view poster
advertisement
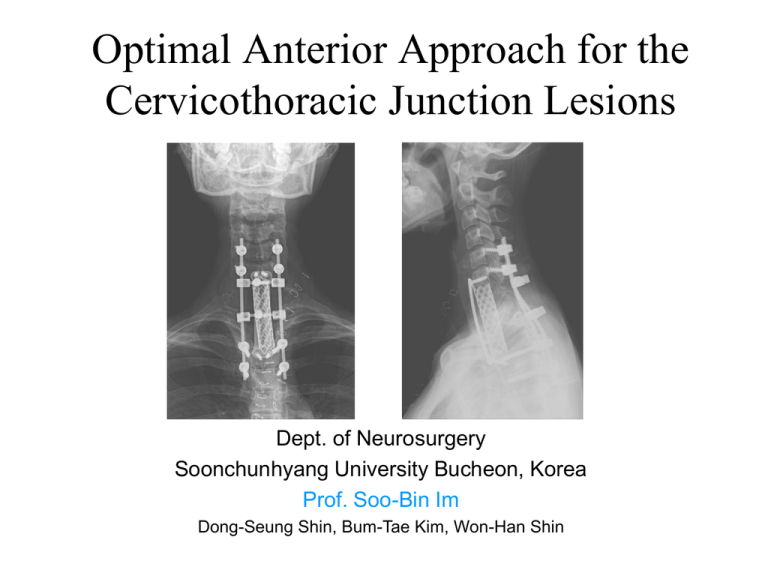
Optimal Anterior Approach for the Cervicothoracic Junction Lesions Dept. of Neurosurgery Soonchunhyang University Bucheon, Korea Prof. Soo-Bin Im Dong-Seung Shin, Bum-Tae Kim, Won-Han Shin Anatomical & Clinical peculiarity Reversal of lordosis to Kyphosis visualization deeper. Limited by sternum, clavicle, vital structures Trachea, esophagus, great vessels, thoracic duct, lung apex, recurrent laryngeal n. brachial plexus Pathologic process usually occurs in anterior segment. Lung apex Anterior Approach for CTJ lesion enables direct decompression & stabilization. Great vessels Case summary of surgery on CTJ Transmanubrial approach 1. 67/F Plasmacytoma 2. 61/M Metastatic tumor 3. 51/M Metastatic tumor 4. 20/F Giant cell tumor 5. 22/F Giant cell tumor (recurred) 5. 46/M TB spondylitis 6. 47/M TB spondylitis 7. 56/F Spondylotic myelopathy 8. 62/F Ruptured disc 9. 69/M Ruptured disc 10. 45/M Bursting fracture with syrynx Supramanubrial approach 11. 44/F Metastatic tumor T2 T1 T3 C7T12 C7T12 T2 T23 C7T1 T12 T12 T2 T1 Operating Scene for approach Extended incision from cervical to manubriosternal junction Finger dissection of posterior surface of the manubrium. Inverted T-shape manubriotomy with oscillating saw Strong short retractor for splitted manubrium Long retractor for visceral structure Spatial relationship between supramanubrial border and Upper and lower parallel line is critical for exposure and decision of manubriotomy length If upper parallel line is below supramanubrial border manubriotomy is inevitable. If only Inferior parallel line is below supramanubrial border relative indication for manubriotomy * Decision for manubriotomy length should be made - By two parallel line to the lesion. - Not by number of vertebrae. T1 C7 * Not need manubriotomy * Relative Ix for manubriotomy * T2 Manubriotomy is mandatory Length of manubriotomy Regardless of the full sternotomy, the caudal extent is limited to T3 by the innominate vein, aortic arch. Inverted T-shape Manubriotomy at the 2nd intercostal space is optimal and usual. Variation of vertebral level and kyphotic angulation deformity Common Pitfall 61/F plasmacytoma with kyphotic angulation Preop. Postop. Postop. 2 yrs Reconstruction Iliac bone graft with anterior plating ------------------------- 1 Flanged titanium mesh only ------------------------------------ 5 Titanium mesh + anterior plating ------------------------------ 2 Mesh + Plate + posterior augmentation --------------------- 2 T1 Result & Complications Neurologic recovery -----------------------------------Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury -------------------Trachea, Esophageal injury ------------------------Local hematoma, infection --------------------------Nonunion or pain on manubriotomy site-----------Thoracic duct injury, Chylothorax ------------------Recurrence of tumor( giant cell tumor, 3 yrs )---- 9 0 0 0 0 1 1 Thoracic duct injury Unfamiliar complication to spine surgeon. Might be avoided by limiting the dissection. medial to the carotid artery, Find and ligation rather than dissection. Chylothorax occurs chest tube drainage, lipid free diet. T1 Conclusions Anterior approach for CTJ lesion is challenging but provides direct decompression and effective reconstruction method. Inverted T-partial manubriotomy is optimal for the T1-T3. Manubriotomy can be decided by upper and lower parallel line to the lesion. The spatial relationship between upper parallel line and supramanubrial border is critical for exposure. *