Test Crosses & Dihybrid Crosses
advertisement

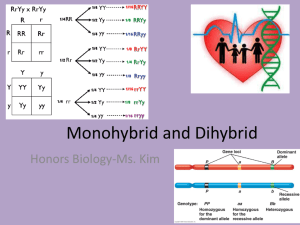
Test Crosses & Dihybrid Crosses • Y=yellow, y=green, R=round, r=wrinkled • According to the Law of Independent Assortment, a plant that is hybrid for 2 traits will form FOUR different gametes YyRr YR Yr yR yr Independent assortment and Segregation.. • Possible gametes Dihybrid Cross • EXAMPLE: #1 • What are the possible gametes for the following parents (B=black coat, b= white, R= regular eyes and r= bulging eyes); • a) BBRr • b) BbRr • c) bbRR Mendel used Peas again: Character Traits Alleles Seed coat Round R RRYY Round Yellow Wrinkled r RRYy Round Yellow RRyy Round Green Cotyledon colour Genotypes Phenotypes Yellow Y RrYY Round Yellow Green y RrYy Round Yellow Rryy Round Green rrYY Wrinkled Yellow rrYy Wrinkled Yellow rryy Wrinkled Green The expected probability of each type of seed can be calculated: Probability of an F2 seed being round = 75% or ¾ Probability of an F2 seed being wrinkled = 25% or ¼ Probability of an F2 seed being yellow = 75% or ¾ Probability of an F2 seed being green = 25% or ¼ Therefore, Probability of an F2 seed being round and yellow = = = 56.25% Probability of an F2 seed being round and green = = = 18.75% Probability of an F2 seed being wrinkled and yellow = = = 18.75% Probability of an F2 seed being wrinkled and green = = = 6.25% Probabilities… From this we can predict how many seeds we could expect to get in a sample: In 556 seeds we could expect: 556 x round yellow 556 x round green 556 x wrinkled yellow 556 x wrinkled green = 313 = 104 = 104 = 35 NOTICE: HETEROZYGOUS CROSS HAS RATIO OF 9:3:3:1 • Was the inheritance of one character affected by the inheritance of another? It appears that the inheritance of seed shape has no influence over the inheritance of seed colour. The two characters are inherited INDEPENDENTLY. The pairs of alleles that control these two characters assort themselves independently = Mendel's Second Law, THE LAW OF INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT. EXAMPLE #2: • A pea plant that heterozygous for the traits tall (T) and round seeds (R), is crossed with a dwarf with wrinkled seeds. Determine the phenotype and genotype ratios of the F1 generation • • • • P: _________________________ P phenotype: ______________________ Gametes: __________________________ F1: TR tr Tr tR tr EXAMPLE #3: • Yellow seeds (Y) are dominant over green seeds (y). Round seeds (R) are dominant over wrinkled seeds (r). If two plants that are heterozygous for BOTH traits (dihybrid) are crossed, what will be the phenotype and genotype ratios of the F1 generation? • • • • P: _________________________ P phenotypes: _______________________________ Gametes: ____________________________________ F1 YR YR Yr yR yr Yr yR yr • A cross between an individual exhibiting the dominant phenotype of a trait and an individual that is homozygous recessive for that trait in order to determine the genotype of the dominant individual. • Recall: A dominant phenotype can be either homozygous dominant (HH) or heterozygous (Hh) ONE PARENT IS ALWAYS HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE!!!!!! Test crosses • When a dominant phenotype is crossed with a homozygous recessive any hidden traits can be revealed • We can determine the genotype of the unknown parent by looking at the ratios expressed in the offspring • If the parent is PP then the phenotype of all the offspring; • Will be ALL purple Possible outcomes…Mono • If the parent is Pp then the phenotype of all the offspring; • Will be purple and white Possible outcomes…Mono Example • Character: Coat colour in mice Traits Alleles Genotypes Phenotypes Grey G GG Grey White g Gg Grey gg White • Grey mice could have one of two different genotypes, GG or Gg. • If they are crossed with a white mouse (gg) these genotypes will give two different results. Homozygous Phenotypes Grey Genotypes GG Gametes G v Heterozygous White Grey gg G g v White Gg g G gg g g Genotypes Phenotypes Grey Proportions 100% White 0% Grey 50% White 50% g • In monohybrid crosses, to know if a dominant trait is homozygous (RR) or heterozygous (Rr) it is necessary to carry out a test cross. This is done with a homozygous recessive (rr) individual. The same is true for a dihybrid cross where the test cross is made with an individual which is homozygous recessive for both characters (rryy). Dihybrid test cross… • Possible outcomes • • • • Parent YYRR all offspring are yellow and round Parent YyRR offspring will be yellow or green AND all round Parent YYRr offspring will be all yellow AND round or wrinkled Parent YyRr offspring will be yellow or green AND round or wrinkled • PARENT YYRR Offspring all yellow/round • PARENT YyRR yr YR yR YyRr yyRr Offspring: yellow/round or green/round • PARENT YYRr yr YR Yr YyRr Yyrr Offspring: yellow/round or yellow wrinkled • PARENT YyRr x yyrr OFFSPRING: Yellow/round, yellow/wrinkled, green round, green wrinkled • When doing an example test cross; 1. State your variable designation 2. Write down your predicted genotype 3. Do a Punnet square to prove your prediction 4. Write a statement • Ex. In the “chocolate moose” brown fur is dominant to yellow fur and round ears are dominant to pointed ears. If a brown and round eared moose is test crossed and the offspring are as follows, what were the genotypes of the original parent? 5 brown round 2 yellow round 2 brown pointed 1yellow pointed • In a test cross to determine whether a fruit fly is homozygous (WW) or heterozygous (Ww) for long wings, 7 long-winged flies & 1 short winged-fly are produced. Which is a valid conclusion? • • • • A. the unknown fruit fly is WW B. the unknown fruit fly is Ww C. the unknown fruit fly is ww D. more offspring are needed • In hamsters, long tails (L) are dominant to short tails (l). A student wishes to perform a test cross to determine whether a female long-tailed hamster is homozygous or heterozygous for long tail length. She mates the hamster with a male long-tailed hamster & studies the offspring, which are 100% long-tailed. She conclude that the female hamster's genotype is "LL". What mistake(s) did the student make? • A. she should have mated the female hamster with a male that was known to be hybrid • B. she should have mated the female hamster with a shorttailed male hamster • C. she should have mated the female hamster with another long-tailed female • D. she has to mate members of the litter before she can make a conclusion In Border Collies, black coat (B) is dominant to red coat (b). A breeder has a black male that has won numerous awards. The breeder would like to use the dog for breeding if he is purebred or BB. To learn this information, she testcrosses him with a red female (bb). Answer the following questions A, B, C, and D. A. If the black male is BB, what kind of gamete (sperm) can he produce? Only _________ B. If the red female is bb, what kind of gamete (eggs) can she produce? Only __________ C. If the black male is Bb, what kind(s) of gametes (sperm) can he produce? Either _______ or ______ D. If any of the puppies are red, what is the father's genotype? Only __________