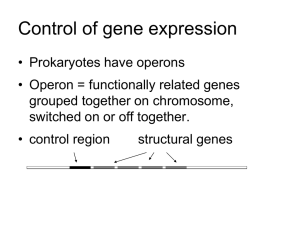
1/4 rr
advertisement

Grades Three hourly exams plus final exam (450 pts), You will have 1.5 hours to complete each exam, You will be allowed one (1) 11” x 8.5” crib sheet, both sides, for each exam, …may seem really hard. Exams - 150 points each, Final Exam cumulative. Quizzes will be given every Wednesday (total 100 pts), will cover the basics of the assigned reading (including that day's assignment), quizzes 12.5 points each, ~15 minutes, No Make-up Quizzes, absolutely no exceptions, can drop two (2) lowest quiz scores (except 1&2). Total course points - 550 …should be relatively easy. Know This… 1 1/2 1/4 1/2 1 1/2 1/2 1/4 1/2 1 Assignment: Correlate this with the observed phenotype. Mendel’s Results, F2 Dihybrid P generation cross: YYRR x yyrr F1 generation cross: YyRr x YyRr • Y_ R_ = 315 =9 • yyR_ = 108 =3 • Y_rr = 101 =3 • yyrr = 32 =1 Forked-Line Method 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 YYRR 1/4 YY 1/4 RR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/2 Yy 1/4 RR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8 YyRR 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 YyRr 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8 Yyrr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyRR 1/4 yy 1/4 RR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 YYRr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 YYrr 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 yyRr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyrr Genotypes Y--R-1/4 YY 1/2 Yy 1/16 + 1/4 RR 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 YYRR 1/2 Rr 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 YYRr 1/4 RR 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8 YyRR 1/2 Rr 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 YyRr 2/16 + 2/16 + yellow/round 4/16 = 9/16 Genotypes Y--rr 1/4 YY 1/2 Yy 1/4 yy 1/4 RR 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 YYRR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 YYRr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 YYrr 1/4 RR 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8 YyRR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 YyRr 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8 Yyrr 1/4 RR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyRR 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 yyRr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyrr Genotypes Y--rr 1/4 YY 1/4 rr 1/2 Yy 1/4 rr 1/16 + 2/16 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 YYrr 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8 Yyrr = 3/16 yellow/wrinkled Genotypes yyR-1/4 YY 1/2 Yy 1/4 yy 1/4 RR 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 YYRR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 YYRr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 YYrr 1/4 RR 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8 YyRR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 YyRr 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8 Yyrr 1/4 RR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyRR 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 yyRr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyrr Genotypes yyR-1/4 yy 1/2 Rr 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 yyRr 1/4 yy 1/4 RR 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyRR 2/16 + 1/16 = 3/16 green/round Genotypes yyrr 1/4 YY 1/2 Yy 1/4 yy 1/4 RR 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 YYRR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 YYRr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 YYrr 1/4 RR 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8 YyRR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 YyRr 1/2 x 1/4 = 1/8 Yyrr 1/4 RR 1/2 Rr 1/4 rr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyRR 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 yyRr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyrr Genotypes yyrr 1/4 yy 1/4 rr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyrr 1/16 green/wrinkled F2 via Forked Line • Y--R-- yellow/round 9/16 • Y--rr yellow/wrinkled 3/16 • yyR-- green/round 3/16 • yyrr green/wrinkled 1/16 Why use Forked-Line Method? • Based on a classic dihybrid cross (YyRr x YyRr), what is the probability that an organism in the F2 generation will have round seeds and breed true for green cotyledons? OK? YR Yr YR Yr yR yr YYRR YYRr YyRR YyRr YYRr YYrr YyRr Yyrr YyRR YyRr yyRR yyRr YyRr Yyrr yyRr yyrr yR yr 3/16 p = 0.1875 Better 1/4 yy 1/4 RR 1/2 Rr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyRR 1/4 rr 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16 yyrr 3/16 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/8 yyRr p = 0.1875 Best (?) 1/4 yy 3/4 R_ Sum Law: 1/4 RR + 1/2 Rr 1/4 x 3/4 = 3/16 yyR_ Forked-Line Method (phenotypes) 3/4 yellow 1/4 green 3/4 round 9/16 yellow round 1/4 wrinkled 3/16 yellow wrinkled 3/4 round 3/16 green round 1/4 wrinkled 1/16 green wrinkled Example P Rr YY x rrYy Probability Rr YY in offspring; 1/2 Rr 1/2 rr 1/2 YY 1/2 Yy 1/4 RrYY Example P Rr Yy x RRYy Probability of Rr Yy in offspring; 1/2 Yy 1/4 YY 1/4 yy 1/2 Rr 1/2 RR 1/4 RrYy Using Probability Lecture 3 Example YYSs x YySs YY x Yy Independent Assortment Ss x Ss gametes YY or Yy .5 .5 (p) Y_ = 1 SS Ss ss .25 .5 .25 Random Segregation probability (p) S_ = .75 Product Rule: (p) Y_S_ = .75 (p) ss = .25 Product Rule: (p) Y_ss = .25 Humans ? • Is it possible to ascertain the mode of inheritance of genes in organisms where designed crosses and the production of large numbers of offspring are not practical? Pedegree: an orderly diagram of a families relevant genetic features. Assignment: figure out this pedigree. Albinism is a recessive trait in humans. From Previous Page Assignment: figure out this pedigree. Symbols More Symbols And more… 2 Where Do you Start? Aa Aa or AA Aa Aa aa aa aa Recessive Trait? or Dominant Trait? What More Can You Say? Aa Aa or AA Aa Aa aa aa aa Recessive Trait Predictions What if you were a genetic counselor? What are the odds that this individual carries the trait? Predictions What if you were a genetic counselor? What are the odds that this individual carries the trait? Conditional Probability Aa Aa ? 1/4 AA Monohybrid Cross 1 1/4 Aa : 1 1/4 Aa : 1/4 aa 1 (p)Aa = 2/3 = .66 Conditional Probability …is the probability of an event occurring given that another event also occurs... P(event) without the condition p(condition) Conditional Probability Example: With a 6-sided die, what is the probability of rolling a 2, given that an even number is rolled on the die: p(2 roll | even #) = p(2 roll | even #) = = p(2 roll) p(even#) 1/6 1/2 1/3 probability without the condition probability of the condition Aa Aa ? p(probability of being a heterozygote) = 1/2 p(probability of A_) = 3/4 p( heterozygous | A_ ) = 1/2 3/4 = 2/3 Conditional Probability p(A|B) = p(event) without the condition • Use the formula, p(condition) • Or use a Punnett Square, • Or... 1/4 AA 1 1/4 Aa : 1 1/4 Aa : 1 1/4 aa A a A AA Aa a Aa aa Kidney Disease If 1 and 2 had an offspring, what is the probability that their first kid would show the phenotype? A Simplification • Unless otherwise specified (or the pedigree suggests otherwise), the traits that we will track will be rare, • We will assume a p = 0 that a non-familial mate carries the trait. Kidney Disease • non-familial mates: from outside of the family, • if k is the recessive trait, then these individuals are KK. Kidney Disease If 1 and 2 had an offspring, what is the probability that their first kid would show the phenotype? p(P1) heterozygous x p(P2) heterozygous x p(FF) homozygous recessive 1/2 x 1 x 1/4 = 1/8 = .125 Kidney Disease If 1 and 2 had an offspring, what is the probability that the first kid would be a boy, and show the phenotype? Kidney Disease And, what is the probability that this boy is a carrier? If 1 and 2 had an offspring, what is the probability that the first kid would be a boy, and show the phenotype? p(P1) heterozygous p (boy) x p(P2) heterozygous x p(FF) homozygous recessive 1/2 x 1 x 1/4 x 1/2 = 1/16 Practice #1 Round (R) and Yellow (Y) are dominant. Practice #2 Practice #3 Questions • Don’t rely on the answers in the back of the book to solve your problems… • Don’t just solve them, but understand the principles needed to solve them. a b f c e d Assignments • Read from Chapter 3, 3.6 (pp. 100-105), • Master Problems…3.12, 3.15, 3.20, • Chapter 4, Problems 1, 2, • Questions 4.1 - 4.4, 4.6, 4.7, 4.9, 4.11 - 4.14, 4.16, 4.19 - 4.20.