Animal-like Protists and Funguslike Protists
advertisement
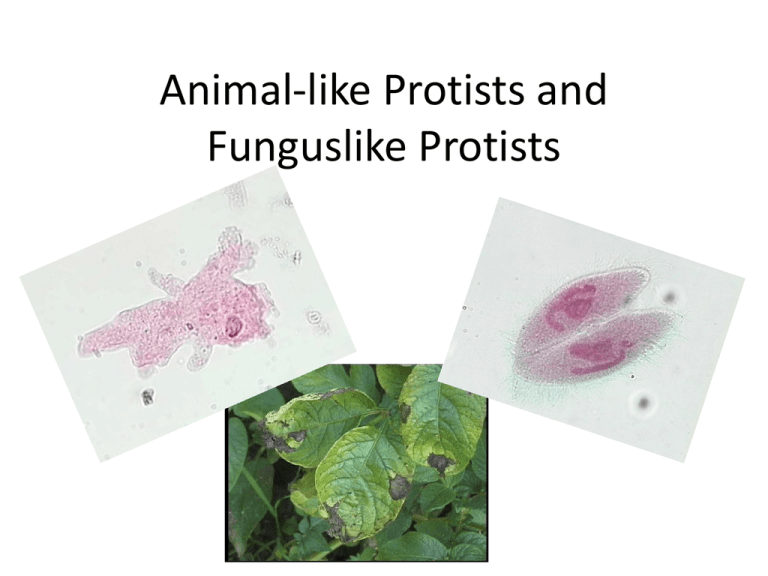
Animal-like Protists and Funguslike Protists Before we begin…some review • • • • What does the term “eukaryotic” mean? What does the term “heterotroph” mean? What does the term “autotroph” mean? What is the difference between “unicellular” and “multicellular”? What is a Protist? • Diverse kingdom – sometimes called “junk drawer kingdom” • Are all eukaryotes • All live in moist environments • Mix of unicellular and multicellular • Mix of autotrophs and heterotrophs • Most have contractile vaculoes – pump water out of the organism Example Protists The Amoeba The Paramecium Algae Grouping Protists • Protists are classified into three groups: – Animal-like protists – Funguslike protists – Plant-like protists Animal-like Protists • Also called protozoans • All heterotrophs • All unicellular • Divided into four groups – – – – Protozoans with Pseudopods Protozoans with Cilia Protozoans with Flagella Others Protozoans with Pseudopods • These protists are called sarcodines. • They all have pseudopds that allow them to move and trap food. – Pseudopod – “false foot”; temporary bulge of the cell membrane that fills with cytoplasm • Example – Our old friend, the amoeba The Amoeba Protozoans with Cilia • These protists are called ciliates. • They all have cilia that allow them to move, obtain food, and sense the environment. – Cilia – hairlike projections from a cell that move in a wavelike pattern. • Example – paramecium Paramecium Protozoans with Flagella • These protists are called zooflagellates. • They all have flagella that help them move. – Flagella – long, whiplike tail • Many live in symbiosis in other organisms. – Symbiosis – interaction between two species • Example - Giardia Giardia Other Protozoans • These are called sporozoans. • They are all parasites that feed on the cells and body fluids of their hosts. • Example – Plasmodium, causes malaria Funguslike Protists • Have cell walls • Use spores to reproduce • Are heterotrophs • Three types: – Water molds – Downy mildews – Slime molds Water Molds and Downy Mildews • Live in water and moist places • Grow as tiny threads that look fuzzy • Can also attack food crops – Water mold destroyed potato crops in 1845-1846 and caused the Irish Potato Famine that killed over a million people! Water Molds and Downy Mildew Water mold growing on a fish. It is a parasite that will eventually kill the fish. Downy mildew growing on lettuce. Slime Molds • Live in moist soil and on decaying plants and trees • Can form pseudopods and eat bacteria











