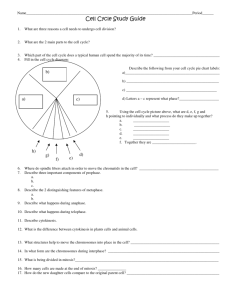
Cell Division Vocabulary
advertisement
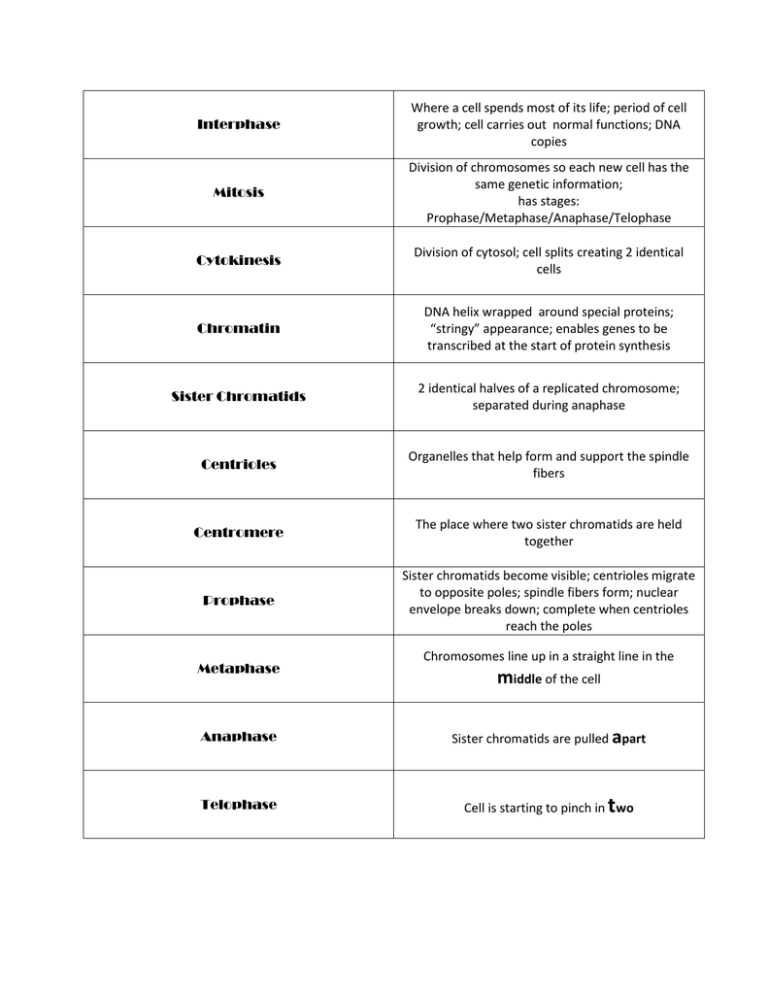
Interphase Where a cell spends most of its life; period of cell growth; cell carries out normal functions; DNA copies Mitosis Division of chromosomes so each new cell has the same genetic information; has stages: Prophase/Metaphase/Anaphase/Telophase Cytokinesis Division of cytosol; cell splits creating 2 identical cells Chromatin DNA helix wrapped around special proteins; “stringy” appearance; enables genes to be transcribed at the start of protein synthesis Sister Chromatids 2 identical halves of a replicated chromosome; separated during anaphase Centrioles Organelles that help form and support the spindle fibers Centromere The place where two sister chromatids are held together Prophase Sister chromatids become visible; centrioles migrate to opposite poles; spindle fibers form; nuclear envelope breaks down; complete when centrioles reach the poles Metaphase Chromosomes line up in a straight line in the middle of the cell Anaphase Sister chromatids are pulled apart Telophase Cell is starting to pinch in wo t Spindle Fibers Protein fibers that pull chromatids apart during anaphase Diploid Cells with the total chromosome number (humans=46) Haploid Cells with half the normal chromosome number (humans=23); half Homologous Chromosomes In each pair, one chromosome is from mom and one is from dad; carry genes for the same traits Crossing over Exchanging of genetic material Meiosis Occurs in the ovaries and testes and produces eggs and sperm; starts with a diploid germ cell and ends with haploid sex cells Apoptosis Programmed cell death Growth Factors Proteins that can act as a trigger for cells to divide; “green lights” Nondisjunction When chromosomes fail to separate correctly during anaphase