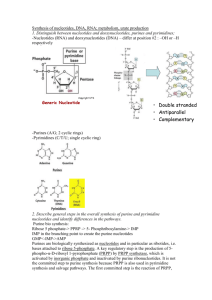
Pyrimidine and purine
advertisement

Pyrimidines and Purines Eric Niederhoffer, Ph.D. SIU-SOM Outline • Pyrimidine and purine synthesis • Pyrimidine and purine salvage/degradation • Pathway disorders Pyrimidine and Purine Synthesis HCO3- + Gln R5P CPSII RPK CP Asp PRPP Oro UMPS Gln Gly UMP UTP CDP N10fTHF CO2 Asp dCDP dUMP N5,N10-mTHF TS dTMP RNA DNA IMP GDP ADP RR dGTP dATP Pyrimidine and Purine Salvage UTP CDP dCDP IMP dUMP N5,N10-mTHF TS RR GDP dTMP ADP RR dGTP UMP TMP UTPT RNA DNA U T PRPP HGPT A G adenosine ADA inosine PNP PRPP HX XO APT urate X XO dATP Pathway Disorders Rare autosomal recessive disorders • UMP synthase – deficiency in either orotate • • • phosphoribosyltransferase or OMP decarboxylase leads to hereditary orotic aciduria, megaloblastic anemia appearing weeks to months after birth that does not respond to cobalamin, folic acid, or iron, orotic crystalluria and nephropathy, cardiac malformations, strabismus, and recurrent infection. Urine orotic acid overexcretion. Enzyme assay of RBC. Treatment with oral uridine. Adenosine deaminase – (Severe combined immunodeficiency disorder) variety of clinical phenotypes, history of infections, diarrhea, dermatitis, and failure to thrive, ribs and vertebrae abnormalities (defects in cartilaginous structures). Lymphopenia, B and T cell production affected. Enzyme assay of RBC/WBC. Treatment by bone marrow/stem cell transplantation or enzyme replacement. Purine nucleotide phosphorylase – (Immunodeficiency) lymphopenia, thymic deficiency, recurrent infections, and hypouricemia, developmental delay, ataxia, or spasticity. T cell production affected. Enzyme assay of RBC, lymphocytes, fibroblasts. Treatment by bone marrow/stem cell transplantation. Adenine phosphoribosyl transferase – frequent infections, renal colic, renal failure. Elevated urine levels of 2,8dihydroxyadenine, 8-hyroxyadenine, and adenine; serum uric acid normal. Enzyme assay. Treated with dietary purine restriction, high fluid intake, and avoidance of urine alkalinization, Allopurinol to prevent oxidation of adenine. Pathway Disorders X-linked recessive disorder • Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase – (Lesch-Nyhan syndrome) usually presents at 3 to 12 months with orange sandy urine precipitate, dystonia, intellectual disability, self-mutilation (lips, tongue, fingers), and gout. Elevated serum and urine uric acid levels. Enzyme assay on RBC, lymphocytes, fibroblasts. Molecular genetics of gene. Treated supportively with low-purine diet, allopurinol, and plenty of hydration.