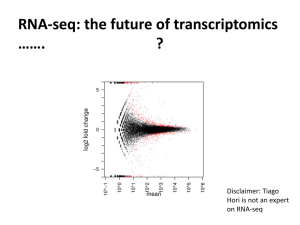
Transcriptome Profiling in Human Congenital Heart Disease
advertisement
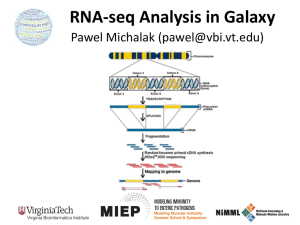
Transcriptome Profiling of Human Cardiac Tissues in Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Karl D. Stamm, MS Donna K. Mahnke, MS; Mary A. Goetsch, MS; D. Woodrow Benson, MD, PhD; Xing Li, PhD; Aoy Tomita-Mitchell, PhD; Timothy J. Nelson, MD, PhD; James S. Tweddell, MD; Michael E. Mitchell, MD September 2013 Research Update Overview • Medical Research • Trouble with humans • Rare diseases are common in a large enough population • Next-Generation Sequencing Tech • Illumina HiSeq methodology • Differential expression • Further Mining • Principle components analyses • Gene profiles and the self-organizing-map Trouble with Humans • Small sample sizes • Low statistical power • High interpersonal variability • Ethnic backgrounds imply metabolic differences • Phenocopy • Multiple distinct diseases showing identical presentation • Confounds clustering or association studies • Ruins Case/Control study power • PHI – Private/Protected Health Information • Data security is paramount • Cross-disciplinary collaborations are limited • DNA is theoretically but not practically identifiable Congenital Heart Defect Incidence • Down Syndrome 1:700 live births • 50-60% have some structural heart defect • 22qD Syndrome 1:4000 live births • 75-90% have some structural heart defect • ‘Healthy’ 99:100 live births • 0.8% have some structural heart defect Proportion Explained: C.H.D. in particular Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome 1 in 40 CHD cases are HLHS 2.5 : 10000 of all births • Complex developmental disorder • 100% fatal before the invention of the Norwood Procedure 1981 • No multigenerational pedigrees • Spontaneous mutation: immune to detection by genetic linkage All sequencing costs for this study provided by Generate Reads – Illumina Tech 10 to 500 million short reads are generated in pairs, 2x50 to 2x100 bp each. http://seqanswers.com/forums/showthread.php?t=21 Align Reads to Reference • • • • Which one? NCBI #37.3 has 3.1 billion bases across 190 contiguous scaffolds UCSC hg19 has 3.2 billion bases across 163 contiguous scaffolds Haploid reference contains disease alleles and chimeric sequence like an A+B+O blood type. Image of patches modifying the CHR17 reference from 2011 according to Ensembl http://www.ensembl.info/blog/2011/05/20/accessing-non-reference-sequences-in-human/ Millions of Variants • The 1000 Genomes project found 38 million SNPs, 1.4 million short insertions or deletions, and more than 14 thousand larger deletions • The NHLBI Exome Sequencing Project targeted 22MBases across 2,440 individuals and found 563,700 variants, 82% of which were novel. They averaged 200 novel, coding mutations per person. • We find about 150-300 thousand SNVs in an exome, 10% of which are nonsynonymous • SAMTOOLS is the software of choice for variant calling relative to your reference genome. • CCG/Proline -> CTG/Leucine • HOPX is a gene known to regulate heart development! • Very common mutation RNA-Seq vs. Whole Genome 1. 2. 3. 4. Extract and purify mRNA by polyadenylation Convert spliced mRNA to DNA fragments Run standard genome sequencing on the product Result: Expression level dependent sequence coverage Image found at http://www.pacificu.edu/optometry/ce/courses/20591/armdpg3.cfm RNA-Seq Reconstructs Transcripts From the CuffLinks paper, Trapnell et al. http://www.nature.com/nbt/journal/v28 /n5/abs/nbt.1621.html Nature Biotechnology Volume: 28, Pages: 511–515 Year published: (2010) IGV – aligned reads viewer CoverageBED Simple arbitrary feature read depth counting. -Count by gene, exon, whatever BEDTOOLS : a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. http://code.google.com/p/bedtools/ Example of bad alignment Variance and mean linked by local regression - for robust parameter estimation. • Negative Binomial • Models count as ‘binomial successes until a set number of failures’ which better fits the RNA-Seq fragment generation (limited reagent) • Allows/captures the ‘overdispersion’ seen in RNA-Seq experiments. Scale the totals for compatible means Mean-Variance Connection Detection in Low Values Per-gene mean by difference ratio DESeq • Starting from 18,000 Rsids minus 1200 NA • 1000 entries p<0.05 Theme • • • • Big lists Noisy data Complex correlation Heterogeneous background Precious Tissue Samples • Collecting tissue during surgery is an extra burden placed on overloaded surgical teams. • Samples must be processed carefully to avoid degradation of sensitive molecules. • Many steps and costs prior to gene sequencing. • Collaborators have provided 35 patients’ atrial septal tissues. • Still no ethical source of healthy control. • Hope to see separation between red/notred or solid/notsolid points • Lack of discrimination in major variation dimensions • Implying uncontrolled heterogeneity dominates Therefore, more difference person to person than between subtypes Top25 Consistent Genes • Anyone know what it means when Adducin2 and HomeoboxA4 are overexpressed? Is it significant that a dehydrogenase is under-expressed? Group Profiles at Selected Dimensions Self-Organizing Map • • • • Kohonen 1990 Halfway between neural networks and k-means (horrible oversimplification) Enforced grid layout and local neighborhood similarity Data points (here 25-dimensional vectors) lay out in natural organization Stochastic - Iteration Pairwise Similarity • Co-clustering frequency determines sample similarity • Sub-clusters are identified organically Results • Lists of genes differential across conditions • Many conditions, uncertain homogeneity • List cutoff subjective • No healthy control group • We can mine these lists for pathways or biological processes • Resulting in more lists of more complex results Transcriptome Project Future Work • A few more samples are coming… Can we build a classifier? • Predict non-measured variables? Signatures of immune response point towards treatment targets. • Predict compensatory effects? Samples are taken just days after birth, but 8 months after the heart started beating. • How else we could look at this rich, unique dataset? Thanks for listening