this poster
A meta-analysis of QTL associated with ear rot resistance in maize
Kui Xiang
1
, GuangTang Pan
1
, Lana M. Reid
2
, ZhiMing Zhang
1
and XiaoYang Zhu
2
1 Maize Research Institute, Sichuan Agricultural University, Yaan 625014, Sichuan, P.R. China
2 Eastern Cereal and Oilseed Research Centre, Agricultural & Agri-Food Canada, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada K1A 0C6
Introduction
Maize ear rot (ER) is one of the most prevalent types of maize disease worldwide. The three predominant ER diseases, Aspergillus ear rot (AER), Fusarium ear rot
(FER) and Gibberella ear rot (GER), are responsible for the most disease-related reductions in yield and quality.
Meta-analysis is a set of statistical procedures for synthesizing research results from a number of different studies. Many studies showed that QTL meta-analyses can be used to combine results from independent published QTL studies.
Materials and methods
Fourteen studies on maize ER QTL published from 2001-
2009 were used in the current study. In these studies, the resistance of maize was measured by kernels exhibiting visible symptoms that were converted to percent of infection such as rot and mycelial growth.
QTL identified in one population evaluated in a given environment were defined as an experiment. The identified QTL were projected onto a reference map for meta-analysis. The original map position, logarithm of odds score, confidence interval and R 2 (% phenotypic variance explained by the given trait) of each QTL were used for projection. Information pertaining to all genetic maps was collected or estimated according to the published maps, then QTL in their original maps were projected on IBM2 neighbors 2008 (Intermated
B73
×
Mo17 Map) using BioMercator v 2.1 (Arcade et al.
2004). Some controversial markers between original and reference maps were deleted from the analysis to ensure the accuracy of the projection (Chardon et al. 2004).
Results and discussion
Eighty-seven initial QTL were used in the meta-analysis, which resulted in 29 consensuses ER meta-QTL (MQTL) comprising
65 initial QTL and 22 remaining individual QTL. All these MQTL occurred on all chromosomes with the exception of chromosomes 9 and 10, with two to six initial QTL on each chromosome (Table 1). Ten MQTL pooled three initial QTL, while
13 MQTL pooled two initial QTL.
Table1 Characteristics of detected meta-QTL (MQTL) for ear rot (ER) resistance
11
12
13
7
8
9
10
MQTL Chrom.
Number of
Projected
QTL
2
1 1
1
2
2
5
6
3
4
1
2
2
2
2
3
3
3
14
3
3
3
3
3
3
4
4
5
4
3
3
6
2
3
6
15 4 4
Type of ER a
FER, GER
FER, GER
GER
FER, GER
FER, GER
FER, GER
AER, FER
FER, GER
AER, FER, GER
AER, FER
AER, FER, GER
AER, FER, GER
AER, FER
AER, FER
FER, GER
26
27
28
22
23
24
25
MQTL Chrom.
Number of projected
QTL
16
17
5
5
2
3
18
19
20
21
5
6
6
6
3
2
2
2
29
6
6
7
7
7
7
7
8
4
2
3
3
2
2
2
2
Type of ER a
FER
FER, GER
AER, FER, GER
FER
FER
FER,GER
FER
AER, FER
FER
FER, GER
FER, GER
GER
GER
FER a AER = Aspergillus ear rot, FER = Fusarium ear rot, GER = Gibberella ear rot
ER in maize is mainly associated with three types (AER, FER and GER) based on the pathogen causing the ear rot. From meta-analysis, most MQTL consisted of two or three types of ER resistance. Eleven of 29 MQTL contributed to both FER and
GER on chromosomes 1 to 7, especially on chromosomes 2 and
3, suggesting that there were some common QTL/genes for FER and GER resistance in these regions.
Based on 29 MQTL, a total of 21 genes were found to be colocated within 2 cM of identified MQTL positions, located on 13
MQTL (1, 3, 4, 8, 10, 11, 14, 15, 16, 21, 22, 25 and 26).
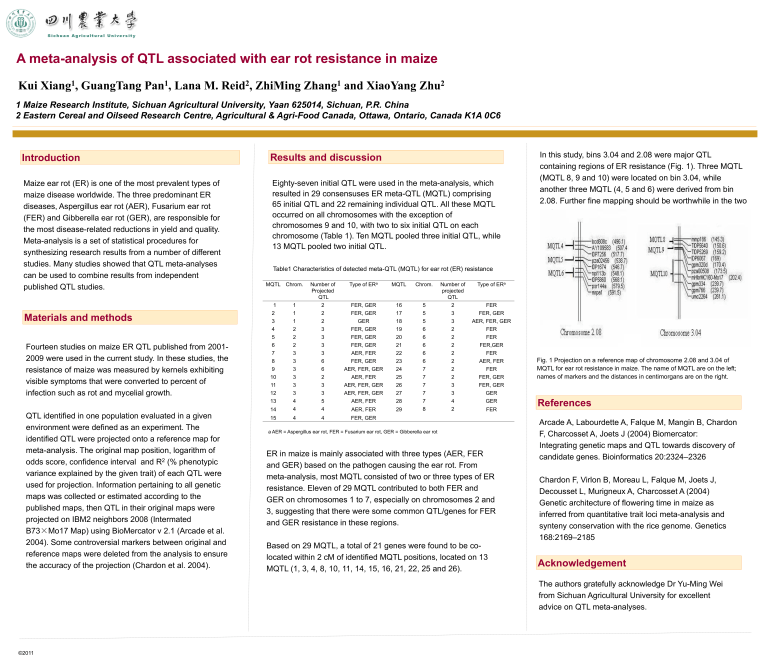
In this study, bins 3.04 and 2.08 were major QTL containing regions of ER resistance (Fig. 1). Three MQTL
(MQTL 8, 9 and 10) were located on bin 3.04, while another three MQTL (4, 5 and 6) were derived from bin
2.08. Further fine mapping should be worthwhile in the two regions.
Fig. 1 Projection on a reference map of chromosome 2.08 and 3.04 of
MQTL for ear rot resistance in maize. The name of MQTL are on the left; names of markers and the distances in centimorgans are on the right.
References
Arcade A, Labourdette A, Falque M, Mangin B, Chardon
F, Charcosset A, Joets J (2004) Biomercator:
Integrating genetic maps and QTL towards discovery of candidate genes. Bioinformatics 20:2324 –2326
Chardon F, Virlon B, Moreau L, Falque M, Joets J,
Decousset L, Murigneux A, Charcosset A (2004)
Genetic architecture of flowering time in maize as inferred from quantitative trait loci meta-analysis and synteny conservation with the rice genome. Genetics
168:2169 –2185
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr Yu-Ming Wei from Sichuan Agricultural University for excellent advice on QTL meta-analyses.
©2011