Document
advertisement

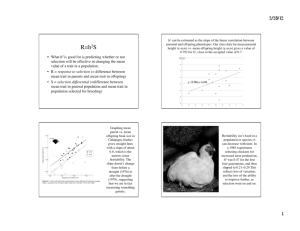
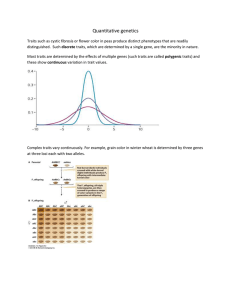
Quantitative Genetics • Theoretical justification • Estimation of heritability – Family studies – Response to selection – Inbred strain comparisons • Quantitative trait loci (QTL) • Genetic correlations Most traits follow a normal distribution When multiple genes affect a trait, expect a continuous distribution But, the environment also contributes variation Isogenic line of Drosophila Quantitative genetics • Partitions genetic and environmental effects • Assumptions – Each locus contributes additively to the trait – Environmental effects are independent • Definitions: – – – – – p = phenotypic value g = genotypic value a = additive genetic value (breeding value) e = environmental effect d = dominance deviation • p = g + e and g = a + d, so p = a + d + e a mean e Trait value p Dominance No dominance = additive • Exists whenever the phenotype of a heterozygote is not the average of the parental values • Attribute of a genotype, not an allele • May be scale dependent • Only relationships which can share genotypes can share dominance, e.g. full-sibs, twins aa Aa AA Complete dominance aa Aa AA Overdominance aa Aa AA Heritability • Vp = Vg + Ve = Va + Vd + Ve • heritability = h2 = Va/Vp, i.e the fraction of phenotypic variation due to additive genetic effects, i.e. those which can be passed from parent to offspring • applies only to population measured • determines the rate of evolution Galton’s parent-offspring regression Note: median offspring values regress toward the parental median h2 = heritability = slope of the regression of midoffspring on midparent The regression estimate of heritability h2 from family resemblance • Offspring and mid-parent: b = Va/Vp = h2 – b is a regression slope • Offspring and one parent: b = Va/2Vp = h2/2 • Full-sibs (r = 1/2): t ≥ Vg/2Vp = h2/2 • Identical (MZ) twins: t ≥ Vg/Vp = h2 • Half-sibs (r = 1/4): t = Va/4Vp = h2/4 – t is a correlation coefficient • Therefore: resemblance (b or t) = rh2 where r = degree of relatedness Example: 2 h estimates for IQ Can the environment alter expression of a trait when h2 = 0.5? French IQ experiment h2 from Artificial Selection h2 = 0 h2 = 1/4 h2 = 1 Response to selection R = h2S is the breeder’s equation where R = the change in means across a generation h2 = heritability S = the change in means within a generation due to selection Response to selection = trait evolution S R Selection for nest building behavior 2 h from inbred strains • Inbreeding leads to genetic uniformity • Ve = variation within an inbred strain or among the F1 progeny • Vp = variation among F2 progeny • h2 “broad sense” = (VF2 - VF1)/VF2 Avoidance learning by inbred strains Heritabilities in Drosophila Note: life history traits tend to have low heritabilities, presumably because selection reduces genetic variation, but almost all traits have some heritable variation QTL analysis •Much current work aims to locate and estimate the effect of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) •Use F2 or backcross individuals •Genotype each individual at multiple genetic markers •Construct linkage map •Measure association between markers and trait Correlated response to selection Troy Bartlett Genetic correlations • Multiple potential causes – – – – Physical linkage (proximity of two loci) Pleiotropy Selection for allelic combinations Nonrandom mating • Persistance – Pleiotropy decays only by mutation – Linkage decays with random mating due to recombination • Can alter response to selection – Negative genetic correlation will cause one trait to become reduced when another is increased – Expect such neg. correlations for life history traits Sample problem • A population of sunfish has an average swimming speed of 80 cm/s, individuals having a mean of 110 cm/s survived a flood to be parents of the next generation; their offspring had a mean speed of 90 cm/s. Calculate the realized heritability for swimming speed. • • Selection differential (S) = mean after selection - mean before selection selection response (R) = mean of offspring generation - mean of previous generation heritability = response / selection, i.e. h2 = R/S So: S = 110 - 80 = 30 R = 90-80 = 10 and h2 = 10 / 30 = 0.33 • • • •