10 Nucleotide metabolism Function of neucleotides Precursors for RNA and DNA synthesis Energy substance in body (ATP) Physiological Mediators (cAMP) Components of coenzymes (NAD+) Allosteric effectors and donor of phosphate group (phosphorylation) Formation of activated intermediates UDP-glucose, CDP-choline Section 10.2 Nucleotide Synthesis and Degradation Digestion and absorption of nucleotide Nucleoprotein Protein Nucleic acid Nucleases Nucleotide Nucleotidase Phosphate Nucleoside Nucleosidase Base Ribose Absorption Blood Metabolism of Purine nucleotides Biosynthesis of purine nucleotides de novo synthesis salvage pathway AMP GMP 1.De novo synthesis of purine nucleotides CO2 Glycine Aspartate One carbon unit One carbon unit Glutamine Characteristics of de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides 1. in cytosol 2. form IMP first, then synthesize AMP and GMP from IMP. 3. formation of purines is based on the ribosyl group of 5’-phosphoribose PP-1-R-5-P( 5’phosphoribose 1’pyrophosphate, PRPP) Glutamine PRPP amidotransferase (GPRT) AMP ATP PRPPK Gln Glu H2N-1-R-5´-P (5´-phosphoribosyl-amine) Gly, one carbon units, Gln, CO2, Asp involved IMP step by step AMP GMP R-5-P (5’-phosphoribose) PP-1-R-5-P( 5’phosphoribose 1’pyrophosphate, PRPP) Glutamine PRPP amidotransferase (GPRT) AMP ATP PRPPK Gln Glu H2N-1-R-5´-P (5´-phosphoribosyl-amine) Gly, one carbon units, Gln, CO2, Asp involved IMP step by step AMP GMP R-5-P (5’-phosphoribose) Regulation of de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides _ _ _ + Adenylsuccinate + R-5-P PRPPK GPAT PRPP _PRA ATP _ IMP XMP _ GTP IMP Adenylsuccinate AMP ADP + XMP + GMP ATP _ AMP ADP ATP GDP ATP GTP GMP GDP GTP 2. Salvage synthesis of purine nucleotides Material: or PRPP, purine (conjunction) nucleosides (phosphorylation) Location: brain and bone marrow adenine+ PRPP APRT HGPRT hypoxanthine+PRPP guanine+ PRPP adenosine AMP + PPi IMP + PPi HGPRT GMP + PPi Adenylate kinase AMP ATP ADP APRT: adenine phosphoribosyltransferase HGPRT: inosine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase Degradation of purine nucleotides nucleotide Nucleotidase nucleosides Nucleoside phosphorylase ribose-1-phosphate purine salvage pathway uric acid IMP Neucleo -tidase Excretion Metabolsm of pyrimidine nucleotides Biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides de novo synthesis salvage pathway 1.De novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides Glutamine 3 4 5 Aspartate CO2 2 6 1 Characteristics of de novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides 1. mostly in cytosol 2. form UMP first, then synthesize other pyrimidine nucleotides from UMP. 3. in the synthesis of UMP, pyrimidine ring is formed first , then combined with PRPP. Process of de novo synthesis of UMP 1. formation of Carbamoyl phsphate (CP) CO2 + glutamine + H2O + 2ATP Carbamoyl phosphate synthaseⅡ (CPSⅡ) O H2N C O ~ PO32- carbamoyl phosphate + 2ADP + Pi The diffirents between Carbamoyl phosphate 氨基甲酰磷酸合成酶 I、II 的区别 synthaseⅠ,Ⅱ CPS-I Location 分布 Mitochondria of 肝细胞线粒体中 liver cells 氨3 NH Source 氮源 of nitrogen 变构激活剂 Activator N-乙酰谷氨酸 N-acetylglutamate 功能 Function 尿素合成 Formation of urea CPS-II cytosol of all 胞液(所有细胞) cells Glutamine 谷氨酰胺 无 None Formation 嘧啶 合成of pyrimidine 2. Formation of UMP O H2 N C O ~ PO32- + Aspartate carbamoyl phosphate Carbamoyl aspartate Orotate PRPP UMP 3. Synthesis of CTP, dTMP or TMP UMPK UDP ATP ADP CTP synthase NDK ATP UTP ADP Gln ATP Glu ADP dUDP dCMP dTMP dUMP TMP synthase Regulation of de novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides ATP + CO2+ glutamine + Carbamoyl phosphate 1. Activated by substrates 2. Inhibited by products aspartate - Carbamoyl aspartate + PRPP UMP UTP - Purine nucleotides ATP + 5-phosphate ribose - Pyrimidine nucleotides CTP - Salvage pathway of pyrimidine nucleotides Uracil + PRPP Uracil phosphate ribosyltransferase Uracil + 1-phosphoribose UMP + PPi Uridine phosphorylase UMP +ADP Uridine kinase Uracil ribonucleoside + ATP UMP +ADP Degradation of pyrimidine nucleotides nucleotide Nucleotidase nucleosides Nucleoside phosphorylase phosphoribose pyrimidine Cytosine Thymine NH3 Uracil β-ureidoisobutyrate dihydrouracil H2O H2O + CO2 + NH3 + β-alanine β-aminoisobutyrare liver Acetyl CoA Succinyl CoA Urea TAC TAC Glucose Excreted in urine Deoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis Ribonucleotide reductase dNDP NDP kinase dNDP + ATP dNTP + ADP Biosynthesis of NDP and NTP AMP Kinase ATP XMP ADP Kinase YTP ADP YDP Kinase ATP XDP ADP Kinase YTP ATP YDP XTP Section 10.3 Dysmetabolism of nucleotides and antimetabolites Dysmetabolism of nucleotides Caused by the genetic defect or regulatory abnormality of some enzymes participating nucleotide metabolism. Gout:pain and tenderness, redness, warmth, and swelling in some joints Causes:too much uric acid forms crystals in joints and cause inflammation Antimetabolites The analogs of ribonucleotide metabolite intermediates synthesized artificially. Can interfere, inhibit and block the ribonucleotide metabolism. Used as drugs. Purine ribonucleotide metabolite analogs 6-mercaptopurine(6-MP) Hypoxanthine (6-MP) Pyrimidine analogs : ribonucleotide metabolite 5-fluorouracil(5-FU), (T) (5-FU) Amino acid analogs azaserine(AS) Folic acid analogs methotrexate(MTX) Nucleoside analogs: arabinosyl cytosine(ara-c), cyclo-cytidine(cyclo-c) Metabolite analogs applied to ribonucleotide reductase hydroxyurea(HU) NAD+ AMP Lipid metabolism β-Oxidation (Ketone Bodies), degradation of glycerophospholipids, cholesterol key enzymes, main steps, products synthesis of palmitic acid, triacylglycerols, glycerolphospholipids, cholesterol key enzymes, main steps, material Lipolysis, •Essential Fatty Acids, lipoproteins (classification, function) , HSL •Hyperlipoproteinemia, hypercholesterolemia, ketonemia, ketonuria, ketoacidosis reason or mechanism. Protein catabolism Nitrogen Balance, Essential Amino Acids , Complementary effect, Putrefaction, Amino acid metabolic pool, Ketogenic amino acids, Ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids. Digestion of dietary proteins, degradation of protein, deamination, decarboxylation key enzymes, main pathway, main products ALT, AST (function) •SAM, PAPS, GSH, Dopamine , creatine phosphate (function, formation) •Ammonia, One Carbon Units carrier, source, utilization •Hyperammonemia, PUK, Albinism damage, mechanism Nucleotide metabolism Function of neucleotides de novo synthesis of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides material, character, main steps, Salvage pathway of purine and pyrimidine Degradation of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides products Deoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis Homework Explain the following concepts: Essential Amino Acids, Lipolysis Amino acid metabolic pool lipoproteins Simple questions: 1. describe the source, transport and metabolic pathway of ammonia. 2. what do you know about ketoacidosis?