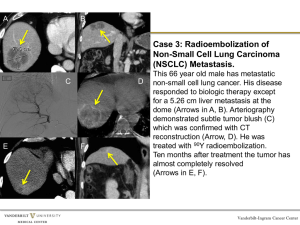
angiogenesis
advertisement

Special approaches of tumor biology and chemotaxis Orsolya Láng 2012. TUMOR CELLS AND MIGRATION PRIMARY TUMOR Angiogenezis Adhesion METASTASIS CELL and CELL CYCLE Apoptosis Chemokines Growth factors Regulatory proteins Adhesion molecules TUMOR CELL CELL KINETICS Doubling time of the tumor volume (Td) Time of the Cell cycle (Tc): Tc= Ts / Li Lymphoma 48 h Lung cancer Usually 15-125 h 108 h Lymphoma 4 weeks Colon adenoma 90 weeks Usually 18-200 days Ts: S phase Li: labeling index (proportoin of cells in S phase) Growth fraction(GF): GF=P / (P+Q’) P: number of the mitotic cells Q: number of the cells in interphase Rate of the cell loss (): = 1-Tpd / Td Tpd= *Ts/Li Tpd: Potential tumor volume doubling time Td: tumor volume doubling time Volume of the tumor tissue ~10 division =*1000 cell number increase (210 =1024) ~20 division= 106 cells = 1 mg= 1 mm3 ~30 division= 109 cells = 1 g= 1 cm3 ~40 division= 1012 cells = 1 kg 1 tumor cell ~27 division = 0,1cm3 Earliest time of diagnosis ~30-33,25 division =1-10 cm3 Time of the clinical symptomes / diagnosis ~40 division = 1012cell Fatal BIOLOGY OF THE TUMORPROGRESSION Tumorigenesis Exogen and endogen factors Genom instability Activation of the oncogene Inactivation of tumorsuppressors Growth rate De-Differentation Invazivity Ectopic survival capacity Epithelial cell Hiperplastic adenoma inhibition Displatic Carcinoma in situ Invasive and metastasis carcinoma Local and systemic factors acceleration Important steps of tumor progression Transformation of the microenvironment: stromal cells, ECM components, proteolytic degradation Induction of the angiogenesis Escaping from immune-mediated rejection Formation of metastasis MICROENVIRONMENT – STROMAL CELLS Cell types: fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, endothelial cells, lymphocytes, macrophages Function: host defence ! ! MALT - B cell helps to maintain lymphomas Growth factors are released by the stromal cells (VEGFangiogenesis) ANGIOGENESIS Hypoxia formation of new vessels, proliferation of the endothelial cells Types: vessels OEDEMA, arteriovenous shunts decresed „dead end” blood flow /lack of smooth muscle , weak vessel wall, irregular shape(insuficient endothelial cell and basement membrane layers)/ sinuses /wall is formed by tumor cells/ Venous circulation VEGF induces angiogensis increases permeability Lack of lymphatic vessels Strategies that tumors use to escape from immune-mediated rejection are: To decrease the antigen expression To inhibit the immune-reactive cells: degrade the chemoattractans decrease their cell adhesion inhibite their phagocytotic activity METASTATIC CASCADE Tumor cell Angiogenesis VEGF Angiogenin FGF Primary tumor Metastasis Angiogenesis Local invasion ECM Adhesion Proteolysis Migration Adhesion Proteolysis Migration Intravasation circulation spreading Extravasation INVASION In situ carcinoma DECREASED CELL ADHESION, INCREASED MOTILITY ECM proteolysis METASTATIC CASCADE Tumor cell Angiogenesis VEGF Angiogenin FGF Primary tumor Angiogenesis Local invasion ECM Adhesion Proteolysis Migration Adhesion Proteolysis Migration Intravasation Metastasis circulation spreading Extravasation CELL ADHESION Significant change in cell-cell and cell-ECM interactions Molecules: selectins integrins immunoglobulin superfamily cadherins catenins SELECTINS Cell-cel junctions Types: E- endothelial cells P- trombocytes L- leukocytes Extracellular C-lectin domain Ca2+ dependent anchorage It binds Sialyl-Lex carbohydrates „ROLLING” ! Tumor cells express increased amount of sialil-Lex or -Lea D R INTEGRINS G Transmembrane receptors Form cell-ECM interaction 8 , 14 subunites ~20 heterodimer Ca2+, Mg2+ dependent anchorage „RGD” sequence is the specific substrate Signalling: outside-in – signalling inside-out – adhesion Increased expression of integrins promotes angiogenesis and helps to bind MMPs at the cell surface EXTRAVASATION, ATTACHMENT Integrin or celladhesion regulated signalling pathways ECM integrin PTEN RAC FAK ILK PI(3)K SHC GRB2/SOS CDC42 PKB/AKT BAD apoptosis RAS RAF MEK MAPK GSK3 Ciklin D1 cellcycle -catenin gene expression motility cellproliferation Integrin or celladhesion regulated signalling pathways ECM integrin PTEN RAC FAK ILK PI(3)K SHC GRB2/SOS CDC42 PKB/AKT BAD apoptsis RAS RAF MEK MAPK GSK3 Ciklin D1 cellcycle -katenin gene expression motility cellproliferation Molecular partners of the integrins Cytoskeletal components: actinin, talin,F- actin, filamin Adaptors: rack 1, ICAP-1 Calcium binding proteins: CIB, calreticulin Protein kinases: pp125FAK, p59 ILK Membrane proteins: CD9, CD16,CD47… caveolin, urokinase-plazminogen-activator receptor Ligands in ECM: collagen, laminin, fibronectin, fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor, osteopontin, elastin IMMUNGLOBULIN SUPERFAMILY has 5 Ig-like domains at the extracellular region forms cell-cell junction interacts with integrins VCAM - 41, PECAM - v3 takes essential part in extravasation ! ! ! ! Over expression of ICAM-1, MUC18 increased inavsion Down-regulation of VCAM-1 increased metastatic potential (faster detachment) CADHERIN Is a transmembrane glycoprotein Forms homophyl cell-cell junctions Ca2+ dependent anchorage Classical types: E- epithelial P- placenta N- neural, Intracellular part interacts with catenins to connect aktin filaments ! Increased expression invasion CATENIN Is an intracellular molecule Fixes cadherins to F-actin ! ! Catenin expression is often decreased in carcinomas -catenin binds to the az APC gén termékéhez Factors influencing the metastatic potential of the melanoma cells Adhesion molecules Signal pathways Increases Ihibits N-Cadherin E-Cadherin B-Catenin aE-Catenin SrC cMET Ras FGFR PTEN METASTATIC CASCADE Tumor cell Angiogenesis Primary tumor Local invasion ECM VEGF Angiogenin FGF Integrins cadherins Selectins CAM Angiogenesis Adhesion Proteolysis Migration Adhesion Proteolysis Migration Intravasation Metastasis Circulation spreading Extravasation PROTEOLYSIS Components of the basement membrane(BM) and ECM: IV collagen, laminin, proteoglycanes Tumorcells (stromal cells) secrete proteases Cathepsin Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) Plazmin, tPA ,Urokinase (plasminogen activator inhibitor 1&2) TIMP INVASION Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases MATRIX METTALLOPROTEINASES (MMP) Zn2+ dependent endopeptidase (MMP28) ECM degradation – tissue remodelling Interstitial collagenase (MMP2) Stromalysin Gelatinase (MMP9) Membrane type MMP Produces biologically active molecules MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF THE MATRIX METTALLOPROTEINASES SUBSTRATE OF TIMP MMP/TIMP EXPRESSION IN BREAST CANCER MMP – TUMORPROGRESSION ?!? METASTATIC CASCADE Tumor cell Angiogenesis Primary tumor Local invasion ECM Adhesion Proteolysis Migration Intravasation VEGF Angiogenin FGF Integrins cadherins Selectins CAM MMP/TIMP Cathepsin Plasminogen Circulation spreading Metastasis Angiogenesis Adhesion Proteolysis Migration Extravasation MIGRATORY MECHANISMS IN TUMOR Small-cell lung cancer FORMS OF MIGRATORY ADAPTATION 2D –3D MIGRATIONS STEPS OF 3D MIGRATION 1. Pseudopod protrusion 2. Formation of focal contact 3. Focal ECM proteolysis 4. Actomyosin contraction 5. Detachment Cell-cell interactions visualized in tumorigenesis METASTATIC CASCADE Tumor cell Angiogenesis Primary tumor Local invasion ECM Adhesion Proteolysis Migration Intravasation VEGF Angiogenin FGF Integrins cadherins Selectins CAM MMP/TIMP Cathepsin Plasminogen Metastasis Angiogenesis Adhesion Proteolysis Migration AMF/gp78 Autotaxin HGF/c-MET Circulation spreading Extravasation HEMATOGENIC DISSEMINATION !! Tumor markers e.g. cytokeratin, mucin EXTRAVASATION Attachment Migration ? LOCALISATION OF THE METASTASIS CHEMOKINES – TISSUE SPECIFIC LOCALISATION motility ? adhesion