Cell ENERGY & ENZYMES
advertisement

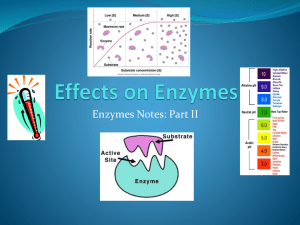
CELL ENERGY & ENZYMES CH. 5.10 - 5.16, CH. 6 & CH. 7 CELLS MUST CREATE AND/OR PROCESS ENERGY USING CHEMICAL REACTIONS. • ENZYMES: • CATALYST: a substance that causes a chemical reaction to ______________ The substance is not changed or used up. WHAT ARE ENZYMES? • Most enzymes are ____________________ • Act as a _____________ to accelerate reactions • ______________________ changed in the process ENZYMES • ___________ for what they catalyze • Are _________ • End in “_____” HOW DO ENZYMES WORK? Enzymes work by ______________________, which lowers the __________________________________ http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_enzymes_work.html THE ENZYME–SUBSTRATE COMPLEX Substrate Joins Enzyme ACTIVE SITE Active Site Substrate Enzyme WHAT AFFECTS ENZYME ACTIVITY? Three factors… 1. 2. 3. ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS • Extreme __________________ are the most dangerous • _________ (most “like” _______________, near neutral) • ____________________________ (_________________) COFACTORS & COENZYMES Example: ____________ must be present in the quaternary structure of hemoglobin in order for it to pick up oxygen. 2 TYPES OF ENZYME INHIBITORS 1. Competitive inhibitors: Substrate Competitive inhibitor Enzyme 2 TYPES OF ENZYME INHIBITORS 2. Non-competitive inhibitors: Substrate Enzyme active site altered Noncompetitive Inhibitor ENZYMATCH.COM • Understanding the importance of finding your perfect lock or key! • Enzymatch.com guarantees to speed up your match making experience! PURPOSE OF ENZYMES: • 1. (ex. synthesis of DNA) • 2. (ex. digestion of foods) • 3. Enzymes A Fun Introduction: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X TUm-75-PL4&feature=related ANABOLIC VS. CATABOLIC CATABOLIC REACTIONS ANABOLIC REACTIONS • • • Example: Photosynthesis • Example: Cellular Respiration MEMORY TRICK! •A •B •C •D EXAMPLES OF ENZYMES Enzyme Name Job Lipase Breaks down lipids (fats) Peptidase Breaks down peptide ponds that hold amino acids together (proteins) Lactase Breaks down lactose found in dairy products Cellulase Breaks down cellulose found in cell walls Pectinase Breaks down pectin found in cell walls Polymerase Builds DNA and RNA LACTOSE INTOLERANCE Lactose Glucose + Galactose Monosaccharide Disaccharide www.unitedstreaming.com - “Lactose Intolerance” GHScardinal greenwich Monosaccharide • CATALASE is an enzyme found in living things. Its job is to break down the poison hydrogen peroxide. 2 H 2O 2 • • • • Substrate(s)? Enzyme? Reactant (s)? Product(s)? catalase 2 H2 O + O 2 • • • OPTIMAL TEMPERATURE: a specific temperature at which an enzyme’s catalytic activity is at its greatest DO ALL ORGANISMS HAVE THE SAME OPTIMUM TEMPERATURE FOR THEIR ENZYMES? An enzyme found in Wild Alaskan Salmon An enzyme found in Bacteria An enzyme found in Humans THE SAME GOES FOR ______ • pH: Each enzyme works within a small pH range. When an enzyme is NOT in its optimal pH environment the active site of the enzyme changes shape. • Acidic pH levels: • Neutral pH level: • Basic pH levels: • OPTIMAL pH: a specific pH level at which an enzyme’s catalytic activity is at its greatest. DO ALL ENZYMES IN AN ORGANISM HAVE THE SAME OPTIMUM PH? Amylase Pepsin Trypsin WHAT HAPPENS WHEN AN ENZYME REACHES PAST IT’S OPTIMAL TEMPERATURE OR pH? DENATURATION (denature): Denatured proteins will not go back to their original shape!! CELL ENERGY Photosynthesis Cell Respiration • Photosynthesis: • Where does photosynthesis occur in plant cells? CHLOROPLAST ANATOMY OF A CHLOROPLAST HOW DOES THE CHLOROPLAST ABSORB SUNLIGHT ENERGY? • Pigments: • Chlorophyll a (green) • Chlorophyll b (green) • Carotenoids (yellow, orange, red) Chlorophylls absorb most strongly in the ____________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ This is why plant parts that contain chlorophyll appear green to the human eye. Reactants (Into the Chloroplast) Word Formula Chemical Formula Products (Out of the Chloroplast) PHOTOSYNTHESIS OVERVIEW PART 1: LIGHT REACTION PART 2: CALVIN CYCLE THOMAS ENGELMANN’S EXPERIMENT What is a valid conclusion based on this graph? O2 production decreases as the wavelength increases from 550 – 650 nm Respiration rate in bacteria is greatest at 550 nm Photosynthetic rate in the algae is greatest in blue light The algae absorb the greatest amount of O2 in red light THOMAS ENGELMANN’S EXPERIMENT Photosynthetic rate in the algae is greatest in blue light Evidence: 1. 2. 3. Animation of experiment PHOTOSYNTHESIS DRAWINGS! Photosynthesis Overview – Page 118 Light Reaction in detail – Page 114 Calvin Cycle in detail – Page 116 Full sheet or Half sheet drawings – IN COLOR CELL ENERGY Photosynthesis Cell Respiration BREAKS DOWN INTO MICROSCOPIC MOLECULES Loaf of bread Bread crumbs GLUCOSE’S FINAL DESTINATION… CELLULAR RESPIRATION The energy is released in the form of ___________!!!! GLUCOSE Cellular Respiration ENERGY (ATP) ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE • ATP: • Cellular Activities that require ATP: • • • • Active Transport of the cell membrane Making new DNA and new cells Muscle contractions Nerve impulses Glucose ATP ATP FUNCTION ENERGY IS RELEASED WHEN: The bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups is broken, forming a molecule called ADP (adenosine diphosphate). CELLULAR RESPIRATION Reactants (Into Mitochondria) Word Formula Chemical Formula Products (Out of Mitochondria) WHAT TYPE OF ORGANISMS PERFORM CELLULAR RESPIRATION? AUTOTROPHS HETEROTROPHS • • • AKA: producer • AKA: consumer, herbivore, carnivore, decomposer, omnivore • Examples: plants, algae & some bacteria • Examples: animals, fungi, & most bacteria CELL RESPIRATION OVERVIEW PART 1: GLYCOLYSIS GLYCOLYSIS SUMMARY TRANSITION TO KREBS / CITRIC ACID CYCLE PART 2: KREBS / CITRIC ACID CYCLE PART 3: OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION WITHOUT O2: FERMENTATION CELL RESPIRATION REACTIONS CELLULAR RESPIRATION DRAWINGS! Cell Respiration Overview – Page 100 Glycolysis – Page 95 Citric Acid / Krebs Cycle – Page 97 ETC (Oxidative Phosphorylation)- Page 98 Fermentation – Page 101 Full sheet or Half sheet drawings – IN COLOR YEAST - MAJOR CHARACTERISTICS Significance of Yeast Food Industry Medical Biofuel Industry ILLUSTRATE INTERDEPENDENCE • Illustrate the interdependent relationship that occurs between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. PHOTOSYNTHESIS • Performed by • This cellular process occurs in organelle called organisms. cells, in the . • Converts sunlight energy into chemical energy • It is an • CO2 and H2O are the • Glucose and O2 are the reaction. CELLULAR RESPIRATION • Performed by organisms. & • This cellular process occurs in & cells, in the organelle called . • Glucose is stored energy for the cell. ATP is usable energy for the cell. • It is a • CO2 and H2O & ATP are the • Glucose and O2 are the reaction.