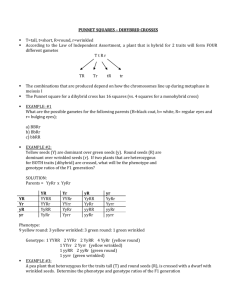
Important Vocabulary
Important Vocabulary
Genotype Phenotype
There are exceptions
to these rules that will
be discussed
Two alleles make up one genotype
Alleles are either dominant or recessive
Important Vocabulary
Genotypes are heterozygous or
homozygous
HH – homozygous dominant
Hh – heterozygous
hh – homozygous recessive
Gregor Mendel developed
many of the principles of
genetics during his research
on pea plants
Monohybrid Cross
A cross between parents that are homozygous
for different alleles of one trait
Complete Dominance – the dominant allele
is completely dominant over the recessive
allele
#1 - Complete Dominance
P:
F1:
RR rr
Genotype
Phenotype
Rr
red
F1 Cross:
Rr Rr
Punnett Square: R
r
F2:
R
RR
Rr
r
Rr
rr
Genotype
RR
Rr
Rr
rr
Type of Genotype
heterozygous
F2 Genotypic Ratio:
1 RR : 2 Rr : 1 rr
F2 Phenotypic Ratio:
3 red: 1 white
Phenotype
red
red
red
white
Type of Genotype
homozygous
heterozygous
heterozygous
homozygous
Monohybrid Cross
A cross between parents that are homozygous
for different alleles of one trait
Incomplete Dominance – the dominant and
recessive allele blend together
#4 - Incomplete Dominance
P:
F1:
RR rr
Genotype
Phenotype
Rr
pink
F1 Cross:
Rr Rr
Punnett Square: R
r
F2:
R
RR
Rr
r
Rr
rr
Genotype
RR
Rr
Rr
rr
Type of Genotype
heterozygous
F2 Genotypic Ratio:
1 RR : 2 Rr : 1 rr
F2 Phenotypic Ratio:
1 red: 2 pink : 1
Phenotype
red
pink
pink
Type of Genotype
homozygous
heterozygous
heterozygous
homozygous
Monohybrid Cross
A cross between parents that are homozygous
for different alleles of one trait
Codominance – both alleles are equally
dominant
#7 - Codominance
P:
F1:
RR WW
Genotype
Phenotype
RW
red &
F1 Cross:
RW RW
Punnett Square: R
W
R
W
F2:
RR
Type of Genotype
heterozygous
RW F2 Genotypic Ratio:
RW WW
Genotype
RR
RW
RW
WW
1 RR : 2 RW : 1 WW
F2 Phenotypic Ratio:
1 red : 2 red &
Phenotype
red
red &
red &
:1
Type of Genotype
homozygous
heterozygous
heterozygous
homozygous
Dihybrid Cross
A cross between parents that are homozygous
for different alleles of two traits
Complete Dominance
#8 - Complete Dominance
P:
F1:
yyrr YYRR
Genotype
Phenotype Type of Genotype
YyRr
yellow/round heterozygous
YR
Yr
yR
yr
F1 Cross:
YyRr YyRr
Punnett Square:
YR YYRR YYRr YyRR YyRr
YyRr
Yyrr
yR YyRR YyRr yyRR
yyRr
Yr
F2:
Genotype
9 Y_R_
3 Y_rr
3 yyR_
1 yyrr
YYRr
yr YyRr
Phenotype
yellow/round
yellow/wrinkled
green/round
green/wrinkled
YYrr
Yyrr
yyRr
yyrr
Additional Crosses
Sex Determination
Sex Linkage
ABO Blood Typing
#11 - Sex Determination
P:
XY XX
X
X
X
XX
XX
Y
XY
XY
Ratio:
1 XX : 1 XY
Sex Linkage
Sex linked genes are located on either
the X or Y chromosome
Most sex linked genetic disorders are
X-linked
X-Linked Genetic Disorders
Normal
XAXA
Carrier
XAXa
Affected
XaXa
XAY
XaY
#12 - Sex Linkage
P:
XHY XHXh
Punnett Square:
XH
Xh
XH XHXH XHXh
Y
F1:
Genotype
XHXH
XHXh
XHY
XhY
XHY
XhY
Phenotype
normal
carrier
normal
hemophilia
Sex
F
F
M
M
Type of Genotype
homozygous
heterozygous
hemizygous
hemizygous
ABO Blood Typing
ABO Blood Typing
% of Blood Types in U.S. Caucasions
B+
9%
B2%
A6%
O+
38%
A+
34%
AB- AB+
1% 3%
O7%
ABO Blood Typing
RECIPIENT
A
D
O
N
O
R
A
B
Y
B
O
Y
Y
AB
O
AB
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
#15 - Blood Typing
P:
I Ai I Bi
Punnett Square:
IB
F1:
i
IA
I AI B
I Ai
i
I Bi
ii
Genotype
IAIB
I Ai
I Bi
ii
Phenotype
AB
A
B
O
Polygenic
Inheritance
Examples:
Skin/Eye/Hair Color,
Height/Body Shape,
Rh (+/- Blood), etc.
Most human traits are
polygenically inherited
Pedigrees
Pedigrees
Normal
Affected
Carrier
Pedigrees
Example:
You are a normal female (homozygous). Both of your
parents are normal. Your younger brother is normal
and your older brother has hemophilia.
XHXh
XhY
XHY
XHY XHXH
You!
#18 - Pedigrees
XCXC
XcY
XCY
XCXc
XCY
XCXC
XCXc
XcY
You!
XCY
Chromosome Mapping
Chromosome
Map
8
%
9%
8
%
9%
#19 - Chromosome Mapping
Gene
Gene
A
B
C
D
E
A
-
8
12
4
1
B
8
-
4
12
9
C
12
4
-
16
13
D
4
12
16
-
3
E
1
9
13
3
-
3 1
D
8
EA
4
B
16
C
Recombinations
per 100
fertilized eggs