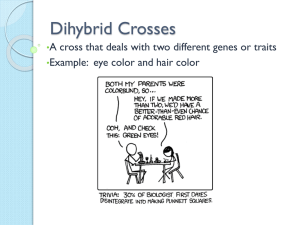
How to make a punnett square
advertisement

A step by step method What is a punnett square? A punnett square is a diagram used to try to predict the outcome of a cross between 2 parents. It does not tell us what will happen, but it does tell us the likelihood that something will happen. Monohybrid crosses These are crosses that only look at a single trait Ex: hair color, eye color, albinism Ex: What are the chances that my baby will have brown eyes? Step 1 Draw a box and divide it into 4 squares. These squares represent the possible offspring Step 2 Determine the genotypes of the parents. ____x_____ Place the alleles for the genotypes of the parents on the sides and top of the square. As a general rule, we put the dad on the top and the mom on the side. R r r R Step 3 Now you multiply the sides with the top to get the genotype of the 4 offspring boxes. R R r Rr Rr r Rr Rr Step 4 Now you can see what the genotypes of the offspring would be. In this case there is a 100% chance of the offspring being heterozygous for the trait because all 4 out of 4 boxes are capital, lower case. R R r Rr Rr r Rr Rr Ratios Genotypic Ask your self: How many homozygous dominants? How many heterozygous? How many homozygous recessives? Phenotypic Ask yourself: How many dominant phenotypes? How many recessive phenotypes? Let’s Practice Homozygous (HO) or Heterozygous (HE) AA ____ HO Bb ____ HE HE Cc ____ HE Dd ____ Ee ____ HE ff ____ HO HO GG ____ HO HH ____ Determine Phenotype Purple flowers are dominant to white flowers Brown eyes are dominant to blue eyes Purple PP _____________ Purple Pp _____________ White pp _____________ Brown BB ____________ Brown Bb ____________ Blue bb ____________ For each phenotype list the genotype Straight hair is dominant to curly. Pointed heads are dominant to round heads. SS PP ____________ straight ____________ pointed ____________ straight ____________ pointed Ss Pp ss pp ____________ curly ____________ round Problem #1 Step 1 Draw punnett square In pea plants, spherical seeds (S) are dominant to dented seeds (s). In a genetic cross of two plants that are heterozygous for the seed shape trait, what fraction of the offspring should have spherical seeds? Problem #1 Determine the genotype of parents, and place alleles on punnett square In pea plants, spherical ________ Ss x ________ Ss Step 2 s S S seeds (S) are dominant to dented seeds (s). In a genetic cross of two plants that are heterozygous for the seed shape trait, what fraction of the offspring should have spherical seeds? s Problem #1 Multiply sides to get possible offspring seeds (S) are dominant to dented seeds (s). In a genetic cross of two plants that are heterozygous for the seed shape trait, what fraction of the offspring should have spherical seeds? Ss x ________ Ss ________ S s s In pea plants, spherical Ss ss S Step 3 SS Ss Problem #1 Step 12 punnett square Interpret theParent possible offspring Step4 3Draw Multiply Determine genotypes SpongeBob SquarePants recently r r met SpongeSusie Roundpants at a ________ rr Rr x ________ dance. SpongeBob is heterozygous for his square shape, but R r SpongeSusie is round (recessive). What is the ratio of round to Rr rr square pants? 2:2 Rr rr Dihybrid crosses Dihybrid crosses are punnett squares used to predict the probability of an offspring having 2 traits at the same time. Ex: What are the chances of my baby having brown eyes AND blond hair. Step 1 Draw a box and divide it into 16 squares. Step 2 Determine the genotypes of the parents Ex: cross two pea plants that are heterozygous for yellow peas and round peas. Yellow is dominant to green and round is dominant to wrinkled. YyRr x YyRr Step 3 Determine all of the possible gamete combinations for each parent by using the F.O.I.L. or Gremlin method FOIL= first, outside, inside last Ex: YyRr First- YR Outside- Yr Inside- yR Last- yr Gremlin YyRr Step 4 Write all of the possible YR combinations of alleles on the sides and top of YR the punnett square. YR Yr Yr yR yR yr yr Yr yR yr Step 5 Do the cross Remember to keep all of one letter together and all of the 2nd letter together. YR Yr yR yr YR YYRR YYRr YyRR YyRr Yr YYRr YYrr YyRr Yyrr yR YyRR YyRr yyRR yyRr yr YyRr Yyrr yyRr yyrr Step 6 Go through the results and determine what the phenotype of each offspring would be Yr yR yr YYRR YYRr YyRR YyRr Yellow round Yellow, round Yellow, round Yellow, round YYRr YYrr YyRr Yyrr Yellow, round Yellow,w rinkled Yellow, round Yellow, wrinkled YyRR YyRr yyRR yyRr Yellow, round Yellow, round Green, round Green, round YyRr Yyrr yyRr Yyrr Yellow, round Yellow, wrinkled Green, round Green, wrinkled YR YR Yr yR yr Step 7 Figure out the phenotypic ratio or answer whatever question they ask you. 9:3:3:1 Example: what are the chances of having a yellow and wrinkled pea? 3/16 Yr yR yr YYRR YYRr YyRR YyRr Yellow round Yellow, round Yellow, round Yellow, round YYRr YYrr YyRr Yyrr Yellow, round Yellow,w rinkled Yellow, round Yellow, wrinkled YyRR YyRr yyRR yyRr Yellow, round Yellow, round Green, round Green, round YyRr Yyrr yyRr Yyrr Yellow, round Yellow, wrinkled Green, round Green, wrinkled YR YR Yr yR yr Let’s Practice Determine the gametes for the following cross: heterozygous tall plant with heterozygous yellow seeds with another of the same genes. Tall and yellow are dominant F.O.I.L TtYy First-TY Outside- Ty Inside- tY Last- ty Gremlin TtYy Problem #4 5 6 Fill Analyze inpunnett results square Step square Step137 and 4the Determine gametes and place on square 2Draw Determine Answer question(s) genotypes In horses, black is dependent upon a bt bt bt bt dominant gene (B), and chestnut ________ x ________ BBTT bbtt color upon its recessive allele (b). BT BT BT BT The trotting gait is due to a BbTt BbTt BbTt BbTt dominant allele, (T), the pacing gait chestnut, chestnut, chestnut, chestnut, to its recessive allele, (t). trotting Bb trotting trottingBbtrotting BbTt BbTt BbTt BbTt Cross a homozygous black, chestnut, chestnut, chestnut, chestnut, homozygous trotting horse with a trotting trotting trotting trotting chestnut, pacing horse. BbTt BbTt BbTt BbTt chestnut, trotting Bb chestnut, Bbchestnut, trotting chestnut, trotting trotting BbTt BbTt BbTt BbTt chestnut, trotting chestnut, trotting chestnut, trotting chestnut, trotting What percentage of offspring could be chestnut and pacing? 0% Problem #5 5 6 Fill Analyze inpunnett results square Step square Step137 and 4the Determine gametes and place on square 2Draw Determine Answer question(s) genotypes Suppose the alpha male and alpha nb nB Nb NB female of a wolf pack are black with ________ x ________ nnbb NnBb blue eyes and normal colored with brown eyes, respectively. Assume nb nb nb nb further that normal coat color (N) is NnBb NnBb NnBb NnBb normal, normal, normal, normal, dominant to black (n) and brown brown brown brown Bb brown Bb eyes (B) are dominant to blue (b). Nnbb Nnbb Nnbb Nnbb normal, normal, normal, normal, The female is also heterozygous for blue blue blue blue both traits. nnBb nnBb nnBb nnBb Bb Bb black, black, black, black, What fraction of the offspring brown brown brown brown could have the following nnbb nnbb nnbb nnbb genotypes? black, black, black, black, blue NNBB: 0/16 NnBb: 4/16 nnbb: 4/16 blue blue blue Problem #6 fs fS Fs FS Fill inpunnett square Step square Step135 and 4the Determine gametes and place on square 2Draw Determine genotypes Carrion beetles lay their eggs in dead animals and then bury them ________ x ________ FfSs FfSs in the ground until they hatch. FS Fs fS Assume that the preference for fs FFSS FFSs FfSS FfSs fresh meat (F) is dominant to the fresh, fresh, fresh, fresh, shallow shallowBbshallow preference for rotted meat and that shallow Bb the tendency to bury the meat FFSs FFss FfSS fresh, fresh, fresh, shallow (S) is dominant to the shallow deep shallow tendency to bury the meat deep. Bb Bb Suppose a female and male carrion beetle heterozygous both traits mate. What is the phenotypic ratio? Problem #6 Step 7 5 Answer 6 Fill in thequestion(s) Analyze results square Carrion beetles lay their eggs in dead fs What is the phenotypic ratio? fS Fs FS animals and then bury them in the ________ FfSs x ________ FfSs ground until they hatch. Assume that the preference for fresh meat (F) is FS Fs fS fs dominant to the preference for rotted FFSS FFSs FfSS FfSs meat and that the tendency to bury the fresh, fresh, fresh, fresh, shallow Bb shallow shallowBbshallow meat shallow (S) is dominant to the tendency to bury the meat deep. FFSs FFss FfSS Ffss fresh, fresh, fresh, fresh, Suppose a female and male carrion shallow deep shallow deep beetle heterozygous both traits mate. FfSS FfSS ffSS ffSs fresh, shallow Bb fresh, Bbrotted, shallow rotted, shallow shallow FfSS Ffss ffSs ffss fresh, shallow fresh, deep rotted, shallow rotted, deep Fresh/shallow: fresh/deep: rotted/shallow: rotted/deep 9:3:3:1