Regulation of Body Fluid Balance
advertisement

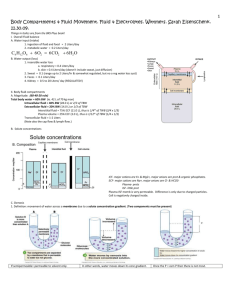
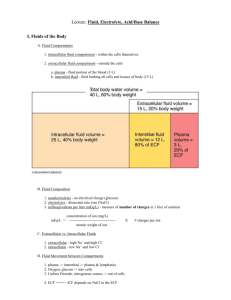
Regulation of Body Fluid Balance Osmotic Relations Between Intracellular Fluid, Interstitial Fluid and Plasma Plasma Na+ Na+ protein protein Intracellular fluid H2O Na+ K+ H2O K+ K+ Interstitial fluid Crucial points • Animal plasma membranes are so delicate that no osmotic gradient between ISF and ICF can exist. • Only impermeant solutes can act as osmotic effectors • Cytoplasmic protein is the major osmotic effector of the ICF; its osmotic effect is balanced by the transmembrane Na+ gradient, otherwise cells would swell. • Plasma proteins are the major osmoeffectors of plasma – they counteract the effect of capillary hydrostatic pressure. • Na+ is the major osmoeffector of ECF versus ICF. ECF volume closely tracks total body Na+ content. Characteristics Of ICF and ECF Compartments Intracellular Fluid Extracellular Fluid 30 L total volume 15 L total volume 9000 mOsm total solute 4500 mOsm total solute Posm = 300 mOsm 2175 mEq total Na+ [Na+] = 145 mEq/L Posm = 300 mOsm The ECF consists of the ISF compartment and the plasma compartment Extracellular Fluid 15 L total volume 4500 mOsm total solute 2175 mEq total Na+ Posm = 300 mOsm Interstitial Fluid Plasma 11.25 L total volume 3.75 L total volume 3375 mOsm total solute Posm = 300 mOsm 1125 mOsm total solute Posm = 300 mOsm There are three basic homeostatic challenges • Gain or loss of isotonic solution – Affects only the ECF volume • Gain or loss of pure water – Both ICF and ECF compartments change volume proportionately – osmotic concentration changes in each are equal • Gain or loss of pure salt – Na+ is confined to the ECF compartment – loss results in volume shift from ECF to ICF; gain results in volume shift from ICF to ECF. Regulation of Renal Function • Intrinsic • Baroreceptor Reflex • Three endocrine systems – ADH system – Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System – Atrial Natriuretic Hormone system Intrinsic regulation Blood Volume Arterial Blood Pressure GFR Intrinsic regulation + Baroreceptor reflex Blood Volume Arterial Blood Pressure Baroreceptor Reflex GFR Afferent arteriole dilates ADH system “Peripheral volume receptors” are stretch receptors located in the right atrium – increased stretch signals a plasma volume increase and exerts an inhibitory effect on ADH secretion Osmoreceptor cell bodies are in ventromedial hypothalamus – sensitive mainly to [Na+] ADH = arginine vasopressin – an octapeptide with two major peripheral effects: Increased water permeability of collecting duct Vasoconstriction (at high levels) Response of ADH system in gain of pure water Response of ADH system to loss of pure water The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System – response to loss of pure Na+ or loss of isotonic solution • Macula densa (Juxtaglomerular apparatus) secretes renin (a protease) when: – Blood [Na+] falls below normal – Glomerular blood volume flow decreases Angiotensin cascade Angiotensinogen Renin Angiotensin I Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) in lung Angiotensin II Adrenal Cortex Distal tubule (also sweat glands, salivary glands, colon, etc. Aldosterone Increased Na+ reabsorption 3 Major factors that increase Aldo secretion Increased Plasma [K+] Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone (ACTH) Angiotensin II Adrenal Cortex Aldosterone Kidney distal tubule Na+ reabsorption K+ secretion H+ secretion Aldosterone effects • Steroid hormone that increases expression of Na+/K+ ATPase in target epithelia • Directly regulates total body Na+ Indirectly regulates ECF volume. • Also involved in K+ regulation – by a direct effect on the adrenal cortex: increased plasma [K+] increases aldo secretion Atrial natriuretic peptide – response to gain of isotonic solution • Stretched atria release 22 aa peptide which – increases GFR by vasodilating renal afferent arterioles and constricting efferent arterioles – Inhibits Aldo secretion and antagonizes tubular effect of aldosterone – Inhibits ADH secretion and blocks its action • Causes marked diuresis (volume loss) and natriuresis (net loss of Na+ ) Study Goals • Be able to trace the responses of each of the 3 major renal endocrine systems to each of the 3 simple homeostatic challenges. • Integrate your understanding of these systems with what you know about the baroreceptor reflex and capillary filtration to arrive at a complete picture of whole-body responses to blood loss and plasma volume expansion – i.e. short term and long term regulation of mean arterial pressure.